Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following nerves arises from the anterior division of the brachial plexus and innervates muscles that function primarily as flexors?
Which of the following nerves arises from the anterior division of the brachial plexus and innervates muscles that function primarily as flexors?
- Median nerve (correct)
- Musculocutaneous nerve (correct)
- Radial nerve
- Axillary nerve
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of the axillary lymph nodes?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of the axillary lymph nodes?
- They drain lymph vessels from the thoracoabdominal walls above the umbilicus.
- They are typically arranged in six groups.
- They drain lymph vessels from the posterior compartment of the forearm. (correct)
- They drain lymph vessels from the lateral quadrants of the breast.
- They drain lymph vessels from the superficial lymph vessels.
Which of the following groups of axillary lymph nodes is NOT mentioned in the provided text?
Which of the following groups of axillary lymph nodes is NOT mentioned in the provided text?
- Inferior (infrascapular) group (correct)
- Central group
- Posterior (subscapular) group
- Anterior (pectoral) group
- Lateral group
Which of the following is a true statement about the nerves arising from the brachial plexus?
Which of the following is a true statement about the nerves arising from the brachial plexus?
Which of the following nerves is NOT directly responsible for innervating muscles in the upper limb?
Which of the following nerves is NOT directly responsible for innervating muscles in the upper limb?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
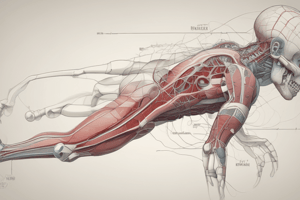
The Axilla Overview
- The axilla is a pyramid-shaped space located between the upper arm and the side of the chest.
- Serves as a crucial passage for nerves, blood, and lymph vessels from the neck to the upper limb.
Apex and Base
- Apex (cervico-axillary canal): The upper end of the axilla, bordered by:
- Anterior: Clavicle
- Posterior: Upper border of the scapula
- Medial: Outer border of the first rib
- Base: Formed by:
- Anterior: Pectoralis major muscle
- Posterior: Latissimus dorsi and teres major muscles
- Medial: Chest wall
Axillary Walls
- Anterior wall: Made up of pectoralis major, subclavius, and pectoralis minor muscles.
- Lateral wall: Composed of coracobrachialis and biceps muscles located in the bicipital groove of the humerus.
- Medial wall: Consists of upper ribs and intercostal spaces covered by the serratus anterior muscle.
- Posterior wall: Formed by subscapularis, latissimus dorsi, and teres major muscles.
Contents of the Axilla
- Axillary artery: Supplies blood to the upper limb.
- Axillary vein: Drains blood from the upper limb back to the heart.
- Lymph vessels and lymph nodes: Play a role in immune response.
- Brachial plexus: A network of nerves supplying the arm.
Axillary Artery
- Begins at the lateral border of the first rib, continuing from the subclavian artery.
- Terminates at the lower border of the teres major muscle, where it transitions into the brachial artery.
- Enclosed within the axillary sheath alongside the brachial plexus.
Axillary Artery Parts
- First part: Extends from the first rib to the upper border of the pectoralis minor.
- Branches: Highest thoracic artery.
- Second part: Lies behind the pectoralis minor.
- Branches:
- Thoracoacromial artery
- Lateral thoracic artery
- Branches:
- Third part: Extends from the lower border of the pectoralis minor to the teres major.
- Branches:
- Subscapular artery
- Posterior circumflex humeral artery
- Anterior circumflex humeral artery
- Branches:
Axillary Vein
- Formed at the lower border of the teres major by the union of the venae comitantes and the basilic vein.
- Runs medially to the axillary artery, becoming the subclavian vein at the first rib.
Brachial Plexus
- Composed of anterior rami from C5, C6, C7, C8, and T1 spinal nerves.
- Roots branch:
- Dorsal scapular nerve (C5)
- Long thoracic nerve (C5, C6, C7)
- Upper trunk branches:
- Suprascapular nerve (C5, C6)
- Nerve to subclavius (C5, C6)
- Cords branches:
- Lateral cord: Lateral pectoral nerve, musculocutaneous nerve.
- Posterior cord: Upper subscapular nerve, thoracodorsal nerve, lower subscapular nerve, axillary nerve, radial nerve.
- Medial cord: Medial pectoral nerve, medial cutaneous nerves of the arm and forearm, ulnar nerve, medial root of the median nerve.
Axillary Lymph Nodes
- Comprises 20 to 30 nodes draining lymph from:
- Lateral quadrants of the breast
- Superficial lymph vessels
- Thoracoabdominal walls above the umbilicus
- Upper limb vessels
- Arranged in six groups:
- Anterior (pectoral)
- Posterior (subscapular)
- Lateral
- Central
- Infraclavicular (deltopectoral)
- Apical
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.