Podcast
Questions and Answers
What are the two bones involved in the TMJ?
What are the two bones involved in the TMJ?
- Cranial and mandibular bones (correct)
- Mandible and zygomatic bones
- Glenoid fossa and articular eminence
- Temporal and occipital bones
What type of joint is the Temporo-mandibular Articulation?
What type of joint is the Temporo-mandibular Articulation?
- Fibrous joint
- Cartilagenous joint
- Synovial joint (correct)
- Synostosis
What is the articular surface of the temporal bone also known as?
What is the articular surface of the temporal bone also known as?
- Glenoid fossa
- Articular tubercle
- Cranial component (correct)
- Postglenoid tubercle
What is the classification of the joint based on the movement it provides?
What is the classification of the joint based on the movement it provides?
What is the shape of the articular eminence?
What is the shape of the articular eminence?
What connects the two bones in a fibrous joint?
What connects the two bones in a fibrous joint?
What is the function of the articular tubercle?
What is the function of the articular tubercle?
What is the shape of the condyle of the mandible?
What is the shape of the condyle of the mandible?
What is the anatomical classification of the Temporo-mandibular Articulation?
What is the anatomical classification of the Temporo-mandibular Articulation?
What is the anterior articular area of the glenoid fossa formed by?
What is the anterior articular area of the glenoid fossa formed by?
How many Temporo-mandibular Articulations are present in the human body?
How many Temporo-mandibular Articulations are present in the human body?
What is the name of the bone that articulates with the mandible in the Temporo-mandibular Articulation?
What is the name of the bone that articulates with the mandible in the Temporo-mandibular Articulation?
What is the surface of the glenoid fossa like?
What is the surface of the glenoid fossa like?
What type of movement does the Temporo-mandibular Articulation provide?
What type of movement does the Temporo-mandibular Articulation provide?
What is the shape of the mandible in the TMJ?
What is the shape of the mandible in the TMJ?
What is the cavity that surrounds the joint?
What is the cavity that surrounds the joint?
What is the mediolateral diameter of the condyle?
What is the mediolateral diameter of the condyle?
What is the structure that divides into the inferior lamella and superior lamella?
What is the structure that divides into the inferior lamella and superior lamella?
What is the primary function of the articular disc?
What is the primary function of the articular disc?
What is the approximate volume of the upper joint space?
What is the approximate volume of the upper joint space?
Which of the following ligaments is NOT a true ligament of the TMJ?
Which of the following ligaments is NOT a true ligament of the TMJ?
What is the morphology of the articular disc?
What is the morphology of the articular disc?
What is the central region of the articular disc?
What is the central region of the articular disc?
What attaches the disk to the lateral and medial poles of each condyle?
What attaches the disk to the lateral and medial poles of each condyle?
What is the embryological origin of the articular disc?
What is the embryological origin of the articular disc?
Flashcards
TMJ Bones
TMJ Bones
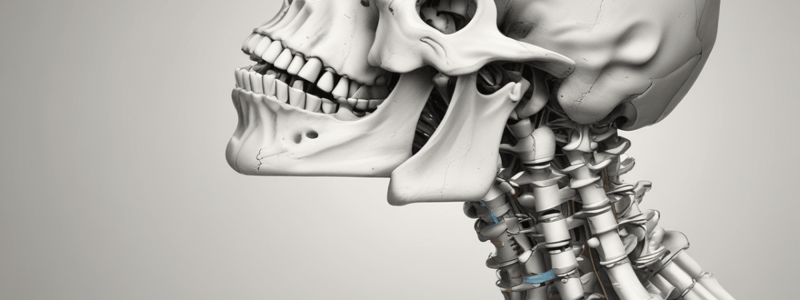
The two bones that form the Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) are the cranial bone (specifically the squamous part of the temporal bone) and the mandibular bone.
TMJ Joint Type
TMJ Joint Type
The Temporomandibular Joint is a synovial joint, meaning it's a freely movable joint with a synovial cavity and articular cartilage.
Cranial Component
Cranial Component
The articular surface of the temporal bone in the TMJ is also known as the cranial component.
TMJ Movement Classification
TMJ Movement Classification
Signup and view all the flashcards
Articular Eminence Shape
Articular Eminence Shape
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibrous Joint Connection
Fibrous Joint Connection
Signup and view all the flashcards
Articular Tubercle Function
Articular Tubercle Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mandibular Condyle Shape
Mandibular Condyle Shape
Signup and view all the flashcards
TMJ Anatomical Classification
TMJ Anatomical Classification
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glenoid Fossa Formation
Glenoid Fossa Formation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Number of TMJs
Number of TMJs
Signup and view all the flashcards
TMJ Articulating Bone
TMJ Articulating Bone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glenoid Fossa Surface
Glenoid Fossa Surface
Signup and view all the flashcards
TMJ Movement
TMJ Movement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mandibular Shape in TMJ
Mandibular Shape in TMJ
Signup and view all the flashcards
Synovial Cavity
Synovial Cavity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Condyle Mediolateral Diameter
Condyle Mediolateral Diameter
Signup and view all the flashcards
Posterior Disc Attachment Division
Posterior Disc Attachment Division
Signup and view all the flashcards
Articular Disc Function
Articular Disc Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Upper Joint Space Volume
Upper Joint Space Volume
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mandibulo-malleolar Ligament
Mandibulo-malleolar Ligament
Signup and view all the flashcards
Articular Disc Morphology
Articular Disc Morphology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Articular Disc Central Region
Articular Disc Central Region
Signup and view all the flashcards
Collateral Ligament Attachment
Collateral Ligament Attachment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Articular Disc Embryological Origin
Articular Disc Embryological Origin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Bones Involved
- Glenoid fossa of the temporal bone
- Condyle of the mandible
Articulatory System
- 2 articular surfaces: upper roof and lower floor
- Upper roof: 2 parts of temporal bone
- Lower floor: superior surface of disc
- Roof: inferior surface of disc
- Floor: articulating surface of the mandibular condyle
Temporo-mandibular Joint (TMJ)
- Definition: a diarthrodial freely movable articulation between the condyle of the mandible and squamous part of the temporal bone
- Classification: synovial joint, bilateral condylar variety
- Types of movement: hinging or rotation movement in one plane, sliding movement
Articular Eminence
- Small prominence in the zygomatic arch
- Strongly convex anteroposteriorly and concave mediolaterally
- Serves as a major functional component of the TMJ
Articular Tubercle (Postglenoid Tubercle)
- Non-articulating process on the lateral aspect of the zygomatic root of the temporal bone
- Serves as a point of attachment of collateral ligaments
Glenoid Fossa
- Anterior articular area formed by the inferior aspect of temporal squama
- Smooth and oval surface
Mandibular Component
- Ovoid condylar process (head) with narrow mandibular neck
- Rounded mediolaterally and convex anteroposteriorly
- Broad laterally and narrow medially
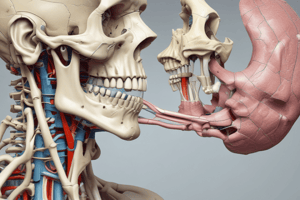
Articular Disc
- Morphology: biconcave, sagitally thicker anteriorly and thinner posteriorly, oval, avascular, and non-innervated in the middle
- Derived from mesoderm of 1st pharyngeal arch
- Divided into 3 general regions: anterior band, central intermediate zone, and posterior band
Function of Articular Disc
- Stabilization of the TMJ
- Reduces wear on the joint
TMJ Ligaments
- Functional ligaments: collateral, capsular, and lateral
- Accessory ligaments: sphenomandibular, stylomandibular, and mandibulo-malleolar (Pinto's ligament)
- Serve as passive restraints on mandibular motion
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.