Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which structure is located below the posterior part of the mylohyoid line?
Which structure is located below the posterior part of the mylohyoid line?
- Inferior alveolar nerve
- Submandibular fossa (correct)
- Sublingual fossa
- Mylohyoid muscle
Where is the sublingual fossa situated in relation to the mylohyoid line?
Where is the sublingual fossa situated in relation to the mylohyoid line?
- At the lateral side of the line
- Above the anterior part of the line (correct)
- Below the posterior part of the line
- Within the mylohyoid space
What is the primary gland associated with the submandibular fossa?
What is the primary gland associated with the submandibular fossa?
- Submandibular gland (correct)
- Buccal gland
- Parotid gland
- Sublingual gland
Which of the following statements is true regarding the location of the sublingual gland?
Which of the following statements is true regarding the location of the sublingual gland?
Which anatomical feature separates the submandibular and sublingual fossae?
Which anatomical feature separates the submandibular and sublingual fossae?
Where is the mandibular foramen located?
Where is the mandibular foramen located?
Which structure is located at the posterior part of the mandible?
Which structure is located at the posterior part of the mandible?
Which of the following is NOT a feature of the mandible?
Which of the following is NOT a feature of the mandible?
What is the function of the coronoid process of the mandible?
What is the function of the coronoid process of the mandible?
Which anatomical structure is primarily responsible for articulation in the mandible?
Which anatomical structure is primarily responsible for articulation in the mandible?
What is the primary function of the parietal bones in the skull?
What is the primary function of the parietal bones in the skull?
Which bones are primarily involved in forming the lateral aspect of the skull?
Which bones are primarily involved in forming the lateral aspect of the skull?
What characteristic is specific to the parietal bones?
What characteristic is specific to the parietal bones?
Which structure provides attachment for the temporal fascia?
Which structure provides attachment for the temporal fascia?
Which joint is formed where the parietal bones meet?
Which joint is formed where the parietal bones meet?
What is the role of the zygomatic process of the temporal bone?
What is the role of the zygomatic process of the temporal bone?
In which edition of the reference text is the anatomy of the parietal bones discussed?
In which edition of the reference text is the anatomy of the parietal bones discussed?
Identify the correct feature associated with the temporal lines.
Identify the correct feature associated with the temporal lines.
Which of the following bones forms the zygomatic arch?
Which of the following bones forms the zygomatic arch?
What anatomical feature connects the zygomatic bone to the temporal bone?
What anatomical feature connects the zygomatic bone to the temporal bone?
What is the function of the suprameatal triangle?
What is the function of the suprameatal triangle?
Where is the suprameatal triangle located in relation to the external auditory canal?
Where is the suprameatal triangle located in relation to the external auditory canal?
Which surgical procedure relies heavily on the identification of the suprameatal triangle?
Which surgical procedure relies heavily on the identification of the suprameatal triangle?
Which anatomical feature does the suprameatal triangle relate to?
Which anatomical feature does the suprameatal triangle relate to?
Why is the suprameatal triangle considered an important landmark?
Why is the suprameatal triangle considered an important landmark?
What is the primary location of the mental spines on the mandible?
What is the primary location of the mental spines on the mandible?
Which feature of the mandible does the mylohyoid line describe?
Which feature of the mandible does the mylohyoid line describe?
Which tooth is referenced as near the distal end of the mylohyoid line?
Which tooth is referenced as near the distal end of the mylohyoid line?
What anatomical feature is described by the term 'genial tubercles'?
What anatomical feature is described by the term 'genial tubercles'?
In which direction does the mylohyoid line run from the mental spines?
In which direction does the mylohyoid line run from the mental spines?
Flashcards
Parietal bones
Parietal bones
Bones that form parts of the sides and roof of the skull.
Cranium
Cranium
The part of the skull that encloses the brain.
Norma lateralis
Norma lateralis
Side view of the skull.
Skull
Skull
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bone
Bone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Zygomatic Process of Temporal Bone
Zygomatic Process of Temporal Bone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Temporal Process of Zygomatic Bone
Temporal Process of Zygomatic Bone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Supramastoid Crest
Supramastoid Crest
Signup and view all the flashcards
Zygomatic Arch
Zygomatic Arch
Signup and view all the flashcards
Superior Temporal Line
Superior Temporal Line
Signup and view all the flashcards
Suprameatal triangle
Suprameatal triangle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cortical mastoidectomy
Cortical mastoidectomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
External auditory meatus
External auditory meatus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Landmark
Landmark
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mastoid process
Mastoid process
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mandible
Mandible
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mandibular Foramen
Mandibular Foramen
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oblique Line
Oblique Line
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mental Foramen
Mental Foramen
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mental Protuberance
Mental Protuberance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mental Spines
Mental Spines
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mylohyoid Line
Mylohyoid Line
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mandible Body
Mandible Body
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where is the mylohyoid line located?
Where is the mylohyoid line located?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the purpose of the mental spines?
What is the purpose of the mental spines?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Submandibular Fossa
Submandibular Fossa
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sublingual Fossa
Sublingual Fossa
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where is the submandibular fossa located?
Where is the submandibular fossa located?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where is the sublingual fossa located?
Where is the sublingual fossa located?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Skull Anatomy
- Reference: Snell's clinical anatomy by regions, 10th edition
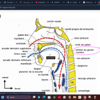
- Norma Lateralis: The parietal bones form the sides and roof of the cranium. The skull is complete at the side by the squamous part of the occipital bone, and parts of the temporal bone (squamous, tympanic, mastoid, styloid, zygomatic processes). The greater wing of the sphenoid and the ramus and body of the mandible also complete the skull at the side, lying inferiorly.
Temporal Bone
- Parts:
- Squamous part
- Tympanic part
- Mastoid process
- Styloid process
- Zygomatic process
- Petrous part (not shown in norma lateralis)
Zygomatic Arch
- Structure: Formed by the articulation of the temporal process of the zygomatic bone with the zygomatic process of the temporal bone.
- Posterior Root: Passes above the external auditory meatus and joins the supramastoid crest.
- Components:
- Temporal process of zygomatic bone
- Zygomatic process of temporal bone
- Supramastoid crest
Temporal Lines
- Superior Temporal Line: Provides attachment for the temporal fascia.
- Inferior Temporal Line: Provides attachment for the temporalis muscle.
Temporal Fossa
- Location: Lies below the inferior temporal line, separated from the lateral side of the skull by the zygomatic arch.
- Division: The zygomatic arch divides the lateral side of the skull into the temporal fossa and the infratemporal fossa.
Pterion
- Location: The thinnest part of the lateral skull wall, situated at the junction of the frontal, parietal, greater wing of the sphenoid, and temporal bones.
- Significance: Overlies the anterior division of the middle meningeal artery and vein. Trauma to this area can lead to epidural bleeding.
Mastoid Antrum
- Description: An air space in the petrous part of the temporal bone, posterior to the middle ear, and connected to it.
- Function: Voice resonance, acoustic insulation, and reduction of cranium mass.
Suprameatal Triangle
- Location: Defined by the superior border (supramastoid crest), the posterior border (line tangential to the posterior border of the external auditory canal), and the anterior border (posterior margin of the external auditory canal).
- Significance: An important landmark for cortical mastoidectomy.
Mandible
- Description: The largest and strongest bone of the face, articulating with the skull at the temporomandibular joint, composed of a body and rami.
- Components:
- Body
- Ramus
- Angle
- Coronoid process
- Condylar process
- Neck
- Mental protuberance
- Mental foramen
- Foramina/Canals:
- Mandibular foramen
- Incisive canal
- Mental foramen
- Surfaces:
- Medial Surface
- Lateral Surface
- Fossae:
- Submandibular
- Sublingual
- Digastric
Fontanelles (Skull development)
- Anterior: Between frontal and parietal bones (bregma) Ossification: 18 months.
- Posterior: Between parietal and occipital bones (lambda) Ossification: 6 months.
- Anterolateral: Between frontal, parietal, and squamous temporal bones (pterion) Ossification: 3 months.
- Posterolateral: Between parietal, temporal, and occipital bones (asterion) Ossification: 3 months.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.