Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the main objective of the Inception Phase in RUP?
What is the main objective of the Inception Phase in RUP?
- To analyze the project and design the basic structure
- To develop and write the software
- To move the software from development to production
- To understand the project and estimate cost (correct)
The Green Phase in Test Driven Development involves writing new tests for new requirements.
The Green Phase in Test Driven Development involves writing new tests for new requirements.
False (B)
What is the primary goal of the Transition Phase in RUP?
What is the primary goal of the Transition Phase in RUP?
To make the software available to users.
In the Test Driven Development process, after the Red Phase and Green Phase, the next step is to _____ the code.
In the Test Driven Development process, after the Red Phase and Green Phase, the next step is to _____ the code.
Which phase of RUP is focused on developing and writing most of the software?
Which phase of RUP is focused on developing and writing most of the software?
Match the RUP phases with their main focuses:
Match the RUP phases with their main focuses:
RUP helps create software through a single phase that handles all tasks.
RUP helps create software through a single phase that handles all tasks.
What factors should be considered when choosing a software process model?
What factors should be considered when choosing a software process model?
What is a key advantage of the Spiral Model?
What is a key advantage of the Spiral Model?
The Waterfall Process is highly flexible and suitable for complex projects.
The Waterfall Process is highly flexible and suitable for complex projects.
What is the main focus during the 'Identify and Resolve Risks' step of the Spiral Model?
What is the main focus during the 'Identify and Resolve Risks' step of the Spiral Model?
In Evolutionary Prototyping, developers create a simple version of the software known as a __________.
In Evolutionary Prototyping, developers create a simple version of the software known as a __________.
Match the software process types with their characteristic advantage:
Match the software process types with their characteristic advantage:
What is a common disadvantage of Evolutionary Prototyping?
What is a common disadvantage of Evolutionary Prototyping?
In the Waterfall Process, errors should be identified primarily in the last phase.
In the Waterfall Process, errors should be identified primarily in the last phase.
What is the primary goal during the 'Refine Prototype' phase in Evolutionary Prototyping?
What is the primary goal during the 'Refine Prototype' phase in Evolutionary Prototyping?
What is a primary reason for selecting the right method in project management?
What is a primary reason for selecting the right method in project management?
Team expertise is not important when selecting a project method.
Team expertise is not important when selecting a project method.
What analogy is used to describe an API?
What analogy is used to describe an API?
System design is like creating a detailed plan for building a _______.
System design is like creating a detailed plan for building a _______.
Match the project aspects with their significance:
Match the project aspects with their significance:
Which of the following factors should be considered to avoid project failure?
Which of the following factors should be considered to avoid project failure?
The high-level design phase involves deciding on construction materials and techniques.
The high-level design phase involves deciding on construction materials and techniques.
What is the primary goal of system design?
What is the primary goal of system design?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Software Process Overview
- Software processes involve steps for designing, developing, testing, and maintaining software.
- Effective error detection in early phases avoids complications in later stages.
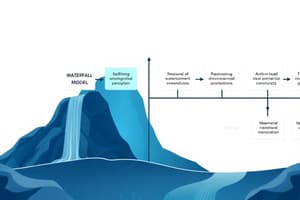
Waterfall Process
- Sequential phases: only advance after review.
- Advantage: Early error detection.
- Disadvantage: Inflexibility to changes; not suitable for emerging technologies or learning developers.
- Best suited for simple projects.
Spiral Process
- Main steps include defining objectives, identifying risks, developing and testing, and planning next iterations.
- Repeats steps to refine software progressively.
- Advantage: Early identification of problems and adapts easily to changes; allows client feedback.
- Disadvantage: Complexity and higher costs.
Evolutionary Prototyping
- Steps involve starting with a concept, creating a prototype, refining it based on feedback, and finalizing for release.
- Encourages iterative feedback from customers for adjustments.
- Advantage: Quick feedback integration.
- Disadvantage: Uncertainty in timelines for completion as improvements are continually made.
Rational Unified Process (RUP)
- Inception phase focuses on understanding project requirements and budgeting.
- Elaboration phase involves analysis and basic software design.
- Construction phase concentrates on development of the software.
- Transition phase focuses on deploying software to users.
- Each phase is distinct to ensure thorough project management.
Agile & Test Driven Development (TDD)
- Red Phase: Write tests based on requirements.
- Green Phase: Write code to pass tests.
- Refactor Phase: Improve code while ensuring all tests still pass.
- Cycle continues with new tests and requirements.
- Emphasizes iterative development based on tests to maintain quality.
Factors for Choosing a Software Process Model
- Understanding Requirements: Knowledge of what the software must do is critical.
- Project Lifetime: Consider whether the project is short-term or long-term.
- Level of Risk: Analyze familiarity with the project scope and technology.
- Schedule and Resources: Assess the time and resources available for development.
- Interaction with Management and Customers: Determine frequency of customer engagement.
- Expertise of the Team: Availability of knowledgeable team members for the chosen method.
Key Points
- Selecting the right software process is crucial for project success.
- Careful consideration of project factors prevents potential failure.
System Design
- Analogous to creating a house blueprint: involves understanding requirements, design layout, and ensuring effective documentation.
- Organizes components for optimal system performance and reliability.
- Utilizes design patterns to address common issues and allow for scalability.
API (Application Programming Interface)
- Compares to a restaurant menu: provides options without needing to understand internal workings.
- APIs facilitate requests and responses between clients and servers without exposing underlying complexity.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.