Podcast
Questions and Answers
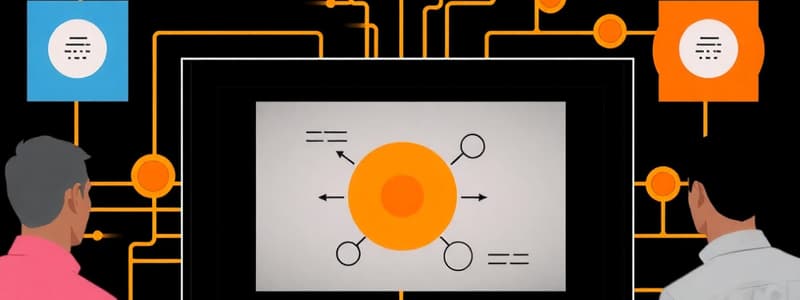
How is the number of interfaces related to the number of subsystems?
How is the number of interfaces related to the number of subsystems?
- Interfaces increase linearly with subsystems.
- Interfaces are calculated as $n(n+1)/2$.
- Interfaces are calculated as $n(n-1)/2$. (correct)
- There is no relationship between interfaces and subsystems.
What characterizes a black box system?
What characterizes a black box system?
- It is a system that can be easily understood.
- The processor of the system is undefined. (correct)
- The inputs and outputs are not defined.
- All of its components are clearly visible.
Which of the following is an example of a physical system?
Which of the following is an example of a physical system?
- Weather forecasting.
- Social clubs.
- A programmed computer. (correct)
- Economic theory.
Which type of system operates in an unpredictable manner?
Which type of system operates in an unpredictable manner?
What is a defining characteristic of a social system?
What is a defining characteristic of a social system?
Which type of system is an example of an artificial system?
Which type of system is an example of an artificial system?
What is a permanent system characterized by?
What is a permanent system characterized by?
Which type of system combines human and machine interaction?
Which type of system combines human and machine interaction?
What is the first step in the essence of software engineering practice?
What is the first step in the essence of software engineering practice?
Which principle emphasizes simplicity in software engineering?
Which principle emphasizes simplicity in software engineering?
What characterizes the software evolution process?
What characterizes the software evolution process?
What is the purpose of creating a software prototype in the development process?
What is the purpose of creating a software prototype in the development process?
What best describes the software process?
What best describes the software process?
What is a significant challenge addressed during software evolution?
What is a significant challenge addressed during software evolution?
Why is re-creating software from scratch often considered unfeasible?
Why is re-creating software from scratch often considered unfeasible?
Which principle indicates that what is produced will be used by others?
Which principle indicates that what is produced will be used by others?
What is essential for a system analyst to effectively motivate users during the system acceptance process?
What is essential for a system analyst to effectively motivate users during the system acceptance process?
Which interpersonal skill is crucial for a system analyst when interacting with various stakeholders?
Which interpersonal skill is crucial for a system analyst when interacting with various stakeholders?
What technical skill is necessary for a system analyst to propose innovative system designs?
What technical skill is necessary for a system analyst to propose innovative system designs?
Which of the following best describes the role of a system analyst in understanding user behavior?
Which of the following best describes the role of a system analyst in understanding user behavior?
Which skill is vital for a system analyst to ensure effective user training?
Which skill is vital for a system analyst to ensure effective user training?
What is a key characteristic of an orderly and disciplined system analyst?
What is a key characteristic of an orderly and disciplined system analyst?
In addition to creativity, which skill is important for logical problem-solving by a system analyst?
In addition to creativity, which skill is important for logical problem-solving by a system analyst?
Which of the following represents a crucial understanding necessary for a system analyst?
Which of the following represents a crucial understanding necessary for a system analyst?
What is the primary goal of the software processes?
What is the primary goal of the software processes?
Which activity is focused on defining what the system should do?
Which activity is focused on defining what the system should do?
Who is primarily responsible for ensuring customers understand their requirements?
Who is primarily responsible for ensuring customers understand their requirements?
What does validation check in the software process?
What does validation check in the software process?
What is typically involved in the detailed design phase of software development?
What is typically involved in the detailed design phase of software development?
What distinguishes verification from validation in the software process?
What distinguishes verification from validation in the software process?
During which phase are individual pieces of software coded and tested?
During which phase are individual pieces of software coded and tested?
What is the focus of the high-level design phase in software development?
What is the focus of the high-level design phase in software development?
What is the primary purpose of a Decision Support System (DSS)?
What is the primary purpose of a Decision Support System (DSS)?
What components make up a Decision Support System (DSS)?
What components make up a Decision Support System (DSS)?
How does an Expert System (ES) interact with users?
How does an Expert System (ES) interact with users?
What is the role of Knowledge Engineers in the context of Expert Systems?
What is the role of Knowledge Engineers in the context of Expert Systems?
What does an Enterprise Architecture (EA) framework provide?
What does an Enterprise Architecture (EA) framework provide?
What is the importance of documenting each view in an EA framework?
What is the importance of documenting each view in an EA framework?
Which of the following best defines knowledge representation in Expert Systems?
Which of the following best defines knowledge representation in Expert Systems?
What impact do integrating technologies have on systems as noted in the context?
What impact do integrating technologies have on systems as noted in the context?
What is the primary purpose of system analysis in the context of system development?
What is the primary purpose of system analysis in the context of system development?
Which step is NOT part of the system analysis process?
Which step is NOT part of the system analysis process?
What is identified during the problem identification phase of system analysis?
What is identified during the problem identification phase of system analysis?
In the context of system development life cycle (SDLC), what are the two main phases?
In the context of system development life cycle (SDLC), what are the two main phases?
Which of the following accurately describes the system development life cycle (SDLC)?
Which of the following accurately describes the system development life cycle (SDLC)?
What aspect does the feasibility study in system analysis primarily focus on?
What aspect does the feasibility study in system analysis primarily focus on?
What may the root cause of a problem identified in system analysis be?
What may the root cause of a problem identified in system analysis be?
Which statement is true regarding modifications in system analysis?
Which statement is true regarding modifications in system analysis?
Flashcards
Number of Interfaces
Number of Interfaces
The number of interfaces in a system is calculated as n(n-1)/2, where n is the number of subsystems.
Black Box Subsystem
Black Box Subsystem
A subsystem where the internal workings (how input transforms to output) are unknown or hidden.
Physical System
Physical System
A system composed of tangible, concrete elements; people, materials, machines, etc.
Abstract System
Abstract System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Deterministic System
Deterministic System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Probabilistic System
Probabilistic System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Social System
Social System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Manufactured System
Manufactured System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decision Support System (DSS)
Decision Support System (DSS)
Signup and view all the flashcards
DSS Components
DSS Components
Signup and view all the flashcards
Software Evolution
Software Evolution
Signup and view all the flashcards
Expert System (ES)
Expert System (ES)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Software Process
Software Process
Signup and view all the flashcards
Knowledge Representation (ES)
Knowledge Representation (ES)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Knowledge Acquisition (ES)
Knowledge Acquisition (ES)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Software Engineering Principles
Software Engineering Principles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Enterprise Architecture Framework (EA Framework)
Enterprise Architecture Framework (EA Framework)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Software Development Life Cycle
Software Development Life Cycle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Enterprise Architecture Principles
Enterprise Architecture Principles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Requirements Gathering
Requirements Gathering
Signup and view all the flashcards
Architecture Framework Benefits
Architecture Framework Benefits
Signup and view all the flashcards
Software Prototype
Software Prototype
Signup and view all the flashcards
Testing and Quality Assurance
Testing and Quality Assurance
Signup and view all the flashcards
UML
UML
Signup and view all the flashcards
System Development Methodology
System Development Methodology
Signup and view all the flashcards
System Analysis
System Analysis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Problem Identification
Problem Identification
Signup and view all the flashcards
Feasibility Study
Feasibility Study
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Signup and view all the flashcards
System Requirement Analysis
System Requirement Analysis
Signup and view all the flashcards
System Design
System Design
Signup and view all the flashcards
SDLC: System Development Life Cycle
SDLC: System Development Life Cycle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Software Process Activities
Software Process Activities
Signup and view all the flashcards
Specification
Specification
Signup and view all the flashcards
Requirements
Requirements
Signup and view all the flashcards
Development
Development
Signup and view all the flashcards
Validation
Validation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Verification
Verification
Signup and view all the flashcards
Evolution
Evolution
Signup and view all the flashcards
System Analyst's Role
System Analyst's Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Analyst's Interpersonal Skills
Analyst's Interpersonal Skills
Signup and view all the flashcards
Analyst's Technical Skills
Analyst's Technical Skills
Signup and view all the flashcards
Understanding Customer Problems
Understanding Customer Problems
Signup and view all the flashcards
Motivating Users and Developers
Motivating Users and Developers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Analyst's Orderly Mind
Analyst's Orderly Mind
Signup and view all the flashcards
Analyst's Communication Ability
Analyst's Communication Ability
Signup and view all the flashcards
Analyst's Flexibility
Analyst's Flexibility
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Software Engineering Study Notes
- Software Engineering: A branch of engineering dealing with the design, development, operation, and maintenance of software. It applies engineering principles and methods
- Software: A set of computer programs, data, and documentation that enable computers to perform specific tasks.
- Good Software Qualities: Software should be maintainable, reliable, efficient, and usable.
- Software Life Cycle: A structured set of stages involved in developing and maintaining software
- Software Crisis: The difficulties faced in efficiently developing complex software systems.
- Software Requirements Specification (SRS): A formal documentation of the needs of the software system to ensure there is a shared understanding between developers and customers.
- UML (Unified Modeling Language): A graphical language for specifying, visualizing, constructing, and documenting the artifacts of software systems.
- Class Diagrams: Static view of a system, showing classes and their relationships (attributes, operations, and associated elements).
- Object Diagrams: Specific (instance) view of a system, similar to class diagrams, but showing specific objects and their relationships at a particular moment.
- Use Case Diagrams: Describe a system's functionalities from the user's perspective (use cases, actors, and associations)
- Sequence Diagrams: Show the flow of messages—ordered by time—between objects in a system
- Collaboration Diagrams: Similar to sequence diagrams, but focusing on the structural organization of the objects interacting within the system.
- State Machine Diagrams: Model an object's state transitions in its lifetime, driven by events.
- Activity Diagrams: Formal flowcharts demonstrating the flow of control through activities in a system.
- Component Diagrams: Displays physical components a system and their interdependencies; used in implementation.
- Deployment Diagrams: Visual representation of a system's physical topology or architectural deployment—where software components reside on physical nodes.
- Package Diagrams: Shows the dependencies between packages or components within a system.
- UML Building Blocks: Things, Relationships, and Diagrams
- Structured English: A method for communicating the logic of a program in English combined with structured programming constructs.
- Pseudocode: A straightforward, English-like representation of code logic that may be used in early analysis and design phases prior to actual coding in any language.
- Data Flow Diagrams (DFD): The flow of data in an information system, graphically representing transformational processes within the system
- Normalization: A technique to organize data in a database to eliminate redundancy and improve data integrity
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.