Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary structural role of collagen in the body?
What is the primary structural role of collagen in the body?
- Forming connective tissues such as tendons and ligaments (correct)
- Providing elasticity to blood vessels
- Facilitating nerve signal transmission
- Regulating skin pigmentation
Which type of collagen is considered the major component of the dermis?
Which type of collagen is considered the major component of the dermis?
- Type 3 Collagen
- Type 1 Collagen (correct)
- Type 4 Collagen
- Type 2 Collagen
What condition is associated with the stretching of the dermis and results in dermal scarring?
What condition is associated with the stretching of the dermis and results in dermal scarring?
- Keloids
- Eczema
- Psoriasis
- Striae (correct)
Which cells are responsible for the synthesis of collagen in the skin?
Which cells are responsible for the synthesis of collagen in the skin?
Which of the following factors is NOT typically associated with the formation of striae?
Which of the following factors is NOT typically associated with the formation of striae?
What are the characteristics of malignant melanoma cells?
What are the characteristics of malignant melanoma cells?
During which phase do melanomas primarily remain localized without early metastasis?
During which phase do melanomas primarily remain localized without early metastasis?
How do melanoma cells progress during the vertical growth phase?
How do melanoma cells progress during the vertical growth phase?
What is a key feature of the papillary dermis mentioned in the context?
What is a key feature of the papillary dermis mentioned in the context?
What happens to melanocytes in the vertical growth phase of melanoma?
What happens to melanocytes in the vertical growth phase of melanoma?
What characteristic of the stratum granulosum primarily contributes to its role in immune defense?
What characteristic of the stratum granulosum primarily contributes to its role in immune defense?
Which of the following statements about the keratinocytes in the stratum granulosum is true?
Which of the following statements about the keratinocytes in the stratum granulosum is true?
Which hormone produced by the skin plays a crucial role in body weight regulation?
Which hormone produced by the skin plays a crucial role in body weight regulation?
How does the stratum granulosum primarily contribute to the skin's barrier function?
How does the stratum granulosum primarily contribute to the skin's barrier function?
What is the clinical significance of lobular and septal panniculitis?
What is the clinical significance of lobular and septal panniculitis?
Which process involves the conversion of androstenedione into estrone?
Which process involves the conversion of androstenedione into estrone?
What is the primary cause of thickness variation in the stratum granulosum?
What is the primary cause of thickness variation in the stratum granulosum?
What is the physiological process that leads to the shedding of cells in the stratum granulosum?
What is the physiological process that leads to the shedding of cells in the stratum granulosum?
What condition is characterized by the selective loss of body fat?
What condition is characterized by the selective loss of body fat?
In which layer of the skin is leptin produced?
In which layer of the skin is leptin produced?
Which of the following components is NOT typically found in the stratum granulosum?
Which of the following components is NOT typically found in the stratum granulosum?
What contributes to the soft and flexible keratin produced in the stratum granulosum?
What contributes to the soft and flexible keratin produced in the stratum granulosum?
What describes the arrangement of cells in the stratum granulosum?
What describes the arrangement of cells in the stratum granulosum?
Which type of collagen is the major component of the basal lamina?
Which type of collagen is the major component of the basal lamina?
What is the primary function of Type VII collagen within the skin?
What is the primary function of Type VII collagen within the skin?
What characterizes the rare autoimmune disease associated with collagen VII?
What characterizes the rare autoimmune disease associated with collagen VII?
What does BP 230 refer to in the context of hemidesmosomal proteins?
What does BP 230 refer to in the context of hemidesmosomal proteins?
Which of the following best describes epidermolysis bullosa?
Which of the following best describes epidermolysis bullosa?
What type of injuries are most commonly associated with sub-epithelial blistering diseases?
What type of injuries are most commonly associated with sub-epithelial blistering diseases?
What role do anchoring fibrils play in the skin?
What role do anchoring fibrils play in the skin?
Which type of collagen is predominantly found in the anchoring fibrils of the epidermal basement membrane zone?
Which type of collagen is predominantly found in the anchoring fibrils of the epidermal basement membrane zone?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
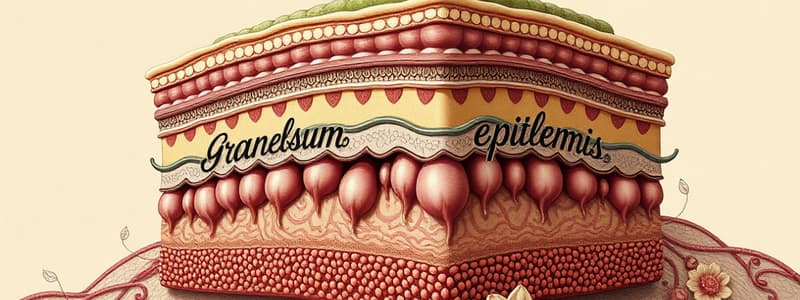
Stratum Granulosum
- Anucleate layer, uppermost in the epidermis.
- Contains keratohyalin granules comprising flattened, dead cells filled with soft keratin filaments.
- Hygroscopic nature contributes to soft and flexible keratin.
- Thickness varies, especially in callused skin.
- Dead keratinocytes in this layer secrete defensins, part of the immune defense.
- Continuous shedding of cells occurs (desquamation).
- Cornified layer populated by cornified cells known as squames.
- Most differentiated layer, responsible for callus formation as a reactive process.
- Keratinized cells have a thick plasma membrane coated with an extracellular lipid layer.
Types of Collagen
- Type IV Collagen: Major component of the basal lamina; most abundant.
- Type VII Collagen: Forms anchoring fibrils located in the epidermal basement membrane zone, providing structural support.
Hemidesmosomal Proteins
- Comprise basement membrane proteins, including BP 230 (Bullous Pemphigoid Antigen 2).
- Autoantibodies against BP 230 are associated with blistering diseases.
Skin Cancer
- Characterized by atypical cells at various epidermal levels.
- Malignant Melanoma: Most serious skin cancer, originating from melanocytes.
- Melanoma cells have large, irregular nuclei and eosinophilic characteristics, forming nests or scattered clusters.
- In early stages, melanoma cells do not metastasize; during the vertical growth phase, they exhibit mitotic activity and potential metastasis to lymph nodes.
Dermis Structure
- Papillary Dermis: Thin zone below the epidermis with loosely arranged collagen bundles, highly vascular with a circulation mainly of capillaries.
- Contains fibrocytes and accounts for dermal patterns on fingertips.
Collagen Striae
- Composed of 15 types of collagen in human skin, mainly synthesized by fibroblasts.
- Type I collagen is predominant in the dermis.
- Decreased collagen expression leads to striae (stretch marks), typically forming due to rapid weight change or hormonal factors.
Skin Functions
- Acts as an energy repository, producing leptin for body weight regulation via the hypothalamus.
Clinical Correlations
- Lobular & Septal Panniculitis: Inflammation of adipose tissue.
- Lipodystrophy: Selective loss of body fat.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.