Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the digestive system?
What is the primary function of the digestive system?
- To absorb nutrients
- To store food
- To eliminate waste
- To convert large food molecules into smaller substances (correct)
Which of the following is NOT a major structure of the digestive system?
Which of the following is NOT a major structure of the digestive system?
- Esophagus
- Liver (correct)
- Mouth
- Large intestine
What is the term used to describe the extent to which the digestive tract absorbs a nutrient and how well the body uses it?
What is the term used to describe the extent to which the digestive tract absorbs a nutrient and how well the body uses it?
- Gastrointestinal function
- Nutrient absorption
- Digestive efficiency
- Bioavailability (correct)
What is the purpose of cooking food?
What is the purpose of cooking food?
Which of the following is an accessory organ of the digestive system?
Which of the following is an accessory organ of the digestive system?
What is the term used to describe the muscular tube that extends from the mouth to the anus?
What is the term used to describe the muscular tube that extends from the mouth to the anus?
What is the process that converts large food molecules into smaller substances?
What is the process that converts large food molecules into smaller substances?
Which of the following nutrients do not need to undergo digestion?
Which of the following nutrients do not need to undergo digestion?
What is the medical term for the complete loss of taste?
What is the medical term for the complete loss of taste?
What is the primary function of the esophagus?
What is the primary function of the esophagus?
What is the term for a condition characterized by having difficulty swallowing or being unable to swallow?
What is the term for a condition characterized by having difficulty swallowing or being unable to swallow?
Why do children often reject strong-flavored foods?
Why do children often reject strong-flavored foods?
What is the flap of tough tissue that prevents food from entering the larynx and trachea during swallowing?
What is the flap of tough tissue that prevents food from entering the larynx and trachea during swallowing?
What is the term for waves of muscular activity that help propel material through the digestive tract?
What is the term for waves of muscular activity that help propel material through the digestive tract?
Why do people with dysphagia often experience weight loss and dehydration?
Why do people with dysphagia often experience weight loss and dehydration?
What is the term for a distorted sense of taste?
What is the term for a distorted sense of taste?
What happens to breathing when you swallow?
What happens to breathing when you swallow?
What is the sense that contributes to your ability to sense the taste of food?
What is the sense that contributes to your ability to sense the taste of food?
What is the primary function of the salivary glands in the digestive system?
What is the primary function of the salivary glands in the digestive system?
What is the name of the enzyme that breaks down starch in the mouth?
What is the name of the enzyme that breaks down starch in the mouth?
Which part of the tongue has more taste buds than the center?
Which part of the tongue has more taste buds than the center?
What is the primary function of the sense of taste?
What is the primary function of the sense of taste?
What is the name of the taste associated with the presence of amino acids?
What is the name of the taste associated with the presence of amino acids?
What is the term for the inability to smell odors?
What is the term for the inability to smell odors?
What is the role of the tongue in the digestion process?
What is the role of the tongue in the digestion process?
What is the term for the partial or complete loss of the sense of smell?
What is the term for the partial or complete loss of the sense of smell?
What is the name of the enzyme that breaks down fat in the stomach?
What is the name of the enzyme that breaks down fat in the stomach?
What is the primary benefit of being able to detect various tastes?
What is the primary benefit of being able to detect various tastes?
What is the typical capacity of the stomach after a meal?
What is the typical capacity of the stomach after a meal?
What is the function of the lower esophageal sphincter?
What is the function of the lower esophageal sphincter?
What is the purpose of hydrochloric acid (HCl) in the stomach?
What is the purpose of hydrochloric acid (HCl) in the stomach?
What is the result of the mechanical and chemical activity in the stomach?
What is the result of the mechanical and chemical activity in the stomach?
What is the purpose of the mucus layers in the stomach?
What is the purpose of the mucus layers in the stomach?
What is the function of the pyloric sphincter?
What is the function of the pyloric sphincter?
What is the effect of fatty meals on gastric emptying?
What is the effect of fatty meals on gastric emptying?
What is the length of the small intestine on average?
What is the length of the small intestine on average?
What is the diameter of the small intestine?
What is the diameter of the small intestine?
What is the function of burping?
What is the function of burping?
What is the purpose of the alkaline fluids secreted by the pancreas, gallbladder, and the duodenum?
What is the purpose of the alkaline fluids secreted by the pancreas, gallbladder, and the duodenum?
What is the main function of the small intestine's segmentation?
What is the main function of the small intestine's segmentation?
What is the role of microvilli in the small intestine?
What is the role of microvilli in the small intestine?
What is the purpose of the watery fluids secreted by the small intestine?
What is the purpose of the watery fluids secreted by the small intestine?
What is the term used to describe the hollow space in an organ or structure that is surrounded by walls?
What is the term used to describe the hollow space in an organ or structure that is surrounded by walls?
How do some nutrients enter the absorptive cells of the small intestine?
How do some nutrients enter the absorptive cells of the small intestine?
What is the term used to describe the reactions that occur during digestion involving water?
What is the term used to describe the reactions that occur during digestion involving water?
Where do absorbed water-soluble nutrients enter after being absorbed by the small intestine?
Where do absorbed water-soluble nutrients enter after being absorbed by the small intestine?
What is the function of the mucus layer produced by the cells lining the small intestine?
What is the function of the mucus layer produced by the cells lining the small intestine?
What is the purpose of the circular folds in the lining of the small intestine?
What is the purpose of the circular folds in the lining of the small intestine?
What is the primary location where bezoars are most likely to develop in the human gastrointestinal tract?
What is the primary location where bezoars are most likely to develop in the human gastrointestinal tract?
What is the percentage of feces that consists of bacteria that normally live in the large intestine?
What is the percentage of feces that consists of bacteria that normally live in the large intestine?
What is the primary function of mucus in the large intestine?
What is the primary function of mucus in the large intestine?
What is the term used to describe the consumption of nonfood items, including stones and clay?
What is the term used to describe the consumption of nonfood items, including stones and clay?
What is the term used to describe the collective term for viruses, fungi, and bacteria in the large intestine?
What is the term used to describe the collective term for viruses, fungi, and bacteria in the large intestine?
How long does it take for any remaining undigested material to move through the large intestine and become semisolid feces?
How long does it take for any remaining undigested material to move through the large intestine and become semisolid feces?
What is the primary way that feces are expelled from the body?
What is the primary way that feces are expelled from the body?
What is the age by which healthy children are typically able to voluntarily control their external anal sphincter?
What is the age by which healthy children are typically able to voluntarily control their external anal sphincter?
What is the term used to describe the process of swallowing?
What is the term used to describe the process of swallowing?
What is the primary function of the external anal sphincter?
What is the primary function of the external anal sphincter?
What is the primary function of the pancreas in digestion?
What is the primary function of the pancreas in digestion?
What is the role of cholecystokinin in digestion?
What is the role of cholecystokinin in digestion?
What is the primary function of the liver in digestion?
What is the primary function of the liver in digestion?
What is the consequence of a gallstone lodging in the common bile duct?
What is the consequence of a gallstone lodging in the common bile duct?
What is the cause of impaired digestion in people with cystic fibrosis?
What is the cause of impaired digestion in people with cystic fibrosis?
What is the treatment for malabsorption in people with cystic fibrosis?
What is the treatment for malabsorption in people with cystic fibrosis?
What is the term for a tightly tangled bit of fur that becomes trapped in the digestive tract?
What is the term for a tightly tangled bit of fur that becomes trapped in the digestive tract?
What is the risk factor for developing gallstones?
What is the risk factor for developing gallstones?
What happens to the bile flow after the removal of the diseased gallbladder?
What happens to the bile flow after the removal of the diseased gallbladder?
What is the term for a type of bezoar that contains fibrous indigestible plant material?
What is the term for a type of bezoar that contains fibrous indigestible plant material?
What is the main purpose of the hepatic portal vein?
What is the main purpose of the hepatic portal vein?
What is the function of Peyer's patches in the ileum?
What is the function of Peyer's patches in the ileum?
What happens to older absorptive cells in the small intestine?
What happens to older absorptive cells in the small intestine?
What is the function of the pancreas in the digestive process?
What is the function of the pancreas in the digestive process?
What is the result of a lack of nutrients needed for cell division in the small intestine?
What is the result of a lack of nutrients needed for cell division in the small intestine?
What is the function of chylomicrons in the transport of fat-soluble nutrients?
What is the function of chylomicrons in the transport of fat-soluble nutrients?
What is the effect of inflammation in the intestines?
What is the effect of inflammation in the intestines?
What is the function of the lymphatic system in the transport of fat-soluble nutrients?
What is the function of the lymphatic system in the transport of fat-soluble nutrients?
What is the purpose of bicarbonate ions secreted by the pancreas?
What is the purpose of bicarbonate ions secreted by the pancreas?
What is malabsorption?
What is malabsorption?
What is the primary role of yeast in the production of beer, wine, and liquor?
What is the primary role of yeast in the production of beer, wine, and liquor?
What can occur when a person takes antibiotics to treat bacterial infections?
What can occur when a person takes antibiotics to treat bacterial infections?
What is the term for the condition where yeast ferment sugars in the colon, producing alcohol as a by-product?
What is the term for the condition where yeast ferment sugars in the colon, producing alcohol as a by-product?
What is the primary function of probiotics?
What is the primary function of probiotics?
What are prebiotics?
What are prebiotics?
What is the benefit of probiotics in treating people with IBS?
What is the benefit of probiotics in treating people with IBS?
What is the role of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium in probiotics?
What is the role of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium in probiotics?
What is the importance of washing hands after having bowel movements?
What is the importance of washing hands after having bowel movements?
What is the term for the process by which the gut microbiota is influenced by a person's diet?
What is the term for the process by which the gut microbiota is influenced by a person's diet?
What is the term for the organisms that can digest and absorb nutrients from plants, animals, fungi, and bacteria?
What is the term for the organisms that can digest and absorb nutrients from plants, animals, fungi, and bacteria?
What is the primary function of the digestive system in response to dietary changes?
What is the primary function of the digestive system in response to dietary changes?
What is the estimated number of adult Americans who have either ulcerative colitis (UC) or Crohn's disease (CD)?
What is the estimated number of adult Americans who have either ulcerative colitis (UC) or Crohn's disease (CD)?
What is thought to trigger an abnormal response by the intestinal tract's immune cells and lead to IBD?
What is thought to trigger an abnormal response by the intestinal tract's immune cells and lead to IBD?
What is a common symptom of ulcerative colitis (UC)?
What is a common symptom of ulcerative colitis (UC)?
What is the typical Western diet high in?
What is the typical Western diet high in?
What is the name of the inflammatory bowel disease that can affect the entire gastrointestinal tract?
What is the name of the inflammatory bowel disease that can affect the entire gastrointestinal tract?
What is the recommended diet for people with ulcerative colitis during flares?
What is the recommended diet for people with ulcerative colitis during flares?
What is the increased risk for people with ulcerative colitis?
What is the increased risk for people with ulcerative colitis?
What is the name of the section of the small intestine that is often inflamed in Crohn's disease?
What is the name of the section of the small intestine that is often inflamed in Crohn's disease?
What is the treatment for Crohn's disease similar to?
What is the treatment for Crohn's disease similar to?
What happens to people with Crohn’s disease?
What happens to people with Crohn’s disease?
What is the purpose of Alicia Anne's treatment with prednisone?
What is the purpose of Alicia Anne's treatment with prednisone?
What is the consequence of using frequent enemas?
What is the consequence of using frequent enemas?
What is the role of the gastroenterologist in Alicia's diagnosis?
What is the role of the gastroenterologist in Alicia's diagnosis?
What is the consequence of removing badly damaged portions of the intestinal tract?
What is the consequence of removing badly damaged portions of the intestinal tract?
What is Alicia's condition characterized by?
What is Alicia's condition characterized by?
What is the purpose of Alicia's monitoring of food choices?
What is the purpose of Alicia's monitoring of food choices?
What is the result of Alicia's treatment with medication?
What is the result of Alicia's treatment with medication?
What is the consequence of having Crohn's disease?
What is the consequence of having Crohn's disease?
What is the importance of Alicia's regular check-ups with her physician?
What is the importance of Alicia's regular check-ups with her physician?
What is the primary function of the gut microbiota in the human body?
What is the primary function of the gut microbiota in the human body?
What is the result of an imbalance of the normal diversity of microbial populations in the GI tract?
What is the result of an imbalance of the normal diversity of microbial populations in the GI tract?
What is the role of the appendix in the human body?
What is the role of the appendix in the human body?
What is the benefit of eating a high-fiber diet?
What is the benefit of eating a high-fiber diet?
What is gut microbiota transplantation (GMT) used to treat?
What is gut microbiota transplantation (GMT) used to treat?
What is the result of antibiotic use on the gut microbiota?
What is the result of antibiotic use on the gut microbiota?
What is the role of the gut microbiota in producing vitamins?
What is the role of the gut microbiota in producing vitamins?
What is the link between gut microbiota and diseases?
What is the link between gut microbiota and diseases?
What is the term for the condition characterized by the imbalance of the normal diversity of microbial populations in the GI tract?
What is the term for the condition characterized by the imbalance of the normal diversity of microbial populations in the GI tract?
What is the function of the appendix as a 'storage facility'?
What is the function of the appendix as a 'storage facility'?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
The Digestive System
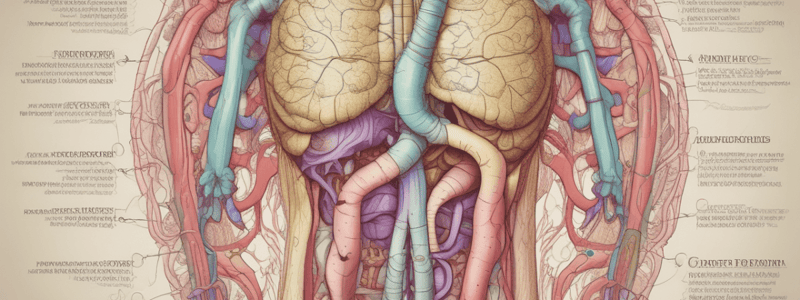
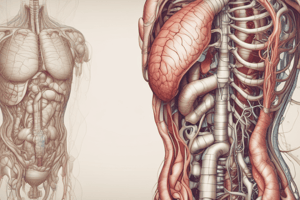
- The digestive system, also known as the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, is a hollow, muscular tube that extends from the mouth to the anus, approximately 16 feet long.
- The major structures of the digestive system are the mouth, esophagus, stomach, and small and large intestines.
Organs of Digestion
- The teeth, tongue, salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas are accessory organs of the digestive system that assist in food digestion, nutrient absorption, and waste elimination.
Mouth
- Digestion begins in the mouth, where teeth mechanically break down food into smaller chunks.
- The tongue helps form a bolus of food and directs it to the back of the mouth for swallowing.
- Saliva from salivary glands contains mucus and enzymes, such as salivary amylase and lingual lipase, which break down carbohydrates and fats.
- Taste buds on the tongue detect sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami tastes.
Esophagus
- The esophagus is a muscular tube that transfers a bolus of food into the stomach.
- The primary function of the esophagus is to propel food into the stomach using peristalsis, a wave of muscular contractions.
- The epiglottis, a flap of tissue, prevents food from entering the larynx and trachea.
Stomach
- The stomach is a muscular sac that expands to hold 4-6 cups of food after a meal.
- Gastric juice, containing hydrochloric acid (HCl) and enzymes, is secreted by the stomach to break down proteins and fats.
- The stomach churns and mixes food with gastric juice, breaking down proteins and fats, and absorbing some nutrients.
Small Intestine
- The small intestine is a tightly-coiled hollow tube, approximately 11 feet long, where most digestion and nutrient absorption occur.
- The small intestine has three sections: duodenum, jejunum, and ileum.
- The duodenum is the first section, where acidic stomach contents mix with alkaline fluids from the pancreas, gallbladder, and duodenum.
- The jejunum and ileum are the middle and last sections, where most digestion and nutrient absorption occur.
Nutrient Absorption in the Small Intestine
- The small intestine relies on peristalsis and segmentation to mix chyme and facilitate nutrient absorption.
- The lining of the small intestine is covered with villi, which increase the surface area for absorption.
- Absorptive cells in the villi have microvilli, which release enzymes to complete the digestion of carbohydrates and proteins.
- Nutrients are absorbed into the bloodstream through the portal venous system and eventually reach the liver for processing.
Large Intestine
- The large intestine is where water and electrolytes are absorbed, and the remaining waste is formed into feces.
- The large intestine is also home to the gut microbiota, which plays a crucial role in health.
Malabsorption
- Malabsorption occurs when the small intestine is unable to absorb nutrients, often due to a lack of nutrients needed for cell division.
- This can lead to a range of health problems, including nutrient deficiencies and gastrointestinal disorders.### Intestinal Tract and Immune Function
- The intestinal tract produces mucus, which forms a barrier to reduce the likelihood of absorption of agents of infection
- Peyer's patches in the ileum have immune system cells that produce antibodies to combat harmful agents
- Antibodies recognize and bind to harmful agents, helping to destroy them before they enter the bloodstream
Pancreas, Liver, and Gallbladder
- The pancreas produces and secretes digestive enzymes and bicarbonate ions to neutralize stomach acid
- The liver processes and stores nutrients, makes cholesterol, and produces bile to prepare fats and fat-soluble vitamins for digestion
- Bile is stored in the gallbladder and released into the small intestine when fat is present
Formation of Gallstones
- Gallstones are small, hard deposits that form in the gallbladder
- They are usually composed of cholesterol and can cause pain and blockage of the bile ducts
- Having excess body fat increases the risk of developing gallstones
Cystic Fibrosis
- Cystic fibrosis is an inherited disease that affects the production of mucus and digestive enzymes
- Thick, sticky mucus blocks passageways in the respiratory and digestive systems
- The disease impairs digestion and nutrient absorption
Bezoars
- Bezoars are dense masses of undigested material that can form in the digestive tract
- They can be classified according to their contents, such as phytobezoars (plant material) and trichobezoars (hair)
- Bezoars can cause symptoms such as vomiting, abdominal pain, and weight loss
Large Intestine
- The large intestine is shorter than the small intestine but has a wider diameter
- Cells in the large intestine produce mucus to protect and lubricate the walls
- The large intestine has no villi, so little additional absorption occurs in this structure
- Feces are formed in the large intestine and consist of bacteria, undigested fiber, and small amounts of water, protein, and fat
Elimination
- Feces are stored in the rectum until they are eliminated through the anus
- The external anal sphincter is under voluntary control, allowing individuals to determine when to have a bowel movement
Microbes in the Digestive Tract
- The large intestine is home to a diverse community of microbes, known as gut microbiota
- Gut microbiota play a crucial role in breaking down undigested food, producing vitamins, and maintaining a balance with each other
- An imbalance of gut microbiota, known as dysbiosis, can lead to diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease
Probiotics and Prebiotics
- Probiotics are live, beneficial microbes that can be found in fermented foods or taken as dietary supplements
- Prebiotics are forms of dietary fiber that support the growth of probiotics in the colon
- Probiotics and prebiotics may help prevent diarrhea and treat certain intestinal disorders
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
-
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of chronic diseases that cause inflammation and swelling of the intestines
-
The two most common forms of IBD are ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease
-
IBD is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic, environmental, and dietary factors
-
The typical Western diet, which is high in animal protein and low in fiber, may contribute to the development of IBD### Ulcerative Colitis (UC)
-
People with UC must take medication for the rest of their lives, unless their large intestine is severely diseased and needs to be surgically removed.
-
Patients with UC have an increased risk of colon cancer, especially when their entire colon is affected and they have had the disease for 8 or more years.
-
Managing inflammation with medication and having regular screening can reduce the risk of colon cancer.
Crohn's Disease (CD)
- More than 500,000 Americans have CD, a form of IBD that can affect the entire gastrointestinal tract, including the mouth.
- The last section of the small intestine (ileum) and the beginning of the colon are most commonly inflamed in CD.
- CD damages deeper layers of the intestines than UC.
- Symptoms of CD include diarrhea, painful abdominal cramps, loss of appetite, and weight loss.
- Treatment for CD is similar to that of UC, involving medication to reduce inflammation and promote healing, as well as avoiding foods that cause "flares".
- Surgery may be necessary in severe cases to remove badly damaged portions of the intestinal tract.
- People with CD have an increased risk of colon cancer.
Alicia's Story
- Alicia Anne, a young woman, was diagnosed with CD at 25 years old.
- She experienced weight loss, diarrhea, and abdominal pain, and eventually discovered blood in her stools.
- She was diagnosed with an inflamed ileum and CD, and was prescribed prednisone to treat her condition.
- Alicia now takes multiple medications to manage her CD, and monitors her diet to avoid "flares".
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.