Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary focus of spinal stabilization exercises?
What is the primary focus of spinal stabilization exercises?
- Increasing the range of motion in the spinal joints.
- Isolating and stretching individual spinal ligaments to improve flexibility.
- Controlling the position and movement of the spine through muscular effort. (correct)
- Strengthening the superficial muscles of the back for power lifting.
In the context of spinal progression, which element is typically emphasized first?
In the context of spinal progression, which element is typically emphasized first?
- Improving maximal muscle strength in global muscle groups.
- Restoring and maintaining neutral spinal alignment. (correct)
- Enhancing power output through plyometric exercises.
- Developing complex movement patterns with external loads.
Which of the following is MOST critical for achieving effective spinal stabilization?
Which of the following is MOST critical for achieving effective spinal stabilization?
- Sustained static contractions of superficial back extensors.
- Aggressive stretching of the hamstrings and hip flexors.
- High repetitions of exercises to induce muscle hypertrophy.
- Precise activation and coordination of deep core musculature. (correct)
During spinal stabilization training, what is the primary role of the transversus abdominis muscle?
During spinal stabilization training, what is the primary role of the transversus abdominis muscle?
Which of these activities would be LEAST suitable to initiate during the early phases of a spinal stabilization program?
Which of these activities would be LEAST suitable to initiate during the early phases of a spinal stabilization program?
Which characteristic is primarily associated with global mobilizer muscles?
Which characteristic is primarily associated with global mobilizer muscles?
Local stabilizer muscles are best characterized by their:
Local stabilizer muscles are best characterized by their:
A muscle with a greater percentage of type I muscle fibers is MOST likely classified as a:
A muscle with a greater percentage of type I muscle fibers is MOST likely classified as a:
In the lumbar spine, which muscle is classified as a global mobilizer?
In the lumbar spine, which muscle is classified as a global mobilizer?
Which cervical spine muscle is categorized as a local stabilizer?
Which cervical spine muscle is categorized as a local stabilizer?
Spinal mobilizer muscles are typically located ________ relative to the axis of motion compared to spinal stabilizer muscles.
Spinal mobilizer muscles are typically located ________ relative to the axis of motion compared to spinal stabilizer muscles.
Extremity muscles, compared to trunk muscles, are described as having:
Extremity muscles, compared to trunk muscles, are described as having:
The primary function of tonic muscles in the stabilization system is to:
The primary function of tonic muscles in the stabilization system is to:
What is a direct benefit of incorporating free weights into a workout routine, according to the provided information?
What is a direct benefit of incorporating free weights into a workout routine, according to the provided information?
Which of the following is NOT listed as a potential cause of stability impairment?
Which of the following is NOT listed as a potential cause of stability impairment?
When addressing regional impairment related to stability, which factor is emphasized as needing attention?
When addressing regional impairment related to stability, which factor is emphasized as needing attention?
What is the MOST accurate definition of hypermobility as described in the text?
What is the MOST accurate definition of hypermobility as described in the text?
What distinguishes 'instability' from 'hypermobility'?
What distinguishes 'instability' from 'hypermobility'?
What is the primary purpose of spinal stabilization exercises, as outlined in the provided text?
What is the primary purpose of spinal stabilization exercises, as outlined in the provided text?
In spinal stabilization, what aspect of muscle function is particularly emphasized?
In spinal stabilization, what aspect of muscle function is particularly emphasized?
What is the FIRST guideline recommended for spinal stabilization according to the provided information?
What is the FIRST guideline recommended for spinal stabilization according to the provided information?
Which of the following is a guideline for spinal stabilization using manual resistance?
Which of the following is a guideline for spinal stabilization using manual resistance?
Transition stabilization is BEST exemplified by which activity?
Transition stabilization is BEST exemplified by which activity?
When using a BP cuff for lumbar spine activation, what is the TARGET pressure drop during muscle activation?
When using a BP cuff for lumbar spine activation, what is the TARGET pressure drop during muscle activation?
For cervical spine activation with a BP cuff, the pressure is progressively increased in increments of:
For cervical spine activation with a BP cuff, the pressure is progressively increased in increments of:
In cervical spine limb loading focusing on flexors, which exercise is emphasized?
In cervical spine limb loading focusing on flexors, which exercise is emphasized?
In lumbar spine limb loading, 'level 2' for flexors is described as:
In lumbar spine limb loading, 'level 2' for flexors is described as:
Lumbar spine limb loading for extensors in quadruped position typically begins with:
Lumbar spine limb loading for extensors in quadruped position typically begins with:
For cervical spine stabilization progressions, the recommended sequence of body positions, once activation is consistent, begins with:
For cervical spine stabilization progressions, the recommended sequence of body positions, once activation is consistent, begins with:
CORE STIX® primarily facilitates core stabilization through:
CORE STIX® primarily facilitates core stabilization through:
A key benefit of strong core musculature in relation to limb function is:
A key benefit of strong core musculature in relation to limb function is:
Flashcards
Stabilization exercises
Stabilization exercises
A type of exercise that focuses on strengthening and controlling the muscles responsible for stabilizing the spine, such as the core muscles.
Spinal progression
Spinal progression
A progression of exercises that gradually increases the difficulty and challenge, starting with simple movements and progressing to more complex ones.
PT6606 exercises
PT6606 exercises
A type of exercise that emphasizes strengthening and controlling the small muscles that help to stabilize the spine.
Comprehensive spinal program
Comprehensive spinal program
Signup and view all the flashcards
Progressive overload
Progressive overload
Signup and view all the flashcards
Joint Hypermobility
Joint Hypermobility
Signup and view all the flashcards
Muscle Weakness and Instability
Muscle Weakness and Instability
Signup and view all the flashcards
Impaired Postural Control
Impaired Postural Control
Signup and view all the flashcards
Impaired Endurance
Impaired Endurance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Joint Instability
Joint Instability
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spinal Stabilization
Spinal Stabilization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Isometric Holding
Isometric Holding
Signup and view all the flashcards
Progressive Limb Loading
Progressive Limb Loading
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mobilizers
Mobilizers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stabilizers
Stabilizers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Global Mobilizer
Global Mobilizer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Local Stabilizer
Local Stabilizer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stabilizer Muscles
Stabilizer Muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Superficial Muscles
Superficial Muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Deep Muscles
Deep Muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phasic Muscles
Phasic Muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Isometric stabilization
Isometric stabilization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transition stabilization
Transition stabilization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Manual resistance stabilization
Manual resistance stabilization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Perturbation
Perturbation
Signup and view all the flashcards
BP cuff stabilization
BP cuff stabilization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Limb loading
Limb loading
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bilateral UE movement stabilization
Bilateral UE movement stabilization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Standing balance
Standing balance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Stabilization Concepts
- Concepts and spinal progression are discussed.
- PT6606 is mentioned.
- D. Dye is mentioned.
- Content is from Kisner, Borstad & Colby Therapeutic Exercise 8th Ed, 2023.
Functional Classification of Muscles
- Mobilizers (Global - Phasic): Generate torque for movement, act as concentric power producers, and absorb shock.
- Stabilizers (Local - Tonic): Maintain joint alignment through tension, exhibit minimal length change (isometric), and are continuously active during movement with high kinematic input.
- Stabilizer (Global - mix) is also classified.
Function Classification with Spinal Muscles
- Mobilizers (Global - Phasic): More superficial, cross multiple vertebral segments, and produce compressive loading during strong contraction.
- Stabilizers (Local - Tonic): Deep, attach to vertebral segments, control segmental motion, and primarily function for endurance.
Function Classification with Spinal Muscles - Table 14.1
- Mobilizers (Global - Phasic): Lumbar spine: Rectus abdominis, External/internal obliques, QL Cervical spine: Erector spinae, Iliopsoas, SCM, Scalenes, Levator, Upper trap, Erector spinae
- Stabilizers (Local - Tonic): Lumbar spine: Transversus abdominis, Multifidus, QL (deep portion) Cervical spine: Rectus capitis anterior and lateralis, Longus colli.
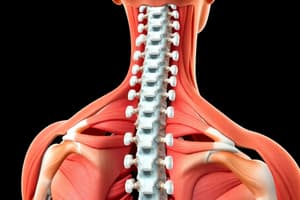
Spine Stabilizers (Diagram)
- Depicts various muscles in the spine, including oblique capitis, rectus capitis, longus capitis, rectus capitis anterior, splenius capitis, middle scalene, longus colli, oblique capitis, inferior muscle , posterior scalene, multifidus, levator costarum, quadratus lumborum, multifidus, spinalis dorsi, longissimus dorsi, iliocostalis dorsi.
- Shows relationships of the muscles and their function.
Muscles of the Hip Complex
- Includes psoas major, iliacus, tensor fasciae latae, gluteus minimus, obturator externus, piriformis, gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, superior gemellus, adductor brevis, adductor longus, pectineus, obturator internus, gracilis, quadratus femoris, inferior gemellus, iliotibial tract
Shoulder Muscles
- Includes deltoid, pectoralis major, coracobrachialis, triceps brachii (lateral, long, medial heads), biceps brachii, brachialis, brachioradialis, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, teres major, latissimus dorsi.
- Shows relationships of muscles.
Questions on Shoulder External Rotation and Rotator Cuff
- What is the major global mobilizer for shoulder external rotation?
- Will power strengthening improve the function of the rotator cuff muscles?
Free Weights and Stabilizer Muscles
- The statement that working out with free weights is a guaranteed way to strengthen stabilizer muscles is not a proven fact.
Stability Impairment
- Regional impairment can result from joint hypermobility (ligamentous laxity), muscle weakness, impaired postural control, and impaired endurance.
- Address joint structures, regional muscles, regional posture, and endurance factors.
- Check for hypomobility as well as hypermobility.
Definitions (Hypermobility and Instability)
- Hypermobility: Excessive movement around a joint.
- Instability: Excessive joint movement without muscular control.
Spinal Stabilization (Ch 16)
- Recognizes spinal segments or muscle imbalances as a common cause of lower back pain (LBP) and cervical pain.
- Focuses on actively training the deep "core" musculature (abdominal, lumbar muscles and pelvic floor) to support the body in all positions.
- Endurance and stabilization are emphasized.
Spinal Stabilization Guidelines (pp 534-535)
- Kinesthetic awareness is priority.
- Mobility restrictions; appropriate posture/position.
- Biofeedback or manual cueing is possible for posture and position.
- Activation - Isometric holding.
- Focus on TrA and multifidus (Mf).
- Biofeedback/manual cueing monitoring.
- Extremity motions: Progressive limb loading; dynamic stabilization.
- Increase endurance and strength, 30-60 sec up to 3 min; add resistance with extremity movements
Spinal Stabilization (pp 534-535) Continued
- Guidelines include manual resistance-alternating isometrics and rhythmic stabilization.
- Transition stabilization: ability to stabilize while changing positions.
- Examples: sit-to-stand, walking and lifting with bilateral upper extremities, lifting overhead.
- Higher-level balance training (perturbation) is used in interventions.
Methods of Activation
- Use of blood pressure cuff or stabilizer.
- Process for finding neutral spine.
- With activation, drops in pressure measurement.
- Holds for 10 seconds and builds gradually up to 10 repetitions.
Limb Loading Emphasis on Flexors - Cervical Spine
- Exercises for cervical spine are presented.
Limb Loading Emphasis on Extensors - Cervical Spine
- Exercises for cervical spine are presented.
Limb Loading Emphasis on Flexors and Extension for Lumbar
- Demonstrates different levels of limb loading for lumbar flexors and extensors.
Progressions (CH 16)
- Body positions: supine, quadruped, prone, plank, sitting, standing, lunges, and squats.
- Positions are not required to be sequential.
- Activation in prone positioning is often emphasized first. Activation in supine or sitting positions is also included.
- Gymnastic ball, foam rollers for unsteadiness.
Foundation and Equipment (San Francisco Spine Institute)
- Founders Dynamic Lumbar Stabilization Program was established in 1989.
- Was a non-profit research organization.
- Core stabilization method (CORE STIX®) using upper extremity (UE) resistance.
Summary
- Stabilization is essential for efficient muscle performance.
- A stable, strong "core" allows for superior power production in the extremities.
- Evidence suggests that core stabilization reduces lower back pain recurrence.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.