Podcast
Questions and Answers
Where does the respiratory drive originate in the body?
Where does the respiratory drive originate in the body?
- Medulla in the brain stem (correct)
- Pituitary gland
- Cerebellum in the brain
- Hippocampus
What is the function of type 2 cells in the alveoli?
What is the function of type 2 cells in the alveoli?
- Aid in mucus production
- Produce surfactant for smooth expansion (correct)
- Initiate cough reflex
- Facilitate gas exchange
Which condition can result from hypoventilation?
Which condition can result from hypoventilation?
- Respiratory acidosis (correct)
- Respiratory alkalosis
- Metabolic alkalosis
- Metabolic acidosis
What is the primary role of alveoli in the respiratory system?
What is the primary role of alveoli in the respiratory system?
What can high levels of carbon dioxide from lung diseases potentially lead to?
What can high levels of carbon dioxide from lung diseases potentially lead to?
Which action involves moving air in and out of the lungs?
Which action involves moving air in and out of the lungs?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
- Respiratory emergencies can result from various conditions like asthma, COPD, heart issues, infections, and allergies.
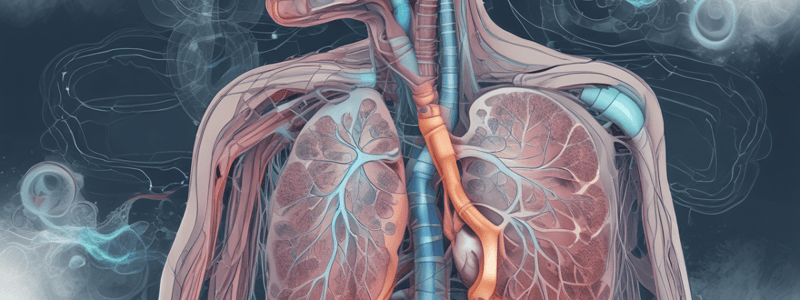
- The respiratory system consists of the upper airway, lower airway, and alveoli where gas exchange occurs.
- Ventilation involves moving air in and out of the lungs, distinct from oxygenation and respiration.
- The respiratory drive originates in the medulla in the brain stem, with inspiration involving diaphragm and intercostal muscle contraction.
- Alveoli are crucial for gas exchange, with type 1 cells facilitating exchange and type 2 cells producing surfactant for smooth expansion.
- Chronic lung diseases can lead to increased red blood cells, thickening blood, and straining the right side of the heart (cor pulmonale).
- High levels of carbon dioxide can result from lung diseases, impairing the body's response and potentially shifting to hypoxic drive.
- Hypoventilation can cause respiratory acidosis due to an increase in carbon dioxide levels, while hyperventilation can lead to a decrease in carbon dioxide levels.
- Patients experiencing difficulty breathing may have obstructed gas exchange, air passages, or blood flow to the lungs, along with reporting symptoms like air hunger and chest tightness.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.