Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which lobe of the cerebrum is primarily responsible for integrating sensory information such as touch, temperature, and pain?
Which lobe of the cerebrum is primarily responsible for integrating sensory information such as touch, temperature, and pain?
- Occipital Lobe
- Parietal Lobe (correct)
- Temporal Lobe
- Frontal Lobe
Which of the following functions is NOT primarily managed by the brain stem?
Which of the following functions is NOT primarily managed by the brain stem?
- Sneezing
- Heartbeat
- Posture (correct)
- Breathing
What is the primary function of the ciliary muscles in the eye?
What is the primary function of the ciliary muscles in the eye?
- Preventing light from entering the eye from anywhere but the pupil
- Detecting color
- Holding the iris open by default
- Contracting or expanding to adjust focus at different distances (correct)
Which part of the eye is responsible for preventing foreign pathogens from entering?
Which part of the eye is responsible for preventing foreign pathogens from entering?
Why is binocular vision essential for humans?
Why is binocular vision essential for humans?
What type of neuron is responsible for transmitting signals between sensory and motor neurons?
What type of neuron is responsible for transmitting signals between sensory and motor neurons?
Which type of receptor is responsible for detecting changes in pressure?
Which type of receptor is responsible for detecting changes in pressure?
If someone is experiencing difficulty with emotional regulation and problem-solving, which lobe of the brain is most likely affected?
If someone is experiencing difficulty with emotional regulation and problem-solving, which lobe of the brain is most likely affected?
Which of the following correctly pairs a part of the eye with its function?
Which of the following correctly pairs a part of the eye with its function?
Which of the following lists the major sections of the brain?
Which of the following lists the major sections of the brain?
Flashcards
Brain Sections
Brain Sections
The brain consists of the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem.
Frontal Lobe
Frontal Lobe
Responsible for emotional regulation, planning, reasoning, and problem-solving.
Temporal Lobe
Temporal Lobe
Processes auditory information and some sensory features.
Occipital Lobe
Occipital Lobe
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parietal Lobe
Parietal Lobe
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brain Stem Function
Brain Stem Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cerebellum Function
Cerebellum Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Choroid
Choroid
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sensory Neurons
Sensory Neurons
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interneurons
Interneurons
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
The Brain: Central Nervous System (CNS)
- The brain consists of three major sections: the cerebrum, the cerebellum, and the brainstem.
Cerebrum
- The cerebrum consists of four lobes.
- Frontal Lobe: Primarily responsible for emotional regulation, planning, reasoning, and problem-solving.
- Temporal Lobe: Primarily responsible for hearing and some sensory feature processing.
- Occipital Lobe: Primarily responsible for receiving and processing signals from the optic nerve.
- Parietal Lobe: Primarily responsible for integrating sensory information, such as touch, temperature, pressure, and pain, and helps discern objects.
Brainstem
- The brainstem manages most involuntary functions such as heartbeat, sneezing, and breathing.
Cerebellum
- The cerebellum manages posture, balance, and coordination.
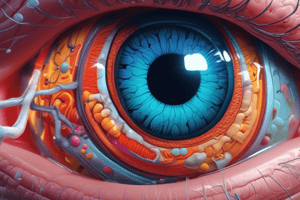
The Eye
- The eye is one of the two primary sense organs.
- Sight accounts for 80-90% of sensory input.
Parts of the Eye
- Choroid: Tissue layer surrounding the eye that prevents light from entering except through the pupil.
- Sclerotic Layer: Thick layer providing rigidity and protection to the eye.
- Cornea: Thin, clear tissue that prevents foreign pathogens from entering.
- Iris: Opaque tissue that dilates or contracts to change the size of the pupil.
- Lens: Convex-shaped tissue that reflects light onto the retina.
- Vitreous Humor: Gel-like substance that provides structure to the eye.
- Aqueous Humor: Gel-like substance that provides structure to the elements in front of the lens.
- Pupil: Hole in the eye that allows light to enter and dilates in darker environments.
- Suspensory Ligaments: Ligaments that hold the iris open by default.
- Ciliary Muscles: Muscles that contract or expand to adjust focus.
- Optic Nerve: Nerve that transmits visual information to the brain.
- Yellow Spot (Fovea): A spot with fewer color receptors.
- Retina: Layer of color detection cells across the back of the eye.
- Blind Spot: Spot in front of the optic nerve where no receptors are present.
Binocular Vision
- Binocular vision is the ability to see with two eyes facing in the same direction, facilitating depth perception.
- Either eye has a semi side view of any object using binocular vision.
Neurons
- There are 3 major types of neurons.
Sensory Neurons
- Sensory neurons detect changes to certain stimuli.
- Interneurons transmit signals between neurons.
- Motor neurons are different for different functions.
Receptors
- Photoreceptors: Detect light.
- Thigmoreceptors: Detect changes in pressure.
- Thermoreceptors: Detect changes in temperature.
- Nocireceptors: Detect pain.
- Mechanoreceptors: Detect movement.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.