Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle fibers?
What is the primary function of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle fibers?
- To generate ATP
- To store calcium ions (correct)
- To produce myofibrils
- To facilitate blood flow
What structures form a triad in skeletal muscle fibers?
What structures form a triad in skeletal muscle fibers?
- Sarcoplasmic reticulum, T-tubules, thick filaments
- Mitochondria, myofibril, nucleus
- T-tubules sandwiched by two terminal cisternae (correct)
- Terminal cisternae, sarcolemma, thin filaments
How does the release of Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum affect muscle contraction?
How does the release of Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum affect muscle contraction?
- It triggers muscle contraction (correct)
- It inhibits muscle contraction
- It activates myofibrils to relax
- It reduces mitochondrial activity
What role do T-tubules play during muscle contraction?
What role do T-tubules play during muscle contraction?
Which of the following correctly describes the relationship between the mitochondria and ATP production in muscle fibers?
Which of the following correctly describes the relationship between the mitochondria and ATP production in muscle fibers?
What is a primary function of skeletal muscle?
What is a primary function of skeletal muscle?
Which type of muscle tissue lacks striation?
Which type of muscle tissue lacks striation?
What distinguishes thick filaments from thin filaments in muscle fibers?
What distinguishes thick filaments from thin filaments in muscle fibers?
Which statement about skeletal muscle fibers is true?
Which statement about skeletal muscle fibers is true?
What role do skeletal muscle proteins play?
What role do skeletal muscle proteins play?
Which nervous system primarily regulates skeletal muscle activity?
Which nervous system primarily regulates skeletal muscle activity?
What percentage of total adult body weight is occupied by the muscular system?
What percentage of total adult body weight is occupied by the muscular system?
Which of the following is primarily a function of skeletal muscle?
Which of the following is primarily a function of skeletal muscle?
What is the basic contractile unit of skeletal muscle called?
What is the basic contractile unit of skeletal muscle called?
What type of muscle tissue is characterized by intercalated disks?
What type of muscle tissue is characterized by intercalated disks?
Which type of muscle can initiate its own contraction?
Which type of muscle can initiate its own contraction?
What neurotransmitter is primarily involved at the neuromuscular junction of skeletal muscle?
What neurotransmitter is primarily involved at the neuromuscular junction of skeletal muscle?
In skeletal muscle, what structure allows the rapid transmission of action potentials into the interior of the muscle fiber?
In skeletal muscle, what structure allows the rapid transmission of action potentials into the interior of the muscle fiber?
How many nuclei are typically found in a mature skeletal muscle fiber?
How many nuclei are typically found in a mature skeletal muscle fiber?
What is the primary function of myoglobin in skeletal muscle?
What is the primary function of myoglobin in skeletal muscle?
What connective tissue layer surrounds an entire skeletal muscle?
What connective tissue layer surrounds an entire skeletal muscle?
Which type of muscle tissue is NOT under voluntary control?
Which type of muscle tissue is NOT under voluntary control?
What role does the autonomic nervous system play in muscle contraction?
What role does the autonomic nervous system play in muscle contraction?
Which part of a muscle fiber is involved in converting electrical signals into chemical signals?
Which part of a muscle fiber is involved in converting electrical signals into chemical signals?
What structural component of skeletal muscle is responsible for organizing muscle fibers into bundles?
What structural component of skeletal muscle is responsible for organizing muscle fibers into bundles?
Where are the nuclei located in skeletal muscle fibers?
Where are the nuclei located in skeletal muscle fibers?
What characteristic distinguishes skeletal muscle from other muscle types?
What characteristic distinguishes skeletal muscle from other muscle types?
During muscle contraction, what sequence occurs after the neurotransmitter is released?
During muscle contraction, what sequence occurs after the neurotransmitter is released?
Which proteins are classified as contractile proteins in skeletal muscle?
Which proteins are classified as contractile proteins in skeletal muscle?
What role does nebula play in skeletal muscle fibers?
What role does nebula play in skeletal muscle fibers?
Which of the following best describes the structure of the sarcomere?
Which of the following best describes the structure of the sarcomere?
What is the function of titin in skeletal muscle fibers?
What is the function of titin in skeletal muscle fibers?
Which proteins are classified as regulatory proteins in muscle fibers?
Which proteins are classified as regulatory proteins in muscle fibers?
What is the function of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in skeletal muscles?
What is the function of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in skeletal muscles?
What are the thick filaments primarily composed of in skeletal muscle?
What are the thick filaments primarily composed of in skeletal muscle?
Which of these structures is NOT part of the skeletal muscle fiber's contractile system?
Which of these structures is NOT part of the skeletal muscle fiber's contractile system?
In the structure of a myofibril, what does the A band represent?
In the structure of a myofibril, what does the A band represent?
Where are T-tubules located within skeletal muscle fibers?
Where are T-tubules located within skeletal muscle fibers?
Which two structures make up the triad in skeletal muscle?
Which two structures make up the triad in skeletal muscle?
Tropomyosin primarily functions in muscle contraction by:
Tropomyosin primarily functions in muscle contraction by:
What is the main function of myosin heads during muscle contraction?
What is the main function of myosin heads during muscle contraction?
What role does titin play in muscle fibers?
What role does titin play in muscle fibers?
What is the primary function of the I band in a sarcomere?
What is the primary function of the I band in a sarcomere?
Which region in the sarcomere is lighter than the outer edges of the A band?
Which region in the sarcomere is lighter than the outer edges of the A band?
What structure serves as the attachment site for thick filaments within a sarcomere?
What structure serves as the attachment site for thick filaments within a sarcomere?
Which protein prevents myosin heads from binding to actin in a relaxed muscle?
Which protein prevents myosin heads from binding to actin in a relaxed muscle?
Which component is responsible for the hydrolysis of ATP in muscle contraction?
Which component is responsible for the hydrolysis of ATP in muscle contraction?
How many myosin molecules typically compose a single thick filament in skeletal muscle?
How many myosin molecules typically compose a single thick filament in skeletal muscle?
What part of the troponin complex binds calcium ions?
What part of the troponin complex binds calcium ions?
What is the primary structure of actin filaments?
What is the primary structure of actin filaments?
What is the function of the Hinge region in myosin molecules?
What is the function of the Hinge region in myosin molecules?
What occurs when calcium binds to troponin?
What occurs when calcium binds to troponin?
What is the primary role of nebulin in the sarcomere?
What is the primary role of nebulin in the sarcomere?
What type of band is occupied entirely by thick filaments in a sarcomere?
What type of band is occupied entirely by thick filaments in a sarcomere?
Flashcards
What is skeletal muscle?
What is skeletal muscle?
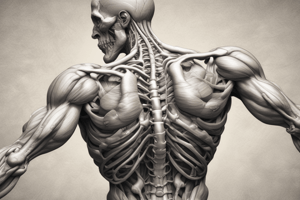
Skeletal muscle is a type of muscle tissue responsible for movement, posture, and other functions. It's characterized by striations (alternating light and dark bands), and multinucleated cells.
What is cardiac muscle?
What is cardiac muscle?
Cardiac muscle is found only in the heart. It's also striated, but unlike skeletal muscle, it's uninucleated and has specialized junctions called intercalated disks for communication between cells.
What is smooth muscle?
What is smooth muscle?
Smooth muscle is found in the walls of internal organs like the stomach, intestines, and blood vessels. It lacks striations and is uninucleated. Its contractions are involuntary and help regulate organ function.
What is a muscle fiber?
What is a muscle fiber?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are thick filaments?
What are thick filaments?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are thin filaments?
What are thin filaments?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is myosin?
What is myosin?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is actin?
What is actin?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are troponin and tropomyosin?
What are troponin and tropomyosin?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the sarcomere?
What is the sarcomere?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum (SR)
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum (SR)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Terminal Cisternae
Terminal Cisternae
Signup and view all the flashcards
T-tubules (Transverse Tubules)
T-tubules (Transverse Tubules)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myofibril
Myofibril
Signup and view all the flashcards
Triad (T-tubule + 2 Terminal Cisternae)
Triad (T-tubule + 2 Terminal Cisternae)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pacemaker activity
Pacemaker activity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cardiac muscle
Cardiac muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Smooth muscle
Smooth muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Autonomic nervous system
Autonomic nervous system
Signup and view all the flashcards
Skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neuromuscular junction
Neuromuscular junction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acetylcholine
Acetylcholine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Muscle fascicle
Muscle fascicle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epimysium
Epimysium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endomysium
Endomysium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sarcolemma
Sarcolemma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transverse (T) tubules
Transverse (T) tubules
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myoglobin
Myoglobin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sarcomere
Sarcomere
Signup and view all the flashcards
T-tubules
T-tubules
Signup and view all the flashcards
Triad
Triad
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thick Filament
Thick Filament
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thin Filament
Thin Filament
Signup and view all the flashcards
A band
A band
Signup and view all the flashcards
M line
M line
Signup and view all the flashcards
I band
I band
Signup and view all the flashcards
H zone
H zone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Z disk
Z disk
Signup and view all the flashcards
Titin
Titin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nebulin
Nebulin
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Nebulin?
What is Nebulin?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are Z disks?
What are Z disks?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What protein forms thick filaments?
What protein forms thick filaments?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What protein forms thin filaments?
What protein forms thin filaments?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the H zone?
What is the H zone?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the A band?
What is the A band?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the I band?
What is the I band?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the M line?
What is the M line?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the myosin-binding site?
What is the myosin-binding site?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Tropomyosin?
What is Tropomyosin?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Troponin?
What is Troponin?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Myosin head?
What is Myosin head?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the ATP-binding site?
What is the ATP-binding site?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Skeletal Muscle Overview
- Skeletal muscle comprises 40-50% of adult body weight.
- Its primary function is converting chemical energy into mechanical energy, generating force leading to muscle shortening, performing work (movement), maintaining equilibrium (posture), transporting substances (circulation and digestion), and generating heat to maintain body temperature.
Skeletal Muscle Objectives
- Explain the structural differences among the three types of muscular tissue.
- Describe the microscopic anatomy of a skeletal muscle fiber.
- Distinguish thick filaments from thin filaments.
- Describe the functions of skeletal muscle proteins.
- Describe the basic unit of the skeletal muscle fiber.
- Describe the ultrastructure of the muscle contractile unit responsible for muscle contraction.
Types of Muscular Tissue
- Three main types: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle.
- Skeletal muscle exhibits striations (repeating light and dark bands).
- Cardiac muscle also shows striations but has specialized junctions called intercalated disks.
- Smooth muscle lacks striations.
General Properties of the Muscular System
- Skeletal muscle is mostly voluntary, controlled by the somatic nervous system.
- Smooth and cardiac muscle are involuntary; controlled by the autonomic nervous system and endocrine system.
- Skeletal muscle cells are multinucleated, formed from the fusion of numerous embryonic myoblasts.
- Smooth and cardiac muscle cells are uninucleated.
Skeletal Muscle Structure
- Skeletal muscles are composed of muscle fibers.
- Muscle fibers are bundled into fascicles, surrounded by connective tissue (perimysium).
- Fascicles are, in turn, enclosed by a connective tissue layer called epimysium.
- The entire muscle is covered by epimysium.
- Connective tissue layers extend beyond the muscle fibers forming tendons, which attach to bones.
Microscopic Structures of a Skeletal Muscle Fiber
- Each skeletal muscle fiber is a fusion of embryonic myoblasts.
- Mature skeletal muscle fibers contain multiple nuclei located beneath the plasma membrane (sarcolemma).
- Sarcolemma has thousands of transverse tubules (T-tubules) that tunnel toward the fiber's center.
- Sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) encircles myofibrils; dilated end sacs (terminal cisternae) alongside T-tubules form triads.
- Myoglobin (red-colored protein) is found in the sarcoplasm (cytoplasm) and binds oxygen, enhancing mitochondrial ATP production.
Functional Unit of Skeletal Muscle
- The sarcomere is the basic unit, extending between two Z disks.
- Z disks are zigzag protein structures serving as attachment sites for thin filaments.
I bands (Light Bands)
- Contain only thin filaments.
- Z disk is located in the middle of the I band.
A bands (Dark Bands)
- Thick and thin filaments overlap.
- The center of the A band is occupied by thick filaments only (H zone).
M line
- Represents proteins forming the attachment site for thick filaments.
- Divides the A band in half.
- H-zone is the center region of the A band, lighter than outer edges, containing thick filaments only.
Contractile Proteins
- Myosin (thick filaments): Multiple myosin molecules form each thick filament; each myosin molecule resembles two golf clubs twisted together, with projections called myosin heads.
- Actin (thin filaments): G-actin molecules polymerize to form F-actin, a long filamentous protein; two F-actin polymers twist into a helix with regulatory proteins (tropomyosin and troponin attachments.
Regulatory Proteins
- Tropomyosin: Covers myosin-binding sites on G-actin molecules in a relaxed muscle, preventing myosin-actin interactions.
- Troponin: A heterotrimer (TnT, TnC, TnI) complex; TnT binds to tropomyosin, TnC binds calcium, and TnI covers myosin-binding sites; calcium release initiates muscle contraction.
Structural Proteins
- Titin: A spring-like protein linking Z disks to M line that contributes to passive muscle elasticity.
- Nebulin: Along the thin filament, regulating thin filament length and actin alignment.
Sample Questions and Answers
(Provided in the OCR text, but not reformatted into study notes structure)
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.