Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which type of cells in the alveolar wall are directly involved in gas exchange?
Which type of cells in the alveolar wall are directly involved in gas exchange?
- Pulmonary surfactant
- Type II cells
- Red blood cells
- Type I cells (correct)
What is the function of pulmonary surfactant?
What is the function of pulmonary surfactant?
- To reduce surface tension in alveoli (correct)
- To secrete mucus in the airways
- To transport oxygen in the blood
- To prevent the collapse of alveoli during inhalation
How is oxygen primarily carried in the blood?
How is oxygen primarily carried in the blood?
- By dissolving in plasma
- By binding to red blood cells
- By binding to hemoglobin molecules (correct)
- By converting into bicarbonate ions
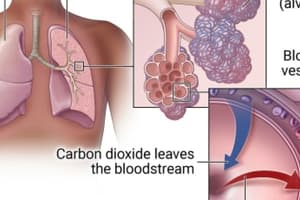
In what forms is carbon dioxide transported in the blood?
In what forms is carbon dioxide transported in the blood?
What is the term for rapid or deep breathing?
What is the term for rapid or deep breathing?
Where is the respiratory center of the brain located?
Where is the respiratory center of the brain located?
What is the term for the contraction and relaxation of muscles involved in respiration?
What is the term for the contraction and relaxation of muscles involved in respiration?
What is the term for the amount of air inhaled or exhaled during normal breathing at rest?
What is the term for the amount of air inhaled or exhaled during normal breathing at rest?
Which term refers to chronic inflammation and narrowing of airways?
Which term refers to chronic inflammation and narrowing of airways?
How does smoking damage the respiratory system?
How does smoking damage the respiratory system?
Which type of cells secrete pulmonary surfactant, a substance that helps reduce surface tension in alveoli and prevents them from collapsing during exhalation?
Which type of cells secrete pulmonary surfactant, a substance that helps reduce surface tension in alveoli and prevents them from collapsing during exhalation?
What is the term for difficulty or discomfort in breathing?
What is the term for difficulty or discomfort in breathing?
Where is the respiratory center of the brain located?
Where is the respiratory center of the brain located?
What is the term for the amount of air inhaled or exhaled during normal breathing at rest?
What is the term for the amount of air inhaled or exhaled during normal breathing at rest?
What does COPD stand for?
What does COPD stand for?
What is the term for the additional air that can be forcefully inhaled after a tidal breath?
What is the term for the additional air that can be forcefully inhaled after a tidal breath?
What is the term for the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the lung tissue?
What is the term for the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the lung tissue?
How does smoking damage the respiratory system?
How does smoking damage the respiratory system?
What changes occur in the respiratory system with age?
What changes occur in the respiratory system with age?
What is the term for the negative feedback loop that helps maintain blood pressure at a constant level?
What is the term for the negative feedback loop that helps maintain blood pressure at a constant level?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying