Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the longest bone in the human body?
What is the longest bone in the human body?
- Femur (correct)
- Humerus
- Tibia
- Fibula
What is the purpose of the head of the femur?
What is the purpose of the head of the femur?
- To connect the femur to the knee joint
- To form the hip joint with the acetabulum of the pelvis (correct)
- To provide a surface for the patella to slide on
- To attach muscles of the gluteal region
What is the angle of projection of the neck of the femur to the shaft?
What is the angle of projection of the neck of the femur to the shaft?
- 120-135 degrees (correct)
- 180-190 degrees
- 90-100 degrees
- 150-160 degrees
Which muscle originates from the greater trochanter of the femur?
Which muscle originates from the greater trochanter of the femur?
What is the function of the intertrochanteric line?
What is the function of the intertrochanteric line?
What is the smaller of the two bony processes on the proximal end of the femur?
What is the smaller of the two bony processes on the proximal end of the femur?
What is the purpose of the trochanteric crest?
What is the purpose of the trochanteric crest?
What is the site of attachment for the iliopsoas muscle?
What is the site of attachment for the iliopsoas muscle?
What is the function of the femur?
What is the function of the femur?
Where does the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) attach to?
Where does the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) attach to?
What type of bone is the patella classified as?
What type of bone is the patella classified as?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the patella?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the patella?
What is the shape of the patella?
What is the shape of the patella?
What is the name of the tubercle on the superior half of the femur where quadratus femoris attaches?
What is the name of the tubercle on the superior half of the femur where quadratus femoris attaches?
Where does the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) attach to?
Where does the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) attach to?
What is the largest sesamoid bone in the body?
What is the largest sesamoid bone in the body?
What is the shape of the cross-section of the shaft of the femur in the middle?
What is the shape of the cross-section of the shaft of the femur in the middle?
What is the name of the groove in the femur where the patella is located?
What is the name of the groove in the femur where the patella is located?
What is the name of the roughened ridges on the posterior surface of the femoral shaft?
What is the name of the roughened ridges on the posterior surface of the femoral shaft?
What is the function of the medial and lateral condyles of the femur?
What is the function of the medial and lateral condyles of the femur?
What is the function of the patella in terms of muscle efficiency?
What is the function of the patella in terms of muscle efficiency?
What is the purpose of the more prominent lateral condyle of the femur?
What is the purpose of the more prominent lateral condyle of the femur?
Which facet of the patella articulates with the medial condyle of the femur?
Which facet of the patella articulates with the medial condyle of the femur?
What connects the apex of the patella to the tibial tuberosity?
What connects the apex of the patella to the tibial tuberosity?
What is the name of the bony elevation on the non-articular area of the condyle where the medial collateral ligament originates?
What is the name of the bony elevation on the non-articular area of the condyle where the medial collateral ligament originates?
What is the depression found on the posterior surface of the femur, between the two condyles?
What is the depression found on the posterior surface of the femur, between the two condyles?
What is the direction in which the shaft of the femur descends?
What is the direction in which the shaft of the femur descends?
What is the effect of a flatter condyle on the patella?
What is the effect of a flatter condyle on the patella?
What is the surface that articulates with the patella?
What is the surface that articulates with the patella?
Which part of the femur forms the hip joint with the acetabulum of the pelvis?
Which part of the femur forms the hip joint with the acetabulum of the pelvis?
What is the name of the bony ridges that connect the two trochanters?
What is the name of the bony ridges that connect the two trochanters?
Which muscle attaches to the lesser trochanter of the femur?
Which muscle attaches to the lesser trochanter of the femur?
What is the angle of projection of the neck of the femur to the shaft?
What is the angle of projection of the neck of the femur to the shaft?
What is the function of the trochanteric crest?
What is the function of the trochanteric crest?
What is the function of the intertrochanteric line?
What is the function of the intertrochanteric line?
Which part of the femur is divided into three areas?
Which part of the femur is divided into three areas?
What is the shape of the head of the femur?
What is the shape of the head of the femur?
What is the function of the greater trochanter?
What is the function of the greater trochanter?
What is the main function of the patella in terms of leg movement?
What is the main function of the patella in terms of leg movement?
Which ligament attaches to the lateral aspect of the medial condyle?
Which ligament attaches to the lateral aspect of the medial condyle?
What is the shape of the base of the patella?
What is the shape of the base of the patella?
What is the function of the patella in terms of protection?
What is the function of the patella in terms of protection?
Which surface of the patella articulates with the femur?
Which surface of the patella articulates with the femur?
What is the attachment site for the quadriceps tendon?
What is the attachment site for the quadriceps tendon?
What connects the patella to the tibial tuberosity?
What connects the patella to the tibial tuberosity?
What type of bone is the patella classified as due to its position?
What type of bone is the patella classified as due to its position?
How many facets are present on the posterior surface of the patella?
How many facets are present on the posterior surface of the patella?
What is the location of the patella in relation to the knee joint?
What is the location of the patella in relation to the knee joint?
What is the purpose of the quadratus femoris attaching to the quadrate tubercle?
What is the purpose of the quadratus femoris attaching to the quadrate tubercle?
What is the shape of the cross-section of the shaft of the femur in the middle?
What is the shape of the cross-section of the shaft of the femur in the middle?
What is the name of the roughened ridges on the posterior surface of the femoral shaft?
What is the name of the roughened ridges on the posterior surface of the femoral shaft?
What lies between the medial and lateral supracondylar lines?
What lies between the medial and lateral supracondylar lines?
What is the purpose of the more prominent lateral condyle of the femur?
What is the purpose of the more prominent lateral condyle of the femur?
What forms the floor of the popliteal fossa?
What forms the floor of the popliteal fossa?
What is the medial epicondyle?
What is the medial epicondyle?
What is the effect of a flatter condyle on the patella?
What is the effect of a flatter condyle on the patella?
What is the direction in which the shaft of the femur descends?
What is the direction in which the shaft of the femur descends?
What is the intercondylar fossa?
What is the intercondylar fossa?
What is the location of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) attachment?
What is the location of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) attachment?
What is the function of the patella in terms of muscle efficiency?
What is the function of the patella in terms of muscle efficiency?
What articulates with the lateral condyle of the femur?
What articulates with the lateral condyle of the femur?
What is the superior aspect of the patella attached to?
What is the superior aspect of the patella attached to?
What is the shape of the patella?
What is the shape of the patella?
What is the purpose of the patella in terms of protection?
What is the purpose of the patella in terms of protection?
What attaches the apex of the patella to the tibial tuberosity?
What attaches the apex of the patella to the tibial tuberosity?
What is the posterior surface of the patella involved in?
What is the posterior surface of the patella involved in?
What is the bony landmark that the patella is located in?
What is the bony landmark that the patella is located in?
What is the function of the patella in terms of leg movement?
What is the function of the patella in terms of leg movement?
What is the direction in which the shaft of the femur descends?
What is the direction in which the shaft of the femur descends?
What is the name of the roughened ridges on the posterior surface of the femoral shaft?
What is the name of the roughened ridges on the posterior surface of the femoral shaft?
What is the function of the medial and lateral condyles of the femur?
What is the function of the medial and lateral condyles of the femur?
What is the purpose of the more prominent lateral condyle of the femur?
What is the purpose of the more prominent lateral condyle of the femur?
What is the name of the depression found on the posterior surface of the femur, between the two condyles?
What is the name of the depression found on the posterior surface of the femur, between the two condyles?
What is the shape of the cross-section of the shaft of the femur in the middle?
What is the shape of the cross-section of the shaft of the femur in the middle?
What is the name of the bony elevation on the non-articular area of the condyle where the medial collateral ligament originates?
What is the name of the bony elevation on the non-articular area of the condyle where the medial collateral ligament originates?
What is the function of the trochanters in the femur?
What is the function of the trochanters in the femur?
What is the shape of the neck of the femur?
What is the shape of the neck of the femur?
What is the effect of a flatter condyle on the patella?
What is the effect of a flatter condyle on the patella?
What is the surface that articulates with the patella?
What is the surface that articulates with the patella?
What is the function of the intertrochanteric line?
What is the function of the intertrochanteric line?
What is the purpose of the pectineal line?
What is the purpose of the pectineal line?
What is the direction of the neck of the femur in relation to the shaft?
What is the direction of the neck of the femur in relation to the shaft?
What is the proximal area of the femur divided into?
What is the proximal area of the femur divided into?
What is the surface of the head of the femur covered with?
What is the surface of the head of the femur covered with?
What is the function of the femur in the body?
What is the function of the femur in the body?
What is the purpose of the trochanteric crest?
What is the purpose of the trochanteric crest?
What is the site of attachment for the gluteus medius muscle?
What is the site of attachment for the gluteus medius muscle?
What is the function of the femur in terms of movement?
What is the function of the femur in terms of movement?
Where does the quadratus femoris muscle attach to on the femur?
Where does the quadratus femoris muscle attach to on the femur?
What is the shape of the cross-section of the shaft of the femur in the middle?
What is the shape of the cross-section of the shaft of the femur in the middle?
What is the function of the linea aspera?
What is the function of the linea aspera?
What lies between the medial and lateral supracondylar lines?
What lies between the medial and lateral supracondylar lines?
What is the significance of the more prominent lateral condyle?
What is the significance of the more prominent lateral condyle?
What is the depression found on the posterior surface of the femur?
What is the depression found on the posterior surface of the femur?
Which ligament originates from the medial epicondyle?
Which ligament originates from the medial epicondyle?
In which direction does the shaft of the femur descend?
In which direction does the shaft of the femur descend?
What is the function of the medial and lateral epicondyles?
What is the function of the medial and lateral epicondyles?
What is the effect of a flatter condyle on the patella?
What is the effect of a flatter condyle on the patella?
What is the location of the patella in relation to the knee joint?
What is the location of the patella in relation to the knee joint?
What is the main function of the patella in terms of leg movement?
What is the main function of the patella in terms of leg movement?
What is the attachment site for the quadriceps tendon?
What is the attachment site for the quadriceps tendon?
How many facets are present on the posterior surface of the patella?
How many facets are present on the posterior surface of the patella?
What connects the patella to the tibial tuberosity?
What connects the patella to the tibial tuberosity?
What is the shape of the patella?
What is the shape of the patella?
Which ligament attaches to the medial aspect of the lateral condyle?
Which ligament attaches to the medial aspect of the lateral condyle?
What is the function of the patella in terms of protection?
What is the function of the patella in terms of protection?
Which facet of the patella articulates with the lateral condyle of the femur?
Which facet of the patella articulates with the lateral condyle of the femur?
What type of bone is the patella classified as due to its position?
What type of bone is the patella classified as due to its position?
What is the function of the proximal area of the femur?
What is the function of the proximal area of the femur?
What is the name of the bony ridges that connect the two trochanters?
What is the name of the bony ridges that connect the two trochanters?
Where does the neck of the femur connect?
Where does the neck of the femur connect?
What is the site of attachment for the iliopsoas muscle?
What is the site of attachment for the iliopsoas muscle?
What is the characteristic of the head of the femur?
What is the characteristic of the head of the femur?
What is the function of the greater trochanter?
What is the function of the greater trochanter?
What is the characteristic of the neck of the femur?
What is the characteristic of the neck of the femur?
What is the function of the intertrochanteric line?
What is the function of the intertrochanteric line?
What is the characteristic of the femur?
What is the characteristic of the femur?
What is the function of the proximal area of the femur in terms of movement?
What is the function of the proximal area of the femur in terms of movement?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
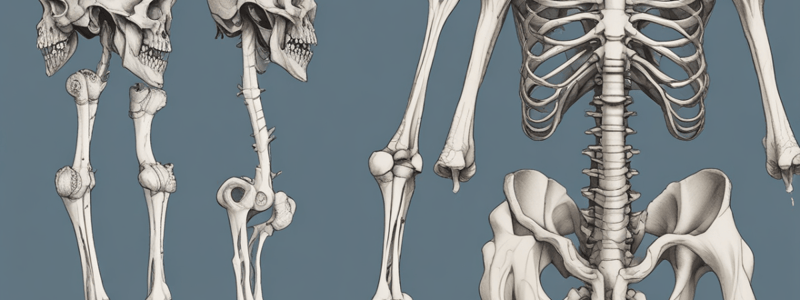
Femur
- Longest bone in the body and the only bone in the thigh.
- Divided into three areas: proximal, shaft, and distal.
Proximal Area
- Forms the hip joint with the acetabulum of the pelvis.
- Consists of a head, neck, and two bony processes (greater and lesser trochanters).
- Head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum of the pelvis to form the hip joint.
- Neck of the femur connects the head to the shaft, projecting in a superior and medial direction at an angle of 120-135 degrees.
Greater Trochanter
- Most lateral palpable projection of the bone.
- Site of attachment for many muscles in the gluteal region, including gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, piriformis, and vastus lateralis.
Lesser Trochanter
- Smaller than the greater trochanter.
- Projects from the posteromedial side of the femur, just inferior to the neck-shaft junction.
- Site of attachment for iliopsoas.
Intertrochanteric Line and Crest
- A ridge of bone that connects the two trochanters together.
- Anteriorly, it is known as the intertrochanteric line, and posteriorly, it is known as the trochanteric crest.
- Site of attachment for the iliofemoral ligament and the hip joint capsule.
Shaft of Femur
- Descends in a slight medial direction, bringing the knees closer to the body's center of gravity and increasing stability.
- A cross-section of the shaft in the middle is circular but flattened posteriorly at proximal and distal aspects.
- Posterior surface has roughened ridges called linea aspera.
Distal End of Femur
- Presence of medial and lateral condyles, which articulate with the tibia and patella to form the knee joint.
- Medial and lateral condyles are rounded areas at the end of the femur.
- Posterior and inferior surfaces articulate with the tibia and menisci of the knee, while the anterior surface articulates with the patella.
Patella (Knee-cap)
- Located at the front of the knee joint, within the patellofemoral groove of the femur.
- Classified as a sesamoid type bone due to its position within the quadriceps tendon.
- Largest sesamoid bone in the body.
Bony Landmarks of Patella
- Triangular shape with anterior and posterior surfaces.
- Apex is situated inferiorly and connected to the tibial tuberosity by the patella ligament.
- Base forms the superior aspect of the bone and provides attachment area for the quadriceps tendon.
Functions of Patella
- Enhances the power that the quadriceps tendon can exert on the femur, increasing the efficiency of the muscle during leg extension.
- Protects the anterior aspect of the knee joint from physical trauma.
Femur Structure
- The femur is the longest bone in the body and the only bone in the thigh.
- Divided into three areas: proximal, shaft, and distal.
Proximal Area of Femur
- Forms the hip joint with the acetabulum of the pelvis.
- Consists of a head and neck, and two bony processes (greater and lesser trochanters).
- The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum of the pelvis to form the hip joint.
- The neck of the femur connects the head of the femur with the shaft and is set at an angle of 120-135 degrees to the shaft.
Greater Trochanter of Femur
- The most lateral palpable projection of the bone.
- Site of attachment for many muscles in the gluteal region, such as gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, and piriformis.
Lesser Trochanter of Femur
- Smaller than the greater trochanter.
- Projects from the posteromedial side of the femur, just inferior to the neck-shaft junction.
- Site of attachment for iliopsoas.
Intertrochanteric Line of Femur
- A ridge of bone that runs in an inferomedial direction on the anterior surface of the femur.
- Connects the two trochanters together.
- Site of attachment for the iliofemoral ligament and the hip joint capsule.
Shaft of Femur
- Descends in a slight medial direction.
- Brings the knees closer to the body's center of gravity, increasing stability.
- A cross-section of the shaft in the middle is circular but flattened posteriorly at proximal and distal aspects.
Distal End of Femur
- Presence of medial and lateral condyles, which articulate with the tibia and patella to form the knee joint.
- The medial and lateral condyles are rounded areas at the end of the femur.
- The posterior and inferior surfaces articulate with the tibia and menisci of the knee, while the anterior surface articulates with the patella.
Patella (Knee-Cap)
- Located at the front of the knee joint, within the patellofemoral groove of the femur.
- Classified as a sesamoid type bone due to its position within the quadriceps tendon.
- The largest sesamoid bone in the body.
Bony Landmarks of Patella
- The patella has a triangular shape, with anterior and posterior surfaces.
- The apex of the patella is situated inferiorly and connected to the tibial tuberosity by the patella ligament.
- The base forms the superior aspect of the bone and provides an attachment area for the quadriceps tendon.
Functions of Patella
- Enhances the power that the quadriceps tendon can exert on the femur, increasing the efficiency of the muscle.
- Protects the anterior aspect of the knee joint from physical trauma.
Femur Structure
- The femur is the longest bone in the body and the only bone in the thigh.
- Divided into three areas: proximal, shaft, and distal.
Proximal Area of Femur
- Forms the hip joint with the acetabulum of the pelvis.
- Consists of a head and neck, and two bony processes (greater and lesser trochanters).
- The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum of the pelvis to form the hip joint.
- The neck of the femur connects the head of the femur with the shaft and is set at an angle of 120-135 degrees to the shaft.
Greater Trochanter of Femur
- The most lateral palpable projection of the bone.
- Site of attachment for many muscles in the gluteal region, such as gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, and piriformis.
Lesser Trochanter of Femur
- Smaller than the greater trochanter.
- Projects from the posteromedial side of the femur, just inferior to the neck-shaft junction.
- Site of attachment for iliopsoas.
Intertrochanteric Line of Femur
- A ridge of bone that runs in an inferomedial direction on the anterior surface of the femur.
- Connects the two trochanters together.
- Site of attachment for the iliofemoral ligament and the hip joint capsule.
Shaft of Femur
- Descends in a slight medial direction.
- Brings the knees closer to the body's center of gravity, increasing stability.
- A cross-section of the shaft in the middle is circular but flattened posteriorly at proximal and distal aspects.
Distal End of Femur
- Presence of medial and lateral condyles, which articulate with the tibia and patella to form the knee joint.
- The medial and lateral condyles are rounded areas at the end of the femur.
- The posterior and inferior surfaces articulate with the tibia and menisci of the knee, while the anterior surface articulates with the patella.
Patella (Knee-Cap)
- Located at the front of the knee joint, within the patellofemoral groove of the femur.
- Classified as a sesamoid type bone due to its position within the quadriceps tendon.
- The largest sesamoid bone in the body.
Bony Landmarks of Patella
- The patella has a triangular shape, with anterior and posterior surfaces.
- The apex of the patella is situated inferiorly and connected to the tibial tuberosity by the patella ligament.
- The base forms the superior aspect of the bone and provides an attachment area for the quadriceps tendon.
Functions of Patella
- Enhances the power that the quadriceps tendon can exert on the femur, increasing the efficiency of the muscle.
- Protects the anterior aspect of the knee joint from physical trauma.
Femur Structure
- The femur is the longest bone in the body and the only bone in the thigh.
- Divided into three areas: proximal, shaft, and distal.
Proximal Area of Femur
- Forms the hip joint with the acetabulum of the pelvis.
- Consists of a head and neck, and two bony processes (greater and lesser trochanters).
- The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum of the pelvis to form the hip joint.
- The neck of the femur connects the head of the femur with the shaft and is set at an angle of 120-135 degrees to the shaft.
Greater Trochanter of Femur
- The most lateral palpable projection of the bone.
- Site of attachment for many muscles in the gluteal region, such as gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, and piriformis.
Lesser Trochanter of Femur
- Smaller than the greater trochanter.
- Projects from the posteromedial side of the femur, just inferior to the neck-shaft junction.
- Site of attachment for iliopsoas.
Intertrochanteric Line of Femur
- A ridge of bone that runs in an inferomedial direction on the anterior surface of the femur.
- Connects the two trochanters together.
- Site of attachment for the iliofemoral ligament and the hip joint capsule.
Shaft of Femur
- Descends in a slight medial direction.
- Brings the knees closer to the body's center of gravity, increasing stability.
- A cross-section of the shaft in the middle is circular but flattened posteriorly at proximal and distal aspects.
Distal End of Femur
- Presence of medial and lateral condyles, which articulate with the tibia and patella to form the knee joint.
- The medial and lateral condyles are rounded areas at the end of the femur.
- The posterior and inferior surfaces articulate with the tibia and menisci of the knee, while the anterior surface articulates with the patella.
Patella (Knee-Cap)
- Located at the front of the knee joint, within the patellofemoral groove of the femur.
- Classified as a sesamoid type bone due to its position within the quadriceps tendon.
- The largest sesamoid bone in the body.
Bony Landmarks of Patella
- The patella has a triangular shape, with anterior and posterior surfaces.
- The apex of the patella is situated inferiorly and connected to the tibial tuberosity by the patella ligament.
- The base forms the superior aspect of the bone and provides an attachment area for the quadriceps tendon.
Functions of Patella
- Enhances the power that the quadriceps tendon can exert on the femur, increasing the efficiency of the muscle.
- Protects the anterior aspect of the knee joint from physical trauma.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.