Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the digestive system?
What is the primary function of the digestive system?
- To take in food, digest it, and excrete waste (correct)
- To pump blood throughout the body
- To produce hormones
- To regulate body temperature
Which of the following is NOT part of the digestive tract?
Which of the following is NOT part of the digestive tract?
- Small Intestine
- Gallbladder (correct)
- Esophagus
- Stomach
What is the role of goblet cells in the digestive system?
What is the role of goblet cells in the digestive system?
- To transport food through the esophagus
- To absorb nutrients from food
- To secrete mucus for protection (correct)
- To produce digestive enzymes
Which layers make up the structure of the digestive tube?
Which layers make up the structure of the digestive tube?
What role do accessory organs serve in the digestive system?
What role do accessory organs serve in the digestive system?
What is the primary function of saliva in the digestion process?
What is the primary function of saliva in the digestion process?
Which structure prevents food from entering the respiratory system during swallowing?
Which structure prevents food from entering the respiratory system during swallowing?
What role do the villi in the small intestine serve?
What role do the villi in the small intestine serve?
What process is involved in moving food through the esophagus?
What process is involved in moving food through the esophagus?
What is the primary function of the large intestine?
What is the primary function of the large intestine?
Which organ produces bile for the digestion of fats?
Which organ produces bile for the digestion of fats?
What digestive issue is characterized by inflammation of the lining of the large intestine?
What digestive issue is characterized by inflammation of the lining of the large intestine?
How does the pancreas contribute to digestion?
How does the pancreas contribute to digestion?
What is a common symptom of diabetes linked to blood glucose level irregularities?
What is a common symptom of diabetes linked to blood glucose level irregularities?
Which part of the digestive system is primarily involved in nutrient absorption?
Which part of the digestive system is primarily involved in nutrient absorption?
Flashcards
What does the digestive system do?
What does the digestive system do?
The digestive system breaks down food into smaller molecules that the body can absorb and use for energy and growth.
What is the digestive tract?
What is the digestive tract?
The digestive tract is a long tube that starts with the mouth and ends with the anus. It's responsible for moving food through the body and breaking it down.
What are accessory organs?
What are accessory organs?
Accessory organs are not part of the digestive tract, but they help the digestive system break down food. Examples include the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.
What is mechanical digestion?
What is mechanical digestion?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is chemical digestion?
What is chemical digestion?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mechanical Digestion
Mechanical Digestion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chemical Digestion
Chemical Digestion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Esophagus
Esophagus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peristalsis
Peristalsis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epiglottis
Epiglottis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stomach
Stomach
Signup and view all the flashcards
Small Intestine
Small Intestine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Villi
Villi
Signup and view all the flashcards
Large Intestine (Colon)
Large Intestine (Colon)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Liver
Liver
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
The Digestive System
- The digestive system takes in food, breaks it down, and excretes waste
- It is made up of a digestive tract and accessory organs
- The digestive tract is a long tube with two openings: mouth and anus
- The digestive tract is composed of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and rectum
The Digestive Tract
- Lined with epithelial tissue made up of different cell types
- Goblet cells secrete mucus
- Mucus protects against digestive enzymes, allowing smooth passage
- Includes layers of muscles and nerves
Accessory Organs
- Not part of the digestive tract but aid in digestion
- Include the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas
Mechanical vs. Chemical Digestion
- Mechanical digestion is the physical breakdown of food
- Chemical digestion breaks down food using enzymes
Mouth
- Begins the process of breaking down food
- Mechanical digestion uses teeth and tongue
- Chemical digestion involves enzymes in saliva breaking down food molecules
Mouth: Saliva
- Provides water and enzymes (amylase) to chemically break down and moisten food
- Produced by epithelial tissue lining the mouth and salivary glands
Esophagus
- Muscular tube connecting the mouth to the stomach
- Food moves through involuntarily via peristalsis
- Peristalsis is involuntary muscle contraction that moves food through the esophagus
Esophagus: Epiglottis
- Tiny flap-like structure that covers the trachea
- Prevents food from entering the respiratory system during swallowing
Stomach
- Holds food and churns it (physical breakdown) to continue digestion
- Stomach lining produces digestive enzymes and acid (for chemical breakdown), as well as mucus
- Mucus protects the stomach lining tissue from acid
Small Intestine
- 6 meters long and narrow
- Site of most digestion and absorption of nutrients
- Goblet cells in the lining release mucus
- Nutrients diffuse through the wall of the small intestine and enter the bloodstream
- Contains smooth muscles that contract and relax involuntarily to move broken-down food
Small Intestine: Villi
- Small intestines contain finger-like projections called villi
- Villi increase the surface area for more nutrient absorption
Large Intestine (Colon)
- Only 1.5 meters long and wider than the small intestine
- Absorbs water from indigestible food
- Contains bacteria that assist in producing vitamins
- Remaining solid waste is excreted as feces from the anus
Accessory Organ: Liver
- Produces bile
- Bile is a fluid that helps mechanically break down fats in food
Accessory Organ: Gallbladder
- Stores bile produced by the liver
Accessory Organ: Pancreas
- Releases enzymes into the small intestine aiding in digestion
- Produces insulin that helps regulate blood glucose levels
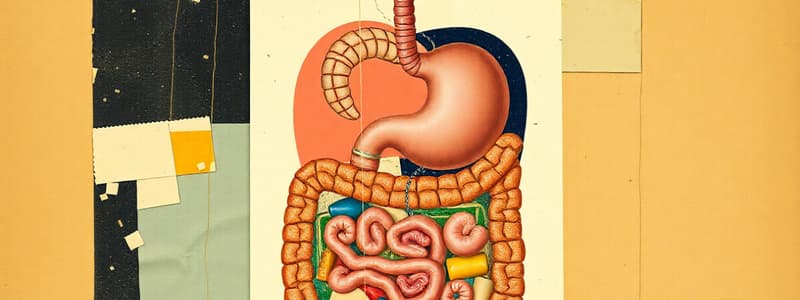
Digestive System Diagram - Parts
- Diagram includes mouth, salivary glands, epiglottis, esophagus, stomach, pancreas, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus, liver, and gallbladder.
Digestive System Problems
- Diabetes: A condition where the pancreas produces too much or too little insulin, regulating blood glucose levels.
- Colitis: Inflammation of the large intestine caused by viruses, bacteria, narrowed blood vessels or immune system failure. Diagnosed with an endoscope and microscopic tissue examination.
When the Digestion Goes Wrong
- Toxins, produced by bacteria or spoiled food (or too much alcohol) are recognized by the body. The digestive tract responds rapidly to remove toxins via vomiting or diarrhea.
Video: The Journey of the Digestive System
- [Video title provided by Amoeba Sisters]
Homework
- Read pages 80-82 in the textbook
- Answer questions 2-4 on page 82
Extra Help
- Digestive system review
Answers
- Q2: for digestion to occur molecules need to be broken down so they can diffuse through intestines into bloodstream
- Q3: Substances added to the food are saliva, stomach acid, enzymes, bile, and mucus
- Q4: Muscle tissue contracts to push food through the digestive system
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.