Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following best describes the primary function of the fallopian tubes in the female reproductive system?
Which of the following best describes the primary function of the fallopian tubes in the female reproductive system?
- To connect the ovaries to the uterus, facilitating the transport of the egg. (correct)
- To serve as the location where a baby develops until birth.
- To produce female sex cells called eggs or ova.
- To protect the entrance of the vagina and house the clitoris.
What is the main role of the prostate gland in the male reproductive system?
What is the main role of the prostate gland in the male reproductive system?
- To produce sperm cells.
- To carry sperm from the testicles to the urethra.
- To produce a fluid that nourishes and transports sperm, forming semen. (correct)
- To store urine before it is expelled from the body.
How do primary and secondary sexual characteristics differ in humans?
How do primary and secondary sexual characteristics differ in humans?
- Primary characteristics are seen only in females, while secondary characteristics are seen only in males.
- Primary characteristics develop during puberty, while secondary characteristics are present at birth.
- Primary characteristics are external, while secondary characteristics are internal.
- Primary characteristics are related to the reproductive systems present at birth, while secondary characteristics appear during puberty. (correct)
Which of the following sequences accurately depicts the path of sperm from production to ejaculation?
Which of the following sequences accurately depicts the path of sperm from production to ejaculation?
A person is experiencing changes associated with puberty. What biological process is primarily responsible for these changes?
A person is experiencing changes associated with puberty. What biological process is primarily responsible for these changes?
Where does the development of a baby occur in the female reproductive system?
Where does the development of a baby occur in the female reproductive system?
If the vasa deferentia in a male were blocked, which of the following would be the most likely consequence?
If the vasa deferentia in a male were blocked, which of the following would be the most likely consequence?
What is the role of the scrotum in the male reproductive system, and why is it located outside the body?
What is the role of the scrotum in the male reproductive system, and why is it located outside the body?
Which of the following accurately describes the role of the placenta during pregnancy?
Which of the following accurately describes the role of the placenta during pregnancy?
What is the term used to describe the developing human from the third month of pregnancy until birth?
What is the term used to describe the developing human from the third month of pregnancy until birth?
Which event marks the beginning of labour?
Which event marks the beginning of labour?
What is the role of the amniotic sac and amniotic fluid during pregnancy?
What is the role of the amniotic sac and amniotic fluid during pregnancy?
A pregnant woman is in her seventh month and notices that her abdomen is significantly larger than it was in the first few months. Which of the following BEST explains this change?
A pregnant woman is in her seventh month and notices that her abdomen is significantly larger than it was in the first few months. Which of the following BEST explains this change?
Assuming a typical pregnancy, approximately how long does the period between fertilisation and birth last?
Assuming a typical pregnancy, approximately how long does the period between fertilisation and birth last?
What is the correct order of events immediately following fertilisation?
What is the correct order of events immediately following fertilisation?
Which of the following correctly describes the function of the umbilical cord?
Which of the following correctly describes the function of the umbilical cord?
Which of the following best describes the primary function of the human reproductive system?
Which of the following best describes the primary function of the human reproductive system?
Which of the following represents a key difference between ovaries and testicles?
Which of the following represents a key difference between ovaries and testicles?
Which of the following characteristics is considered a primary sexual characteristic?
Which of the following characteristics is considered a primary sexual characteristic?
Menstruation involves which of the following processes?
Menstruation involves which of the following processes?
Which of the following accurately describes the role of the vas deferentia?
Which of the following accurately describes the role of the vas deferentia?
What is the biological result of fertilization?
What is the biological result of fertilization?
Which of the following sequences correctly outlines the path sperm take to reach the egg for fertilization?
Which of the following sequences correctly outlines the path sperm take to reach the egg for fertilization?
Which statement accurately connects a process to its timeframe within the female reproductive cycle?
Which statement accurately connects a process to its timeframe within the female reproductive cycle?
Flashcards
Sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction
Creating offspring through the combination of sex cells from two individuals.
Reproductive systems
Reproductive systems
Organs responsible for producing sex cells and enabling reproduction.
Eggs
Eggs
Female sex cells; also known as ova.
Sperm
Sperm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Puberty
Puberty
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovaries
Ovaries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Testicles
Testicles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urethra
Urethra
Signup and view all the flashcards
Secondary Sexual Characteristics
Secondary Sexual Characteristics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Eggs (Ova)
Eggs (Ova)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Menstruation (Period)
Menstruation (Period)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Menopause
Menopause
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sperm (Spermatozoa)
Sperm (Spermatozoa)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Semen
Semen
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fertilization
Fertilization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Zygote
Zygote
Signup and view all the flashcards
Uterus
Uterus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Placenta
Placenta
Signup and view all the flashcards
Umbilical Cord
Umbilical Cord
Signup and view all the flashcards
Amniotic Sac
Amniotic Sac
Signup and view all the flashcards
Foetus
Foetus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Labor
Labor
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Human beings produce offspring through sexual reproduction, which involves two people of different sexes.
- Biological sex is based on the reproductive system at birth.
Reproductive Systems
- The human reproductive system differs between females and males.
- Each system produces different sex cells that are involved in reproduction.
Puberty
- Puberty involves changes in the body as the reproductive systems develop, enabling reproduction.
- It typically begins around age ten and takes about four years to complete.
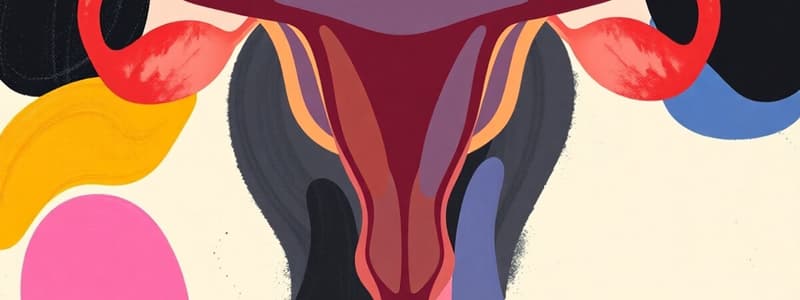
Female Reproductive System
- Ovaries are two organs producing female sex cells (eggs or ova).
- Fallopian tubes connect the ovaries to the uterus.
- The uterus, also called the womb, is a muscular organ with a soft lining where babies develop.
- The vagina is an internal muscular tube connecting the uterus to the outside of the body.
- The vulva is the external set of female organs, including the outer and inner labia.
- The labia protect the entrance of the vagina and the clitoris
Male Reproductive System
- Testicles produce male sex cells called sperm or spermatozoa.
- The scrotum is a bag of skin containing the testicles
- Vasa deferentia are tubes carrying sperm from the testicles to the urethra.
- The urethra is a tube inside the penis that carries urine or semen.
- The penis is an external organ surrounding the urethra, with the glans penis covered by the foreskin.
- The prostate is an organ producing fluid serving as food and transport for sperm.
- Semen is the mixture of sperm and fluids.
Sex Characteristics
- Physical differences between people of different sexes are called sex characteristics
- Primary sexual characteristics are the reproductive systems at birth
- Secondary sexual characteristics appear during puberty.
- Secondary sexual characteristics in girls: widening of hips, breast growth, and hair growth in the pubic area and armpits.
- Secondary sexual characteristics in boys: voice deepening, muscle development, and hair growth on the face and body.
Fertilization
- Eggs (or ova) are the female sex cells, formed in the ovaries.
- At puberty, the eggs mature approximately every 28 days.
- After 14 days, the mature egg is released from the ovary, entering the fallopian tube.
- The egg travels through the fallopian tube, uterus, and vagina.
- The egg, along with some blood and tissue from the uterus, exits the vagina during menstruation, or a period.
- Menopause is when women gradually stop producing mature eggs and menstruation stops.
Male Sex Cells
- Sperm (or spermatozoa) are the male sex cells, formed continuously in the testicles after puberty.
- Sperm leave the testicles, enter the vasa deferentia, and mix with fluid from the prostate to form semen.
- Semen travels through the urethra and is expelled from the penis during ejaculation.
Fertilization Defined
- Fertilization is when a sperm cell joins with an egg cell to produce a zygote, which develops into a new human being.
- Fertilization is internal, occurring inside the woman's body through sexual intercourse when sperm enter and can join the egg.
- A mature egg is released by an ovary.
- Sperm travel through the vagina and uterus to reach the fallopian tube.
- Sperm meets the mature egg in the fallopian tube, where one sperm fertilizes the egg.
- The fertilized egg (zygote) divides into many cells to form an embryo.
- The embryo arrives in the uterus and buries itself into the lining to grow and develop.
Pregnancy and Labour
- Pregnancy is the period between fertilization and birth, lasting nine months.
- During pregnancy, the baby grows inside the mother's uterus
- The placenta supplies oxygen and nutrients from the mother to the embryo
- The placenta grows into the wall of the uterus and is joined to the embryo by the umbilical cord.
- The amniotic sac forms around the embryo, filled with amniotic fluid to protect the embryo.
- At three months, the embryo is called a foetus and begins to look more like a baby.
- By nine months, the foetus is about 50 cm long, weighs about 3 kg, and is ready to be born.
- Pregnant women stop having periods, breasts grow to prepare to feed the baby, and the abdomen enlarges as the foetus grows.
Labour and Birth
- Labour is the physical process when the baby and placenta are pushed out of a woman’s body .
- Labour is in three stages: dilation, birth, and afterbirth.
Labour Stages
- Dilation occurs as the neck of the uterus dilates and the wall of the uterus contracts to push the foetus.
- Birth occurs as the uterus and mother's muscles of the abdomen push the baby out.
- The baby starts to breathe, and the umbilical cord is cut.
- Afterbirth is when the placenta is expelled from the uterus, along with the remains of the umbilical cord.
Lactation
- It's the process of making human milk.
- Breastfeeding involves feeding babies directly from the mother's breasts.
- Breast milk contains nutrients and substances protecting against diseases.
- Babies can also be fed with formula milk, but human milk is the only food babies need in the first months.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.