Podcast
Questions and Answers
Free radicals speed up the ______.
Free radicals speed up the ______.
reaction
Inhibitors such as ______ slow down the reaction.
Inhibitors such as ______ slow down the reaction.
oxygen
An ester is formed when a carboxylic acid is reacted with an ______.
An ester is formed when a carboxylic acid is reacted with an ______.
alcohol
The process of preparing soap is referred to as ______.
The process of preparing soap is referred to as ______.
An addition reaction always occurs on a ______ or triple bond.
An addition reaction always occurs on a ______ or triple bond.
The C=C double bond in ______ has a high concentration of negative charge.
The C=C double bond in ______ has a high concentration of negative charge.
The Br2 molecule splits into Br^+______ and Br^-.
The Br2 molecule splits into Br^+______ and Br^-.
The carbonium ion is then attacked by the ______ ion.
The carbonium ion is then attacked by the ______ ion.
The formation of 1,2-dibromethane occurs when the reaction is carried out in bromine water with ______ ions added.
The formation of 1,2-dibromethane occurs when the reaction is carried out in bromine water with ______ ions added.
Polymers are long chain molecules made by joining together many small ______.
Polymers are long chain molecules made by joining together many small ______.
The repeating unit of a polymer is that part of the polymer whose repetition produces the complete polymer ______.
The repeating unit of a polymer is that part of the polymer whose repetition produces the complete polymer ______.
Ethene can be produced from ethanol by means of an ______ reaction.
Ethene can be produced from ethanol by means of an ______ reaction.
When a primary alcohol reacts with an oxidising agent, it is converted to an ______.
When a primary alcohol reacts with an oxidising agent, it is converted to an ______.
Aldehydes and ketones can be reduced back to alcohols in the presence of ______ and a nickel catalyst.
Aldehydes and ketones can be reduced back to alcohols in the presence of ______ and a nickel catalyst.
To oxidise ethanal with potassium manganate(VII), one needs to add dilute sulfuric ______.
To oxidise ethanal with potassium manganate(VII), one needs to add dilute sulfuric ______.
In the reaction with Fehling's solution, the initial formation of a blue ______ is observed.
In the reaction with Fehling's solution, the initial formation of a blue ______ is observed.
Particles that are too light are deflected too much and hit the side of the ______.
Particles that are too light are deflected too much and hit the side of the ______.
The height of each peak in a mass spectrum represents the relative ______ of particles of that mass.
The height of each peak in a mass spectrum represents the relative ______ of particles of that mass.
Chromatography is a separation technique in which a mobile phase carrying a mixture moves in contact with a selectively ______ stationary phase.
Chromatography is a separation technique in which a mobile phase carrying a mixture moves in contact with a selectively ______ stationary phase.
In paper chromatography, the stationary phase is ______ paper.
In paper chromatography, the stationary phase is ______ paper.
Less soluble materials will appear as a spot closer to the ______ of the paper.
Less soluble materials will appear as a spot closer to the ______ of the paper.
In column chromatography, the stationary phase is ______ gel in a glass tube.
In column chromatography, the stationary phase is ______ gel in a glass tube.
The principle of gas chromatography is that a mixture of components is carried by a gaseous mobile phase and separated based on their different interactions with a solid ______ phase.
The principle of gas chromatography is that a mixture of components is carried by a gaseous mobile phase and separated based on their different interactions with a solid ______ phase.
The process of passing a solvent through a column in chromatography is known as ______.
The process of passing a solvent through a column in chromatography is known as ______.
No red precipitate is observed. Ketones are not oxidised by ______'s solution.
No red precipitate is observed. Ketones are not oxidised by ______'s solution.
Using a graduated disposable pipette, place in a clean test-tube 3 cm^3 of silver nitrate solution and 1 cm^3 of ______ solution.
Using a graduated disposable pipette, place in a clean test-tube 3 cm^3 of silver nitrate solution and 1 cm^3 of ______ solution.
Add aqueous ______ solution drop by drop, with shaking, until the precipitate formed is just dissolved.
Add aqueous ______ solution drop by drop, with shaking, until the precipitate formed is just dissolved.
The lighted taper is extinguished and limewater turns a milky white ______ when sodium carbonate is tested.
The lighted taper is extinguished and limewater turns a milky white ______ when sodium carbonate is tested.
In the synthesis of PVC from ethene, ethene and chlorine react to form ______.
In the synthesis of PVC from ethene, ethene and chlorine react to form ______.
In Mass Spectrometry, the sample material is vaporised into a ______.
In Mass Spectrometry, the sample material is vaporised into a ______.
The chloroethene undergoes a ______ reaction to form polychloroethene (PVC).
The chloroethene undergoes a ______ reaction to form polychloroethene (PVC).
A magnetic field of a particular strength is used to ______ the particles in Mass Spectrometry.
A magnetic field of a particular strength is used to ______ the particles in Mass Spectrometry.
The stationary phase in Gas Chromatography is a coiled column filled with coated ______.
The stationary phase in Gas Chromatography is a coiled column filled with coated ______.
The mobile phase in Gas Chromatography is an inert carrier ______.
The mobile phase in Gas Chromatography is an inert carrier ______.
Gas Chromatography is often paired with Mass ______ for component identification.
Gas Chromatography is often paired with Mass ______ for component identification.
In High Performance Liquid Chromatography, the stationary phase is a coated ______.
In High Performance Liquid Chromatography, the stationary phase is a coated ______.
Ultraviolet Spectroscopy provides a ______ for each compound by measuring how it absorbs UV light.
Ultraviolet Spectroscopy provides a ______ for each compound by measuring how it absorbs UV light.
Infra-red Spectroscopy identifies organic compounds based on how they absorb ______ radiation.
Infra-red Spectroscopy identifies organic compounds based on how they absorb ______ radiation.
In paper chromatography, a solvent is added to the tank to a depth of about ______ mm.
In paper chromatography, a solvent is added to the tank to a depth of about ______ mm.
The mobile phase in High Performance Liquid Chromatography is a suitable liquid ______ under high pressure.
The mobile phase in High Performance Liquid Chromatography is a suitable liquid ______ under high pressure.
The ______ level in the tank must be below the line on which the indicator samples are spotted.
The ______ level in the tank must be below the line on which the indicator samples are spotted.
The process of heating the mixture for a prolonged time without losing volatile materials is called ______.
The process of heating the mixture for a prolonged time without losing volatile materials is called ______.
During Stage 2, the substance removed by distillation was ______.
During Stage 2, the substance removed by distillation was ______.
To precipitate the soap, the function of ______ in Stage 3 was crucial.
To precipitate the soap, the function of ______ in Stage 3 was crucial.
Washing the soap thoroughly in Stage 4 was necessary to remove ______.
Washing the soap thoroughly in Stage 4 was necessary to remove ______.
The co-product of the reaction, also known as propane-1,2,3-triol, was found in the ______ at the end of the process.
The co-product of the reaction, also known as propane-1,2,3-triol, was found in the ______ at the end of the process.
Sodium stearate can dissolve both non-polar oils and ionic salts in sweat due to its ______ structure.
Sodium stearate can dissolve both non-polar oils and ionic salts in sweat due to its ______ structure.
The reaction type that occurred during the soap preparation is known as ______.
The reaction type that occurred during the soap preparation is known as ______.
Flashcards
Chain Reaction (in Chemistry)
Chain Reaction (in Chemistry)
A reaction where one step produces something that starts the next step, repeating the process.
Free Radicals and Reaction Speed
Free Radicals and Reaction Speed
Adding free radicals speeds up reactions involving free radicals.
Esterification
Esterification
Reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol, using sulfuric acid as a catalyst, to form an ester.
Addition Reaction
Addition Reaction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hydrogenation of Vegetable Oils
Hydrogenation of Vegetable Oils
Signup and view all the flashcards
Polarization (in Chemistry)
Polarization (in Chemistry)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Heterolytic Fission
Heterolytic Fission
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ionic Addition Reaction
Ionic Addition Reaction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Polymer Definition
Polymer Definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Repeating Unit (Polymer)
Repeating Unit (Polymer)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Elimination Reaction
Elimination Reaction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ethene Production
Ethene Production
Signup and view all the flashcards
Primary Alcohol Oxidation
Primary Alcohol Oxidation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Secondary Alcohol Oxidation
Secondary Alcohol Oxidation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Aldehyde Reduction
Aldehyde Reduction
Signup and view all the flashcards
1,2-dibromomethane formation
1,2-dibromomethane formation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mass Spectrometry
Mass Spectrometry
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mass Spectrum
Mass Spectrum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chromatography
Chromatography
Signup and view all the flashcards
Paper Chromatography
Paper Chromatography
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stationary Phase
Stationary Phase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mobile Phase
Mobile Phase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Elution
Elution
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gas Chromatography
Gas Chromatography
Signup and view all the flashcards
Refluxing
Refluxing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Saponification
Saponification
Signup and view all the flashcards
Distillation
Distillation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brine
Brine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Co-product of Saponification
Co-product of Saponification
Signup and view all the flashcards
Maximum Yield Calculation
Maximum Yield Calculation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Soap Structure and Function
Soap Structure and Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
R*f* Value
R*f* Value
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gas Chromatography (GC)
Gas Chromatography (GC)
Signup and view all the flashcards
GC-MS
GC-MS
Signup and view all the flashcards
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
Signup and view all the flashcards
HPLC Stationary Phase
HPLC Stationary Phase
Signup and view all the flashcards
HPLC Mobile Phase
HPLC Mobile Phase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Infrared Spectroscopy (IR)
Infrared Spectroscopy (IR)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fehling's Test
Fehling's Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tollen's Reagent
Tollen's Reagent
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does a positive Tollen's test indicate?
What does a positive Tollen's test indicate?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Magnesium Test
Magnesium Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sodium Carbonate Test
Sodium Carbonate Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thermal Cracking
Thermal Cracking
Signup and view all the flashcards
Polymerization
Polymerization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Substitution Reactions
- Substitution reaction: A chemical reaction where an atom or group of atoms in a molecule is replaced by another atom or group.
- Halogenation of alkanes: Alkanes react with halogens (e.g., chlorine, bromine) in the presence of ultraviolet light, undergoing substitution.
- Mechanism of monochlorination of methane: A free-radical substitution mechanism.
- Initiation: A chlorine molecule breaks down into two chlorine atoms.
- Propagation: A chlorine atom attacks a methane molecule, chlorine atom reacts with methyl free radical, methyl free radical attacks a chlorine molecule forming chloromethane and chlorine atom.
- Termination: Chlorine radicals and methyl radicals combine to form Cl2, chloromethane and ethane.
- Evidence: Reaction occurs when exposed to UV light, thousands of chloromethane molecules are formed, free radicals speed up the reaction, and inhibitors slow the reaction down.
Addition Reactions
- Addition reaction: Two or more molecules combine to form a single molecule, always on a double or triple bond causing a change in geometry from planar to tetrahedral bonds.
- Used in hydrogenation of vegetable oils, and to form plastics.
- Polarisation: The C=C double bond in ethene has a high concentration of negative charge; as Br2 approaches, the electrons repel away polarising Br2.
- Heterolytic fission: Br2 splits into Br⁺ and Br⁻ ions.
- Carbonium ion formation: Br+ attacks the electron-rich C=C bond. Forming a carbonium ion.
- Ionic Addition: The cation is attacked by the bromide ion to form 1,2-dibromoethane.
- Evidence: Reaction takes place when exposed to UV light; thousands of chloromethane molecules are formed and free radicals speed up the reaction.
Polymerisation Reactions
- Polymer definition: Long-chain molecules formed by combining many small molecules (monomers).
- Polymers are repeating structures consisting of thousands of monomers linked together. PVC is a common plastic.
- Polymer repeating unit: The part of the polymer whose repetition produces the complete polymer chain, excluding the end groups.
Elimination Reactions
- Elimination reaction: A small molecule is removed from a larger molecule, leaving a double bond in the larger molecule.
Redox Reactions
- Redox reactions: Reactions involving the transfer of electrons between molecules.
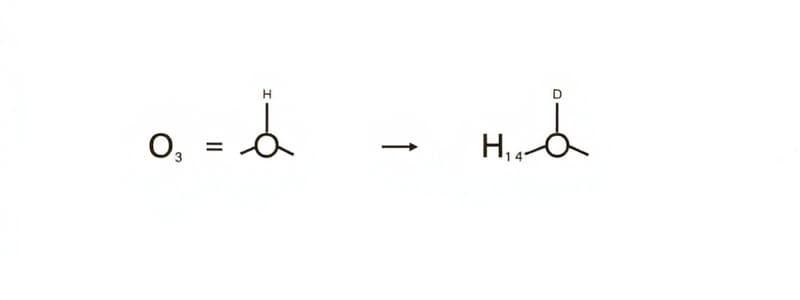
- Primary alcohols oxidised to aldehydes, losing 2 hydrogen atoms.
- Secondary alcohols oxidised to ketones, also losing 2 hydrogen atoms.
- Aldehydes and ketones reduced back to alcohols by hydrogen and a nickel catalyst.
- Mandatory experiment: Studying the reaction of ethanal with acidified potassium permanganate solution, Fehling's reagent, and ammoniacal silver titrate (oxidation by acidified potassium manganate).
Esterification
- Esterification: Carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol in the presence of H2SO4 catalyst, forming an ester. Saponification is the term for the reaction.
- Mandatory experiment: Preparing a sample of soap involves reaction of lard, potassium hydroxide, and ethanol, followed by distillation to remove ethanol, dissolving the residue in hot water, and precipitating the soap via the addition of brine.
Organic Acids
- Carboxylic acid group involves inductive effect, making the carbon atom of the carbonyl group slightly positive; Inductive effect means that the carbon atom pulls electrons from the oxygen atom to the -OH group.
- Stability of carboxylate ion: The negative charge is delocalised between the two oxygens and is not localised to just one oxygen.
- Mandatory experiment: Testing the effects of ethanoic acid with sodium carbonate, magnesium, and ethanol.
Other reactions and experiments
- Mandatory experiment to separate components of ink using paper chromatography.
- Separation from a mixture by paper chromatography (solvent in a beaker that soaks up through the paper separating components based on extent of dissolving).
Mass Spectrometry
- Principle of Mass Spectrometry: Charged particles moving in a magnetic field are deflected by different amounts due to their masses, separating the particles based on mass.
- Processes involved in mass spectrometry: Vaporisation, Ionisation, Acceleration, Separation, Detection.
- Mass spectrum output: Peaks in the mass spectrum, with abundance of particles.
Chromatography (general)
- Chromatography: Separation technique using a mobile phase that carries mixtures and a stationary phase with selective adsorption of components.
- Types of chromatography: Paper chromatography, column chromatography, GC, HPLC.
- Paper chromatography principle: components dissolve different to varying degrees (more soluble = higher it goes) on stationary phase (paper).
- Types of chromatography: Paper chromatography, column chromatography, GC, HPLC.
Spectroscopy
- Spectroscopy, measuring how compounds react to different frequencies (energies) of light or radiation, including infrared (IR), ultraviolet (UV).
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.