Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following is NOT a function of the skeletal system?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the skeletal system?
- Hormone regulation (correct)
- Support
- Blood cell production
- Movement
What classification of bone is characterized by having a long shaft with two expanded ends?
What classification of bone is characterized by having a long shaft with two expanded ends?
- Irregular bone
- Short bone
- Long bone (correct)
- Flat bone
Which mineral is primarily stored in bones and is crucial for various bodily functions?
Which mineral is primarily stored in bones and is crucial for various bodily functions?
- Sodium
- Potassium
- Calcium (correct)
- Iron
The axial skeleton consists of which of the following?
The axial skeleton consists of which of the following?
What is the process of blood cell production in the bones known as?
What is the process of blood cell production in the bones known as?
Which bone structure primarily supports the weight of the body?
Which bone structure primarily supports the weight of the body?
What is the function of the periosteum?
What is the function of the periosteum?
Which part of the long bone is responsible for nutrient transport?
Which part of the long bone is responsible for nutrient transport?
How many phalanges does the big toe have?
How many phalanges does the big toe have?
What is the primary structural unit of compact bone?
What is the primary structural unit of compact bone?
What type of bone fracture is characterized by a complete break through the bone?
What type of bone fracture is characterized by a complete break through the bone?
Which of the following joints is classified as a synovial joint?
Which of the following joints is classified as a synovial joint?
What is the primary characteristic of a compound (open) fracture?
What is the primary characteristic of a compound (open) fracture?
Which type of joint is typically immovable and consists of fibrous connective tissue?
Which type of joint is typically immovable and consists of fibrous connective tissue?
Which of the following best describes a hinge joint?
Which of the following best describes a hinge joint?
What type of reduction involves realigning bone fragments without surgery?
What type of reduction involves realigning bone fragments without surgery?
Which type of joint is a ball-and-socket joint?
Which type of joint is a ball-and-socket joint?
What is the primary feature of an impacted fracture?
What is the primary feature of an impacted fracture?
What is the primary function of the clavicle in the pectoral girdle?
What is the primary function of the clavicle in the pectoral girdle?
Which statement about the scapula is NOT true?
Which statement about the scapula is NOT true?
What is the significance of the radial tuberosity on the radius?
What is the significance of the radial tuberosity on the radius?
Which part of the ulna articulates with the trochlea of the humerus?
Which part of the ulna articulates with the trochlea of the humerus?
Where is the head of the radius located?
Where is the head of the radius located?
What distinguishes the humerus from other bones in the upper limb?
What distinguishes the humerus from other bones in the upper limb?
Which feature of the scapula is involved in the articulation with the humerus?
Which feature of the scapula is involved in the articulation with the humerus?
What is unique about the positioning of the radius compared to the ulna?
What is unique about the positioning of the radius compared to the ulna?
Which bone is NOT part of the axial skeleton?
Which bone is NOT part of the axial skeleton?
What is the primary function of the cranial bones?
What is the primary function of the cranial bones?
Which of the following bones is considered a facial bone?
Which of the following bones is considered a facial bone?
The hyoid bone is unique among bones in the body because it does what?
The hyoid bone is unique among bones in the body because it does what?
Which structure acts as a pivot point for the atlas in the vertebral column?
Which structure acts as a pivot point for the atlas in the vertebral column?
Which curvature of the spine is characterized as concave anteriorly?
Which curvature of the spine is characterized as concave anteriorly?
How many pairs of true ribs are there?
How many pairs of true ribs are there?
What is the primary purpose of the paranasal sinuses?
What is the primary purpose of the paranasal sinuses?
What is the largest single bone of the face?
What is the largest single bone of the face?
What structure lies superior to the larynx?
What structure lies superior to the larynx?
Which component of the rib cage directly connects to the thoracic vertebrae?
Which component of the rib cage directly connects to the thoracic vertebrae?
What is the role of intervertebral discs?
What is the role of intervertebral discs?
Which of the following skull bones is described as having a bat or butterfly shape?
Which of the following skull bones is described as having a bat or butterfly shape?
Which abnormal spinal curvature is characterized by an exaggerated lumbar curve?
Which abnormal spinal curvature is characterized by an exaggerated lumbar curve?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
The Skeletal System Overview
- The skeleton is categorized into two parts: axial and appendicular.
- Key functions: support, protection, blood cell production, mineral storage (calcium, phosphate), and facilitation of movement.
Classification of Bones
- Long bones: characterized by a long shaft with expanded ends.
- Short bones: cube-shaped.
- Flat bones: plate-like with broad surfaces.
- Irregular bones: varied shapes.
- Round bones: circular in shape.
Axial Skeleton
- Major components include the skull, hyoid bone, vertebral column, thoracic cage, and middle ear bones.
Skull
- Comprised of the cranium and facial bones.
- Protects the brain; features immovable joints (sutures).
- Cranium consists of 8 bones: frontal, parietal (2), occipital, temporal (2), sphenoid, and ethmoid.
Hyoid Bone
- Located superior to the larynx.
- Unique as it does not articulate with other bones; anchors the tongue and supports muscles for swallowing.
Vertebral Column
- Composed of cervical (7), thoracic (12), lumbar (5), sacral (5 fused), and coccygeal vertebrae (3-5 fused).
- Provides structural support and protects the spinal cord.
- Normal curvatures include cervical and lumbar (convex anteriorly), thoracic and sacral (concave anteriorly). Abnormalities include lordosis, kyphosis, and scoliosis.
Intervertebral Discs
- Act as shock absorbers and allow motion between vertebrae.
Rib Cage
- Protects heart and lungs; supports pectoral girdle.
- Contains 12 pairs of ribs: true ribs (first 7 pairs directly connected to sternum) and false ribs (next 5 pairs, some float).
- Sternum consists of three fused parts: manubrium, body, and xiphoid process.
Appendicular Skeleton
- Comprises pectoral girdle, upper limbs, pelvic girdle, and lower limbs.
Pectoral Girdle
- Clavicles articulate with the manubrium and stabilize the shoulder.
- Scapulae connect with the humerus at the glenoid cavity.
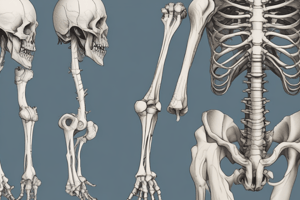
Upper Limb
- Humerus is the main long bone; its head fits into the glenoid cavity.
- Radius: lateral side, articulates with the ulna.
- Ulna: longer forearm bone; features like the coronoid and olecranon processes facilitate elbow movement.
Foot Anatomy
- Seven tarsal bones; the talus allows movement, while the calcaneus supports body weight.
- Five metatarsal bones form the instep, with phalanges making up the toes, featuring two in the big toe and three in others.
Anatomy of a Long Bone
- Composed of periosteum (outer covering), epiphysis (ends), diaphysis (shaft), and medullary cavity (contains yellow marrow).
- Articular cartilage provides a smooth surface for joint movement; endosteum lines the medullary cavity.
Bone Structure
- Compact bone is organized into structural units called Haversian systems or osteons.
- Contains central canals with blood vessels and nerves, lamellae (layers of matrix), and osteocytes (bone cells).
Bone Fractures
- Types include complete, incomplete, simple (closed), compound (open), impacted, spiral, and comminuted.
- Reduction methods for fractures: closed reduction (non-surgical realignment) and open reduction (surgical repair).
Joints (Articulations)
-
Classified by movement:
- Synarthrosis: immovable joints.
- Amphiarthrosis: slightly movable joints.
- Diarthrosis: freely movable joints.
-
Structural classification includes:
- Fibrous joints (immovable).
- Cartilaginous joints (usually slightly movable).
- Synovial joints (freely movable with a joint cavity).
Types of Synovial Joints
- Saddle joint: e.g., carpometacarpal joint of the thumb.
- Ball-and-socket joint: e.g., shoulder and hip.
- Pivot joint: e.g., between ulna and radius.
- Hinge joint: e.g., elbow and knee.
- Gliding joint: e.g., within wrist and ankle.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.