Podcast
Questions and Answers
¿Cuál es la función principal de la nariz en el sistema respiratorio?
¿Cuál es la función principal de la nariz en el sistema respiratorio?
- Permitir la entrada y salida del aire durante la respiración
- Filtrar y calentar el aire entrante (correct)
- Facilitar el paso del aire hacia los pulmones
- Producir moco para proteger las vías respiratorias
¿Cuál es la función principal de la tráquea en el sistema respiratorio?
¿Cuál es la función principal de la tráquea en el sistema respiratorio?
- Contraerse y relajarse para generar cambios de presión que permiten la respiración
- Permitir el paso del aire hacia y desde los pulmones (correct)
- Producir moco para proteger las vías respiratorias
- Facilitar el intercambio de gases entre los pulmones y la sangre
¿Cuál es la función principal del diafragma en el sistema respiratorio?
¿Cuál es la función principal del diafragma en el sistema respiratorio?
- Facilitar el intercambio de gases entre los pulmones y la sangre
- Permitir el paso del aire hacia y desde los pulmones
- Contraerse y relajarse para generar cambios de presión que permiten la respiración (correct)
- Filtrar y calentar el aire entrante
¿Cuál es el principal proceso que ocurre en los pulmones durante la respiración?
¿Cuál es el principal proceso que ocurre en los pulmones durante la respiración?
¿Cuál es una enfermedad común asociada al sistema respiratorio?
¿Cuál es una enfermedad común asociada al sistema respiratorio?
¿Cuál de las siguientes afirmaciones sobre los pulmones es correcta?
¿Cuál de las siguientes afirmaciones sobre los pulmones es correcta?
Además de la entrega de oxígeno y la eliminación de dióxido de carbono, ¿cuál de las siguientes NO es una función del sistema respiratorio?
Además de la entrega de oxígeno y la eliminación de dióxido de carbono, ¿cuál de las siguientes NO es una función del sistema respiratorio?
Durante el proceso de intercambio de gases en los pulmones, ¿qué sucede con el oxígeno y el dióxido de carbono?
Durante el proceso de intercambio de gases en los pulmones, ¿qué sucede con el oxígeno y el dióxido de carbono?
¿Cuál de las siguientes enfermedades o trastornos respiratorios se caracteriza por una inflamación de las vías respiratorias más grandes, a menudo acompañada de tos y producción de mucosidad?
¿Cuál de las siguientes enfermedades o trastornos respiratorios se caracteriza por una inflamación de las vías respiratorias más grandes, a menudo acompañada de tos y producción de mucosidad?
¿Cuál de las siguientes enfermedades o trastornos respiratorios se debe a una reacción alérgica causada por la exposición al polen, el polvo u otros alérgenos?
¿Cuál de las siguientes enfermedades o trastornos respiratorios se debe a una reacción alérgica causada por la exposición al polen, el polvo u otros alérgenos?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Respiratory System
The respiratory system is a crucial component of the human body, responsible for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide via breathing. It is composed of various organs and structures that work together to ensure the proper functioning of the human body. In this article, we will explore the main organs of the respiratory system, their functions, gas exchange in the lungs, common diseases, and disorders associated with the respiratory system.
Main Organs of the Respiratory System
The primary organs of the respiratory system include the nose, trachea (windpipe), diaphragm, and lungs. Additional structures contributing to the respiratory system are the intercostal muscles between the ribs.
The Nose
The first step in respiration involves the nose, which filters and warms the incoming air. It acts as a barrier against foreign particles, thanks to the presence of hairs and mucus-producing cells lining the nasal passage.
Trachea
Following the nose, the air passes through the trachea, a rigid structure reinforced by rings of cartilage, ensuring a steady airflow toward the bottom of the body.
Diaphragm
Located beneath the lungs, the diaphragm plays a crucial role in respiration. Contraction and relaxation of the diaphragm create changes in air pressure, allowing for air to enter the lungs during inhalation and exit during exhalation.
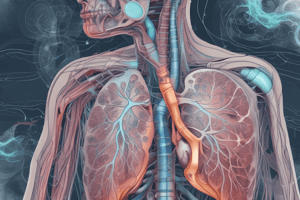
Lungs
The main organ of respiration, the lungs, are located inside the chest cavity, protected by the ribcage and surrounded by a membrane called the pleura. They look like giant sponges filled with tubes branching down into smaller airways and ultimately ending in tiny, bubble-like structures known as alveoli. Inside these alveoli, gas exchange takes place, with oxygen moving into blood vessels and carbon dioxide exiting through exhalation.
Functions of the Respiratory System
Beyond the role of delivering oxygen and removing waste carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves additional functions:
- Warming up incoming air and maintaining body temperature
- Humidifying the air to match humidity requirements
- Protecting the airway from irritants and harmful particles
- Facilitating speech through the vocal cords
Gas Exchange in the Lungs
Oxygen enters the lungs during inhalation and diffuses into capillaries surrounding the alveoli. Simultaneously, carbon dioxide moves from blood vessels into the alveoli, ultimately leaving the body via exhalation.
Blood Circulation
The circulatory system plays a vital role in supplying oxygen-rich blood to cells throughout the body. After absorbing oxygen, blood travels to the heart, which then distributes it to cells via arteries and veins.
Diseases and Disorders of the Respiratory System
Several conditions affect the respiratory system, causing discomfort or impaired respiration:
- Asthma: Characterized by narrowed airways, resulting in wheezing and breathlessness.
- Bronchitis: Inflammation of larger lung airways, often accompanied by coughing and mucus production.
- Emphysema: Damage to alveoli, leading to difficulty breathing and reduced oxygen intake.
- Hay fever: Allergic reactions caused by exposure to pollen, dust, or other allergens.
- Influenza: Viral infection affecting the upper respiratory tract, characterized by flu-like symptoms.
- Laryngitis: Inflammation of the voice box (larynx), often leading to hoarseness or loss of voice.
- Pneumonia: Bacterial or viral infection targeting lung tissue, manifesting as fever, cough, and shortness of breath.
These diseases can cause distressing symptoms and sometimes require medical intervention. It is essential to consult healthcare professionals for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.