Podcast
Questions and Answers
During which months would favorable winds be experienced for sailing from Malindi to Calicut?
During which months would favorable winds be experienced for sailing from Malindi to Calicut?
- June to August
- November to February (correct)
- April to September
- January to March
What characterized the trade routes in comparison to the Silk Roads?
What characterized the trade routes in comparison to the Silk Roads?
- They involved a network of urban centers rather than entire regions. (correct)
- They were primarily overland rather than maritime.
- They only accepted goods from their own region.
- They maintained stable connections with only one region.
What aspect of monsoon winds was crucial for Indian Ocean commerce?
What aspect of monsoon winds was crucial for Indian Ocean commerce?
- They blew predictably alternating between northeast and southwest. (correct)
- They were unpredictable and changed direction monthly.
- They had only a minimal impact on maritime trade routes.
- They blew consistently northeast in winter and southwest in summer.
Which of the following cities would not be part of the Indian Ocean trade network as described?
Which of the following cities would not be part of the Indian Ocean trade network as described?
Which of the following groups contributed to the advancements in shipbuilding and oceanic navigation?
Which of the following groups contributed to the advancements in shipbuilding and oceanic navigation?
What is the main consequence of the network of communication and exchange shown in this map?
What is the main consequence of the network of communication and exchange shown in this map?
What geographic feature influenced the establishment of trade routes in the Indian Ocean?
What geographic feature influenced the establishment of trade routes in the Indian Ocean?
Where do the Silk and Sea Roads intersect geographically?
Where do the Silk and Sea Roads intersect geographically?
What was a key advantage of the Sea Roads over the Silk Roads in terms of transportation?
What was a key advantage of the Sea Roads over the Silk Roads in terms of transportation?
Which Italian city became a major commercial hub in the maritime network by 1000 C.E.?
Which Italian city became a major commercial hub in the maritime network by 1000 C.E.?
Which goods were commonly sought after in the Indian Ocean trade?
Which goods were commonly sought after in the Indian Ocean trade?
What geographical area did the Indian Ocean trade routes primarily connect?
What geographical area did the Indian Ocean trade routes primarily connect?
What drove the Indian Ocean commerce, as per the passage?
What drove the Indian Ocean commerce, as per the passage?
How did transportation costs on the Sea Roads compare to those on the Silk Roads?
How did transportation costs on the Sea Roads compare to those on the Silk Roads?
What type of goods were predominantly carried by the Sea Roads?
What type of goods were predominantly carried by the Sea Roads?
What role did the Egyptian port of Alexandria play in the trade networks?
What role did the Egyptian port of Alexandria play in the trade networks?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
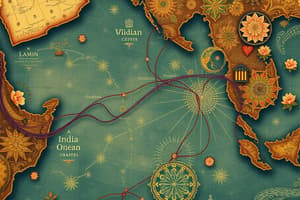
Sea Roads & Indian Ocean Trade
- The Indian Ocean was the largest sea-based system of communication and exchange until the 1500s.
- The Sea Roads connected southern China to eastern Africa, facilitated by monsoon winds.
- Trade routes were facilitated by monsoon winds, which blew predictably northeast in the summer and southwest in the winter.
- Key traded goods included: porcelain from China, spices from Southeast Asia, cotton goods and pepper from India, ivory and gold from East Africa, and incense from southern Arabia.
- Transportation costs on the Sea Roads were lower than on the Silk Roads due to ships carrying larger quantities of goods.
- Goods traded on the Sea Roads included textiles, pepper, timber, rice, sugar, wheat, and luxury items.
- This network of trade led to cultural blending as merchants from various regions interacted and shared ideas.
- Indian Ocean commerce did not involve exchanges between entire regions or countries, but rather between towns and cities.
- Merchants from different regions had more in common with each other than with people in their own hinterlands.
- Urban centers along the Indian Ocean basin served as nodes for this extensive commercial network.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.