Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is a major advantage of the iterative waterfall model?
What is a major advantage of the iterative waterfall model?
- It guarantees the final product will meet all user requirements.
- It eliminates all bugs during the development process.
- It provides feedback paths for error correction within phases. (correct)
- It allows for simultaneous development of all project phases.
In which type of software development projects is the iterative waterfall model particularly applicable?
In which type of software development projects is the iterative waterfall model particularly applicable?
- Small individual applications
- Large and complex software projects (correct)
- Web development projects
- Mobile application development
What is a common characteristic of prototypes in software development?
What is a common characteristic of prototypes in software development?
- They are complete and fully functional systems.
- They require extensive user training before use.
- They often use shortcuts resulting in limited capabilities. (correct)
- They demonstrate all features of the final product.
Why is it valuable to use prototypes during software development?
Why is it valuable to use prototypes during software development?
What should developers generally expect from the first version of a software product?
What should developers generally expect from the first version of a software product?
What is the main characteristic of the spiral model in software development?
What is the main characteristic of the spiral model in software development?
What is a disadvantage of the traditional waterfall model?
What is a disadvantage of the traditional waterfall model?
Which of the following statements best describes the incremental model?
Which of the following statements best describes the incremental model?
How do prototypes help in understanding user interactions?
How do prototypes help in understanding user interactions?
Why might the spiral model be considered complex for ordinary projects?
Why might the spiral model be considered complex for ordinary projects?
What is an important reason that prototypes often exhibit low reliability?
What is an important reason that prototypes often exhibit low reliability?
What role does a system analyst play in the software development process?
What role does a system analyst play in the software development process?
What typically happens to customer confidence during a lengthy development process?
What typically happens to customer confidence during a lengthy development process?
What is a major advantage of the evolutionary approach in development?
What is a major advantage of the evolutionary approach in development?
What factor might deter the use of the spiral model for many projects?
What factor might deter the use of the spiral model for many projects?
What initial activity is crucial before starting software development?
What initial activity is crucial before starting software development?
What is a primary characteristic of a well-structured SRS document?
What is a primary characteristic of a well-structured SRS document?
Why is the SRS document referred to as a black-box specification?
Why is the SRS document referred to as a black-box specification?
What aspect of system requirements is emphasized by the term 'verifiable'?
What aspect of system requirements is emphasized by the term 'verifiable'?
What can be a consequence of not developing an SRS document?
What can be a consequence of not developing an SRS document?
What is essential for conceptual integrity in an SRS document?
What is essential for conceptual integrity in an SRS document?
How should an SRS document respond to undesired events?
How should an SRS document respond to undesired events?
What is the impact of verbose and irrelevant descriptions in an SRS document?
What is the impact of verbose and irrelevant descriptions in an SRS document?
What signifies a complete SRS document?
What signifies a complete SRS document?
What is a primary reason for using a prototyping model in software development?
What is a primary reason for using a prototyping model in software development?
In which scenario is it most beneficial to use the evolutionary model?
In which scenario is it most beneficial to use the evolutionary model?
What is a disadvantage of the evolutionary model?
What is a disadvantage of the evolutionary model?
How does the spiral model differentiate from other development models?
How does the spiral model differentiate from other development models?
What is the primary purpose of the first quadrant in the spiral model?
What is the primary purpose of the first quadrant in the spiral model?
What does each loop of the spiral model represent?
What does each loop of the spiral model represent?
Which of the following activities is typically NOT part of a spiral model phase?
Which of the following activities is typically NOT part of a spiral model phase?
What action may be taken if there is a risk that requirements are inappropriate?
What action may be taken if there is a risk that requirements are inappropriate?
What type of requirements deal with the functionalities required from the system?
What type of requirements deal with the functionalities required from the system?
What is a key benefit of the evolutionary model?
What is a key benefit of the evolutionary model?
Why is it important for the analyst to understand the customer's requirements?
Why is it important for the analyst to understand the customer's requirements?
Which quadrant focuses on developing and validating the next level of the product?
Which quadrant focuses on developing and validating the next level of the product?
What is a key characteristic of the spiral model compared to other life cycle models?
What is a key characteristic of the spiral model compared to other life cycle models?
What is NOT a typical question an analyst should consider while understanding a problem?
What is NOT a typical question an analyst should consider while understanding a problem?
Which aspect does NOT heavily influence major design decisions in a prototyping model?
Which aspect does NOT heavily influence major design decisions in a prototyping model?
Which aspect is covered by non-functional requirements?
Which aspect is covered by non-functional requirements?
What challenge does the classical waterfall model face in practical development?
What challenge does the classical waterfall model face in practical development?
What might a goals of implementation document address?
What might a goals of implementation document address?
Which model is considered to be highly useful for projects with well-understood problems?
Which model is considered to be highly useful for projects with well-understood problems?
What should the analyst do upon detecting inconsistencies or anomalies in requirements?
What should the analyst do upon detecting inconsistencies or anomalies in requirements?
For which types of projects is the prototyping model most suitable?
For which types of projects is the prototyping model most suitable?
Which of the following is an example of a complexity an analyst might face?
Which of the following is an example of a complexity an analyst might face?
What distinguishes the evolutionary approach from other models?
What distinguishes the evolutionary approach from other models?
Which statement about input and output data in a system is true?
Which statement about input and output data in a system is true?
Flashcards
Iterative Waterfall Model
Iterative Waterfall Model
A software development process that combines elements of the classic waterfall model with iterative feedback loops to allow for error correction during the development process.
Early error detection?
Early error detection?
Finding bugs early in the development process helps limit the cost of fixing them, while finding them later incurs greater costs.
Iterative Waterfall Model Advantages
Iterative Waterfall Model Advantages
Provides a working model early which enables easier detection of design/functional flaws, offering earlier corrections and saving budgets.
Iterative Waterfall Model Limitations?
Iterative Waterfall Model Limitations?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prototype in Software Development
Prototype in Software Development
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prototype Uses - Customer Insights?
Prototype Uses - Customer Insights?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prototype Value - Learning from Mistakes?
Prototype Value - Learning from Mistakes?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prototyping Short Cuts?
Prototyping Short Cuts?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spiral Model
Spiral Model
Signup and view all the flashcards
Quadrant 1: Objective Setting
Quadrant 1: Objective Setting
Signup and view all the flashcards
Quadrant 2: Risk Assessment and Reduction
Quadrant 2: Risk Assessment and Reduction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Quadrant 3: Development and Validation
Quadrant 3: Development and Validation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Quadrant 4: Review and Planning
Quadrant 4: Review and Planning
Signup and view all the flashcards
Iterative Waterfall vs. Classical Waterfall
Iterative Waterfall vs. Classical Waterfall
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prototyping Model
Prototyping Model
Signup and view all the flashcards
Evolutionary Approach
Evolutionary Approach
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the problem?
What is the problem?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why is it important?
Why is it important?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the possible solutions?
What are the possible solutions?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Data input and output?
Data input and output?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Likely complexities?
Likely complexities?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Functional Requirements
Functional Requirements
Signup and view all the flashcards
Non-functional requirements
Non-functional requirements
Signup and view all the flashcards
Goals of implementation
Goals of implementation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Incremental Development
Incremental Development
Signup and view all the flashcards
Customer Confidence & Evolutionary Approach
Customer Confidence & Evolutionary Approach
Signup and view all the flashcards
Software Development Models: Comparison
Software Development Models: Comparison
Signup and view all the flashcards
Requirement Analysis
Requirement Analysis
Signup and view all the flashcards
System Analyst
System Analyst
Signup and view all the flashcards
Removing Ambiguities & Inconsistencies
Removing Ambiguities & Inconsistencies
Signup and view all the flashcards
SRS Document
SRS Document
Signup and view all the flashcards
Black-box View
Black-box View
Signup and view all the flashcards
Structured SRS
Structured SRS
Signup and view all the flashcards
Conceptual Integrity
Conceptual Integrity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Exceptional Conditions
Exceptional Conditions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Verifiable SRS
Verifiable SRS
Signup and view all the flashcards
Problems without SRS?
Problems without SRS?
Signup and view all the flashcards
When is Prototyping Useful?
When is Prototyping Useful?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Evolutionary Model
Evolutionary Model
Signup and view all the flashcards
Advantages of Evolutionary Model
Advantages of Evolutionary Model
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spiral Model Phases
Spiral Model Phases
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
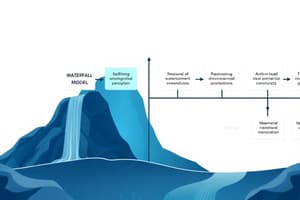
Waterfall Model
- The waterfall model is a linear, sequential approach to software development
- Each phase must be completed before the next phase begins
- Phases include requirements, design, implementation, testing, deployment, and maintenance
- Criticism for the waterfall model include the lack of flexibility in addressing changing requirements.
Iterative Waterfall Model
- An iterative approach to the waterfall model
- Addresses the drawbacks of the classical waterfall model with feedback loops
- Allows for a working model at an early stage allowing for functional flaws to be identified earlier
- Corrective measures can be implemented in the iterative stages.
- Suitable for only large and bulky software development projects.
Prototyping Model
- A prototype is a toy implementation of the system
- Exhibits limited capabilities, low reliability, and inefficient performance compared to the actual system
- Built using shortcuts, including inaccurate or dummy functions.
- Crude version of the actual system
- Used to illustrate input data formats, messages, and reports
- Useful in understanding customer needs, user interface behaviour, and system outputs
Need for a Prototype in Software Development
- Important to illustrate input data, interactive dialogues, and customer needs.
- Provides a framework on how the user interface would behave and how outputs are processed.
- To ensure the final product is perfect
- Helpful when technical solutions are unclear
- Helps examine technical aspects associated with product development
- Useful for major design decisions
- Useful for resolving technical issues.
- Used when a user requirements are incomplete
- Useful when technical issues are not clear
Prototyping Model Diagram
- Sequential steps including : Initial Requirements, Design, Prototyping, Customer Evaluation, Review and Updation, Test, and Development
- Feedback loops exist between several stages in the process
Evolutionary Model
- Also called the successive versions model or incremental model
- Functional improvements and additions to the software are added in iterative stages
- Applicable to large projects with easily identifiable modules
- Commonly used when customers want core features
- Easily applied with object-oriented software development
- Advantages include enabling the user to experiment with partially developed systems and reducing errors through thorough testing of core modules.
- A limitation includes the challenges in partitioning the problem into acceptable increments for the customer.
Evolutionary Delivery Diagram
- Sequential steps, including: Software Concept, Preliminary Requirements Analysis, Design of Architecture and System Core, Develop a Version, Incorporate Customer Feedback, Deliver the Version, and Elicit Customer Feedback
Spiral Model
- A diagrammatic representation with many loops that represents the software development process.
- Each loop represents a phase.
- The innermost loop for Example focuses on Feasibility study, next for design and so on.
- The phases (or quadrants) include: Objective Setting, Risk Assessment and Reduction, Development and Validation, and Review and Planning
- The spiral model is considered a meta-model that encompasses all other life cycle models
- It accounts for risks by continuously validating the developed system at every phase
Comparison of Different Life Cycle Models
- Waterfall: Basic model, lacks flexibility, cannot handle errors in phases
- Iterative Waterfall: Simple and widely used improvement to waterfall model suitable for well understood problem
- Prototyping: Useful for projects where user's requirements or technical aspects are not well understood; especially for user interface;
- Evolutionary: Iterative development and delivery suitable for large projects decomposed into modules
- Spiral: Suitable for challenging software requiring risk handling in phases.
Requirement Analysis and Specification
- Essential to understand and document the exact customer's requirements before software development.
- System analysts collect information from customers and analyze the requirements.
- Questions like 'what is the problem?', 'why is it important to solve?', and 'what are the data inputs/outputs?' are clarified to understand the problem
Parts of Software Requirements Specifications (SRS) Documents
- Functional Requirements
- Non-functional requirements (like maintainability, system portability, usability)
- Goals of implementation
Functional Requirements
- Discusses high-level functionalities of the system
- Each function is a transformation of input data to output data.
Non-functional Requirements
- Deals with system characteristics not expressed as functions (like maintainability and portability)
Goals of Implementation
- Documents general suggestions on development and trade-offs among design goals.
- Includes anticipated future changes, such as new device support, reusability considerations.
Properties of a good SRS Document
- Concise, unambiguous, consistent, and complete
- Structured and easily modifiable.
- Black-box view, specifying the external behaviour of the system, excluding internal implementation details
- Conceptual integrity for understanding
- Responsive to unplanned events
- Verifiable to confirm requirements met
Problems without SRS Document
- The software won’t be developed according to customer needs
- Developers cannot accurately develop the features the customer requires
- Maintenance engineers will struggle to understand functionality
- User manuals will be difficult to create.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.