Podcast
Questions and Answers
How many thoracic vertebrae are there in the human spine?
How many thoracic vertebrae are there in the human spine?
- 5
- 5 fused
- 7
- 12 (correct)
Which of the following best describes neutral spine?
Which of the following best describes neutral spine?
- The spine is completely straight with no natural curves.
- The spine is curved as much as possible for maximum flexibility.
- The spinal curves are excessively pronounced in all regions.
- The spinal curves are neither excessively curved nor straightened. (correct)
What type of spinal curve is characterized by excessive posterior curvature?
What type of spinal curve is characterized by excessive posterior curvature?
- Kyphosis (correct)
- Lordosis
- Neutral spine
- Scoliosis
Which of the following is NOT a function of the vertebrae?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the vertebrae?
Which of the following is NOT a component of each vertebra?
Which of the following is NOT a component of each vertebra?
What is the primary function of facet joints?
What is the primary function of facet joints?
What is the fluid found inside facet joint capsules called?
What is the fluid found inside facet joint capsules called?
What is the process called that causes a back to 'crack'?
What is the process called that causes a back to 'crack'?
What is the primary function of the rectus abdominis?
What is the primary function of the rectus abdominis?
Which muscle is responsible for supporting the abdominal wall and assisting with breathing?
Which muscle is responsible for supporting the abdominal wall and assisting with breathing?
What primary action do the oblique muscles control?
What primary action do the oblique muscles control?
Which muscle assists with cervical flexion and breathing?
Which muscle assists with cervical flexion and breathing?
A patient presents with pain lateral to the spine, muscle spasms and stiffness after a twisting injury. Which injury is most likely?
A patient presents with pain lateral to the spine, muscle spasms and stiffness after a twisting injury. Which injury is most likely?
Which mechanism of injury is MOST likely to cause a ligament sprain in the back?
Which mechanism of injury is MOST likely to cause a ligament sprain in the back?
What are the common signs and symptoms of a herniated disc?
What are the common signs and symptoms of a herniated disc?
Which diagnostic method is NOT used to diagnose a disk injury?
Which diagnostic method is NOT used to diagnose a disk injury?
Which of the following is NOT a typical cause of joint cracking?
Which of the following is NOT a typical cause of joint cracking?
What is the primary function of the intervertebral discs in the spine?
What is the primary function of the intervertebral discs in the spine?
Which part of the intervertebral disc is responsible for bearing compressive forces?
Which part of the intervertebral disc is responsible for bearing compressive forces?
What is the main shortcoming associated with the intervertebral discs?
What is the main shortcoming associated with the intervertebral discs?
Which muscle is primarily responsible for shoulder elevation?
Which muscle is primarily responsible for shoulder elevation?
What movement is primarily associated with the middle trapezius?
What movement is primarily associated with the middle trapezius?
Which action is primarily facilitated by the latissimus dorsi muscle?
Which action is primarily facilitated by the latissimus dorsi muscle?
The rhomboids are primarily responsible for which action?
The rhomboids are primarily responsible for which action?
Which initial treatment is NOT typically recommended for a herniated disc?
Which initial treatment is NOT typically recommended for a herniated disc?
What percentage of individuals with a herniated disc can be successfully treated without surgery?
What percentage of individuals with a herniated disc can be successfully treated without surgery?
According to content, under what condition is long term physical therapy treatment most important for disk injury?
According to content, under what condition is long term physical therapy treatment most important for disk injury?
When is surgical intervention typically recommended for a herniated disc?
When is surgical intervention typically recommended for a herniated disc?
Which of these surgical procedures involves the removal of the affected disc and the joining of vertebrae?
Which of these surgical procedures involves the removal of the affected disc and the joining of vertebrae?
What is the primary purpose of an artificial disc replacement?
What is the primary purpose of an artificial disc replacement?
Which of the following is NOT a stated risk factor for developing a herniated disc?
Which of the following is NOT a stated risk factor for developing a herniated disc?
Regarding scoliosis, the content mentions that if left untreated, it could cause what TWO physical problems?
Regarding scoliosis, the content mentions that if left untreated, it could cause what TWO physical problems?
Which condition is characterized by damage to the developing brain, often occurring before birth, and subsequently affecting movement and muscle tone?
Which condition is characterized by damage to the developing brain, often occurring before birth, and subsequently affecting movement and muscle tone?
What is the primary underlying cause of muscular dystrophy?
What is the primary underlying cause of muscular dystrophy?
Which of the following best describes spina bifida?
Which of the following best describes spina bifida?
Polio is caused by a virus that can lead to paralysis by infecting what?
Polio is caused by a virus that can lead to paralysis by infecting what?
When assessing a patient for scoliosis, what is typically assessed first?
When assessing a patient for scoliosis, what is typically assessed first?
During a scoliosis assessment, what becomes visible when the patient bends forward?
During a scoliosis assessment, what becomes visible when the patient bends forward?
During scoliosis surgery, what is primarily used to provide support and alignment along the spine?
During scoliosis surgery, what is primarily used to provide support and alignment along the spine?
What action do surgeons take to ensure scoliosis does not return after surgery?
What action do surgeons take to ensure scoliosis does not return after surgery?
Which healthcare professionals are MOST likely to be involved in managing spinal conditions?
Which healthcare professionals are MOST likely to be involved in managing spinal conditions?
What is a common nonsurgical option used to treat spinal conditions?
What is a common nonsurgical option used to treat spinal conditions?
Which of the following best describes spondylosis?
Which of the following best describes spondylosis?
Which group is MOST commonly affected by spondylolysis?
Which group is MOST commonly affected by spondylolysis?
A patient reports back pain that increases with activity, especially bending backward. Based on this, which spinal condition is more likely?
A patient reports back pain that increases with activity, especially bending backward. Based on this, which spinal condition is more likely?
What is a key characteristic of spondylolisthesis that differentiates it from the other conditions?
What is a key characteristic of spondylolisthesis that differentiates it from the other conditions?
What is the BEST way to assess posture in athletes, in terms of minimizing injuries?
What is the BEST way to assess posture in athletes, in terms of minimizing injuries?
Which of the following is a typical sign or symptom of spondylolisthesis?
Which of the following is a typical sign or symptom of spondylolisthesis?
Flashcards
Annulus Fibrosus
Annulus Fibrosus
The tough, dense outer layer of the intervertebral disk that helps resist compression and keeps the vertebrae separated.
Nucleus Pulposus
Nucleus Pulposus
The flexible inner layer of the intervertebral disk that acts as a shock absorber and allows for movement.
Degenerative Joint Disease (Osteoarthritis)
Degenerative Joint Disease (Osteoarthritis)
A condition where the cartilage in joints wears down, causing bones to rub against each other, leading to cracking and grinding sounds.
Upper Trapezius
Upper Trapezius
Signup and view all the flashcards
Middle Trapezius
Middle Trapezius
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lower Trapezius
Lower Trapezius
Signup and view all the flashcards
Latissimus Dorsi
Latissimus Dorsi
Signup and view all the flashcards
Erector Spinae
Erector Spinae
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the bones of the spine called?
What are the bones of the spine called?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the four segments of the spine?
What are the four segments of the spine?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How many of each type of vertebrae are there?
How many of each type of vertebrae are there?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is NEUTRAL spine?
What is NEUTRAL spine?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is necessary to keep the spine aligned?
What is necessary to keep the spine aligned?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the curves of the spine?
What are the curves of the spine?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Kyphosis?
What is Kyphosis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Lordosis?
What is Lordosis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Scoliosis?
What is Scoliosis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
If untreated Scoliosis can cause what TWO physical problems?
If untreated Scoliosis can cause what TWO physical problems?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Spondylolisthesis?
What is Spondylolisthesis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Piriformis Syndrome
What is Piriformis Syndrome
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Ankylosing Spondylitis?
What is Ankylosing Spondylitis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Degenerative Disc Disease?
What is Degenerative Disc Disease?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Herniated Disc?
What is Herniated Disc?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Discectomy?
What is Discectomy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rectus Abdominis
Rectus Abdominis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transverse Abdominis
Transverse Abdominis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Obliques
Obliques
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scalenes
Scalenes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sternocleidomastoid
Sternocleidomastoid
Signup and view all the flashcards
Levator Scapulae
Levator Scapulae
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ligament Injuries (Sprains)
Ligament Injuries (Sprains)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Muscle & Tendon Injuries (Strains)
Muscle & Tendon Injuries (Strains)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cerebral Palsy
Cerebral Palsy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Muscular Dystrophy
Muscular Dystrophy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spina Bifida
Spina Bifida
Signup and view all the flashcards
Polio
Polio
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scoliosis
Scoliosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Idiopathic Scoliosis
Idiopathic Scoliosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rib Hump
Rib Hump
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scoliosis Surgery
Scoliosis Surgery
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is spondylolysis?
What is spondylolysis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is spondylosis?
What is spondylosis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does an Anesthesiologist do?
What does an Anesthesiologist do?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does a Physical Therapist do?
What does a Physical Therapist do?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does a Nurse do?
What does a Nurse do?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does a Surgeon do?
What does a Surgeon do?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Introduction to Back and Spinal Injuries
- Unit 8 covers back and spinal injuries.
- Images of the spine and spinal injury are included.
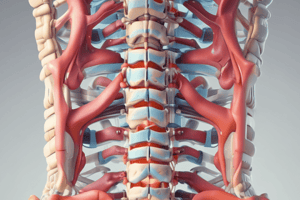
Anatomy of the Spine
- The bones of the spine are called vertebrae.
- The spinal column has four main segments: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral.
- The cervical vertebrae (7) are in the neck region
- The thoracic vertebrae (12) are in the upper back region
- The lumbar vertebrae (5) are in the lower back region
- The sacral vertebrae (5 fused) are in the pelvis region
- The coccyx is also part of the spine, located at the lowest part of the lumbar region (tailbone)
- The sacroiliac joint connects the sacrum to the ilium (pelvis bone).
- A neutral spine maintains proper spinal curves, neither overly curved nor straight.
- This is the strongest, most anatomically stable spine position.
- The spinal column consists of normal curves:
- Cervical lordosis (anterior curve in the neck)
- Thoracic kyphosis (posterior curve in the upper back)
- Lumbar lordosis (anterior curve in the lower back)
- Sacral kyphosis (posterior curve in the pelvis)
- Coccyx (tailbone)
Vertebral Anatomy
- Each vertebra has a body, transverse processes, spinous processes, vertebral foramen/canal, and facets.
- The vertebral foramen/canal houses the spinal cord.
- Facets are joints that allow movement between vertebrae.
- Healthy facet joints have cartilage for smooth movement.
- Synovial fluid in the joints lubricates them for flexibility.
Intervertebral Disks
- Intervertebral disks have two main parts: annulus fibrosus (tough outer layer) and nucleus pulposus (flexible inner layer).
- The disks act as shock absorbers and keep the vertebrae separated.
- They also create space for nerves to leave the spinal cord.
- The disks themselves lack a good blood supply, which is a factor in how they heal or don't heal.
Muscles of the Upper & Lower Back
- Key back muscles include the trapezius (upper, middle, and lower), latissimus dorsi, erector spinae, and rhomboids (major & minor).
- Trapezius: shoulder elevation, neck extension, lateral flexion, and rotation.
- Latissimus Dorsi: shoulder adduction, extension, and medial rotation.
- Rhomboids: scapular retraction.
- Erector spinae: trunk extension and lateral flexion.
Acute Back/Spine Injuries
- Acute injuries include ligament sprains, muscle strains, and intervertebral disc injuries.
- Ligament sprains usually result from trunk flexion with twisting motions.
- Muscle strains often come from extension under stress or sudden twisting movements.
- Intervertebral disc injuries result from poor posture or physical stress from flexing and extending the spine.
Signs & Symptoms
- Signs of spinal injuries include pain over the spine, limited movement (muscle spasm), pain with twisting/rotation, local pain.
- Muscle strains often show pain lateral to the spine.
- For herniated discs, signs/symptoms may appear as burning pain that radiates down the leg.
Diagnosis & Treatment
- Diagnosing disc injuries often uses X-rays, MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), and EMG (electromyography).
- Initial treatment involves ice, rest, and NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs).
- Sometimes corticosteroids are used.
- Long-term treatments can involve physical therapy, addressing poor posture/obesity, and surgery.
- Surgery is more often recommended if conservative methods do not improve symptoms within weeks or there are persistent neurological symptoms, or patient has difficulty performing basic body functions.
Scoliosis
- Scoliosis refers to a lateral curvature of the spine.
- Signs may be uneven shoulders, unequal hips, or a rib hump.
- Assessment commonly assesses shoulder height, and hip height at the iliac crest.
- Measurement uses scoliometer for visual confirmation, and sometimes apps, that are now commonly used.
- Bracing, physical therapy, and surgery are treatment options.
- During scoliosis surgery, screws and metal rods are inserted to stabilize/correct the spine's alignment.
Other Chronic Conditions
- Chronic back conditions include scoliosis, chronic back pain, spondylolisthesis/spondylolysis, piriformis syndrome, ankylosing spondylitis, and degenerative disc disease.
- Spondylolisthesis is when a vertebra slips forward, usually due to a pars fracture (spondylolysis).
- Ankylosing spondylitis is a chronic inflammatory disease that causes fusion/bamboo-like appearance of the spine.
- Degenerative disc disease is part of 'wear and tear' aging process that causes spine changes.
Possible Causes
- Causes for Scoliosis can be genetic, cerebral palsy, muscular dystrophy, spina bifida, poliomyelitis, unequal leg lengths, or fused ribs.
- Cerebral palsy, Muscular dystrophy and Spina bifida describe a group of disorders that affect movement, or can sometimes be a cause of Scoliosis.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.