Podcast
Questions and Answers
Match the sections of the small intestine with their roles:
Match the sections of the small intestine with their roles:
Duodenum = First section of small intestine Jejunum = Middle section of small intestine Ileum = Final section of small intestine Terminal Ileum = Absorbs bile salts and acids
Match the following digestive processes with their locations:
Match the following digestive processes with their locations:
Chewing = Mouth Microbial digestion = Cecum Water absorption = Large Intestine Waste storage = Colon
Match the digestive compartments with their descriptions:
Match the digestive compartments with their descriptions:
Rumen = Largest compartment, shag carpet Reticulum = Site of cud regurgitation Abomasum = True stomach, similar to monogastric Cecum = Catches large particles for digestion
Match the digestive functions with the respective structures:
Match the digestive functions with the respective structures:
Match the following terms with their meanings:
Match the following terms with their meanings:
Match the following structures with their overall roles in digestion:
Match the following structures with their overall roles in digestion:
What is the primary distinction between Bos Taurus and Bos Indicus?
What is the primary distinction between Bos Taurus and Bos Indicus?
What term describes the act of giving birth in animals?
What term describes the act of giving birth in animals?
Which animal has the shortest gestation period?
Which animal has the shortest gestation period?
What is the primary function of colostrum received after birth?
What is the primary function of colostrum received after birth?
Which of the following pairs correctly matches the species classification to its term?
Which of the following pairs correctly matches the species classification to its term?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
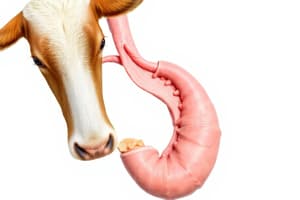
Digestive System Overview
- Mouth facilitates chewing and prehension, with saliva containing the enzyme amylase to begin starch digestion.
- Esophagus serves as a muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach, aiding food transport.
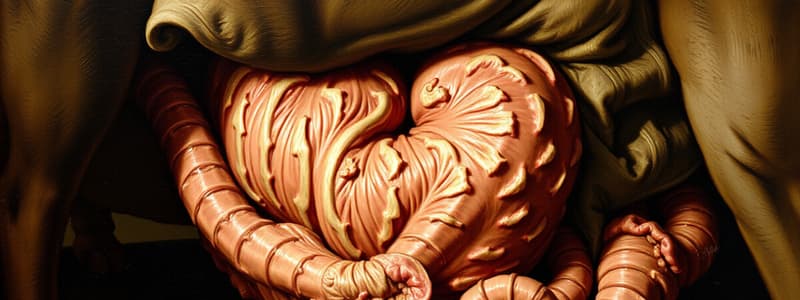
Rumen
- Largest compartment of the ruminant stomach, characterized by shag carpet-like texture and large finger-like projections called papillae.
- Functions as a fermentation vat, where microbial digestion occurs and absorbs volatile fatty acids (VFAs).
Reticulum
- Known for its honeycomb structure, this compartment acts as a site of fermentation and allows for the regurgitation and rechewing of cud, enhancing digestion.
Omasum
- Contains many folds resembling a book and is responsible for water absorption while beginning the absorption of nutrients.
Abomasum
- Referred to as the "true stomach," it secretes lysozyme and acid to aid in enzymatic digestion, resembling the stomach of monogastric animals. It's pear-shaped and has a smooth lining.
Small Intestine
- Divided into three sections: duodenum, jejunum, and ileum, where almost all nutrient absorption occurs, marking the final site of digestion.
- The terminal ileum specifically absorbs bile salts, acids, and remaining nutrients.
Cecum
- Acts as a catchment area for large particles, marking the beginning of microbial digestion.
Large Intestine
- Comprises three sections: cecum, colon, and rectum.
- Primarily functions in water absorption and the formation of feces, storing waste until disposal.
Stomach
- Engages in enzymatic digestion, where food is reduced to a liquid state, with the pyloric region secreting mucus to protect the lining from acid damage.
Cattle Classification
- European cattle are classified as Bos Taurus.
- Cattle influenced by Brahman genetics are categorized as Bos Indicus.
Digestive Systems
- Ruminants possess four stomachs, including cattle, goats, and sheep.
- Non-ruminants or monogastric animals have a single stomach, such as pigs.
Gestation Periods
- Horses have a gestation period of approximately 11 months.
- Cattle typically gestate for about 9 months.
- Sheep and goats have a shorter gestation period of around 5 months.
- Pigs have the shortest gestation, lasting roughly 3 months, 3 weeks, and 3 days.
Reproduction Terms
- Parturition refers to the process of giving birth in animals.
Important Birth-Related Facts
- Colostrum is the initial milk received by newborns right after birth, rich in antibodies and nutrients.
Animal Classifications
- Cattle are known scientifically as bovine.
- Sheep belong to the ovine category.
- Goats are classified as caprine.
- Horses are identified as equine.
- Pigs fall under the porcine classification.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.