Podcast
Questions and Answers
What does the term 'drainage' refer to?
What does the term 'drainage' refer to?
The term 'drainage' refers to the river system of an area.
What are the two major groups of rivers in India?
What are the two major groups of rivers in India?
The two major groups of rivers in India are the Himalayan rivers and the Peninsular rivers.
What is a drainage basin?
What is a drainage basin?
A drainage basin is the area drained by a single river.
What separates two drainage basins?
What separates two drainage basins?
What characterizes Himalayan rivers in terms of water supply?
What characterizes Himalayan rivers in terms of water supply?
How do Peninsular rivers differ from Himalayan rivers?
How do Peninsular rivers differ from Himalayan rivers?
What are some sources of water for Himalayan rivers?
What are some sources of water for Himalayan rivers?
What was the main objective of the National River Conservation Plan (NRCP)?
What was the main objective of the National River Conservation Plan (NRCP)?
How do lakes contribute to regulating the flow of rivers?
How do lakes contribute to regulating the flow of rivers?
What role do rivers play in agriculture in India?
What role do rivers play in agriculture in India?
What are some consequences of improper waste disposal in rivers?
What are some consequences of improper waste disposal in rivers?
Why are riverbanks historically important to human settlements?
Why are riverbanks historically important to human settlements?
What are the main rivers rising in the Nepal Himalaya that contribute to flooding in northern plains?
What are the main rivers rising in the Nepal Himalaya that contribute to flooding in northern plains?
Where is Ambala located and what is situated near it?
Where is Ambala located and what is situated near it?
What is the fall in slope from Ambala to Sunderban?
What is the fall in slope from Ambala to Sunderban?
Which tributaries rise from the peninsular uplands and join the Ganga?
Which tributaries rise from the peninsular uplands and join the Ganga?
What is the source of the Brahmaputra River?
What is the source of the Brahmaputra River?
What happens to the Brahmaputra after it takes a 'U' turn at Namcha Barwa?
What happens to the Brahmaputra after it takes a 'U' turn at Namcha Barwa?
Which tributaries join the Brahmaputra after it enters India?
Which tributaries join the Brahmaputra after it enters India?
What is the Namami Gange Programme?
What is the Namami Gange Programme?
What is the name given to the Brahmaputra in Tibet and Bangladesh?
What is the name given to the Brahmaputra in Tibet and Bangladesh?
Which states share the drainage basin of the Krishna River?
Which states share the drainage basin of the Krishna River?
What is the approximate length of the Krishna River?
What is the approximate length of the Krishna River?
What is a characteristic of lakes in semi-arid regions according to the passage?
What is a characteristic of lakes in semi-arid regions according to the passage?
Name two tributaries of the Kaveri River.
Name two tributaries of the Kaveri River.
What natural phenomenon forms lakes as mentioned in the content?
What natural phenomenon forms lakes as mentioned in the content?
What is the significance of lakes for tourism, based on the context provided?
What is the significance of lakes for tourism, based on the context provided?
What is the name of the second biggest waterfall in India?
What is the name of the second biggest waterfall in India?
Which river’s basin spans parts of Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu?
Which river’s basin spans parts of Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu?
How are some coastal lagoons formed?
How are some coastal lagoons formed?
What is a defining feature of lakes that differ from each other?
What is a defining feature of lakes that differ from each other?
What is the name of the world's largest riverine island formed by the Brahmaputra?
What is the name of the world's largest riverine island formed by the Brahmaputra?
What conservation mission is undertaken by the government of Madhya Pradesh for the Narmada river?
What conservation mission is undertaken by the government of Madhya Pradesh for the Narmada river?
How does the volume of water and silt in the Narmada river compare to its source in Tibet?
How does the volume of water and silt in the Narmada river compare to its source in Tibet?
In which valley does the Tapi river flow?
In which valley does the Tapi river flow?
What is the main water divide in Peninsular India?
What is the main water divide in Peninsular India?
What are the characteristics of the rivers flowing through the coastal plains between the Western Ghats and the Arabian Sea?
What are the characteristics of the rivers flowing through the coastal plains between the Western Ghats and the Arabian Sea?
How do tributaries of the Narmada river typically join the main stream?
How do tributaries of the Narmada river typically join the main stream?
What happens to the Brahmaputra river during the rainy season?
What happens to the Brahmaputra river during the rainy season?
What are some examples of west flowing rivers mentioned in the content?
What are some examples of west flowing rivers mentioned in the content?
Why does the Brahmaputra river have huge deposits of silt?
Why does the Brahmaputra river have huge deposits of silt?
Flashcards
Drainage system
Drainage system
A system of rivers and streams that drain a specific area.
Drainage basin
Drainage basin
The area drained by a single river system.
Water divide
Water divide
A high point or ridge that separates two drainage basins.
Perennial rivers
Perennial rivers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Major drainage systems in India
Major drainage systems in India
Signup and view all the flashcards
Himalayan river water source
Himalayan river water source
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peninsular river characteristics
Peninsular river characteristics
Signup and view all the flashcards
River water volume
River water volume
Signup and view all the flashcards
Silt
Silt
Signup and view all the flashcards
Braided river channel
Braided river channel
Signup and view all the flashcards
Riverine island
Riverine island
Signup and view all the flashcards
River basin
River basin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Riverbed rising
Riverbed rising
Signup and view all the flashcards
River channel shifting
River channel shifting
Signup and view all the flashcards
River flowing in a rift valley
River flowing in a rift valley
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ganga River System
Ganga River System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Himalayan Tributaries of Ganga
Himalayan Tributaries of Ganga
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peninsular Tributaries of Ganga
Peninsular Tributaries of Ganga
Signup and view all the flashcards
Drainage Pattern
Drainage Pattern
Signup and view all the flashcards
Slope of a River
Slope of a River
Signup and view all the flashcards
River Meanders
River Meanders
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brahmaputra River System
Brahmaputra River System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Names of Brahmaputra
Names of Brahmaputra
Signup and view all the flashcards
Krishna River
Krishna River
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kaveri River
Kaveri River
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a drainage basin?
What is a drainage basin?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where does the Krishna River's drainage basin spread?
Where does the Krishna River's drainage basin spread?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What areas are included in the Kaveri River's basin?
What areas are included in the Kaveri River's basin?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Kaveri River famous for?
What is the Kaveri River famous for?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How are large lakes like the Caspian Sea different from regular lakes?
How are large lakes like the Caspian Sea different from regular lakes?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How are lakes created?
How are lakes created?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are lakes that only have water during the rainy season called?
What are lakes that only have water during the rainy season called?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How are oxbow lakes formed?
How are oxbow lakes formed?
Signup and view all the flashcards
National River Conservation Plan (NRCP)
National River Conservation Plan (NRCP)
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do lakes regulate river flow?
How do lakes regulate river flow?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What makes rivers crucial for development?
What makes rivers crucial for development?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does pollution affect rivers?
How does pollution affect rivers?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why are rivers becoming increasingly polluted?
Why are rivers becoming increasingly polluted?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
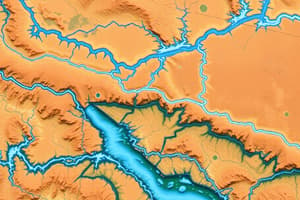
Drainage Systems in India
- Drainage refers to river systems in a specific area.
- Small streams combine to form larger rivers, eventually draining into a larger body of water (lake, ocean).
- A drainage basin is the area drained by a single river system.
- A water divide separates adjacent drainage basins, often found on elevated areas (mountains, uplands).
Drainage Systems of India
- Indian rivers are categorized into Himalayan and Peninsular groups, based on their origin.
- Himalayan rivers (e.g., Indus, Ganga, Brahmaputra) are perennial, meaning they have water year-round. They originate in the Himalayas and flow through gorges, having long courses to the sea. They receive water from rain and melted snow.
- Peninsular rivers (e.g., Godavari, Krishna, Kaveri) are mostly seasonal, relying on rainfall. They originate in the Western Ghats, have shorter courses and drain into the Bay of Bengal.
Himalayan Rivers
- Indus River System: Originates in Tibet, flows west, and enters India in Ladakh, forming gorges. It is joined by tributaries (Zanskar, Nubra, Shyok, Hunza, Satluj etc.). The Indus River eventually flows into the Arabian Sea.
- Ganga River System: Source in the Gangotri Glacier, flows into the plains, and is joined by large tributaries (e.g., Yamuna, Ghaghara, Gandak, Kosi). Rivers flow into the Bay of Bengal.
- Brahmaputra River System: Begins in Tibet (Tsangpo), flows through a gorge in Arunachal Pradesh, and joins the Ganga in Bangladesh to form the mighty delta. It is also known as the Jamuna in Bangladesh.
Peninsular Rivers
- Peninsular rivers are mostly seasonal and originate in the Western Ghats.
- Major Peninsular Rivers: Godavari, Krishna, Kaveri, Mahanadi, Narmada, Tapi are some of the important ones. They flow towards east into the Bay of Bengal.
- Western flowing rivers (Narmada, Tapi): These rivers flow west and create estuaries, distinct from rivers flowing East. Their basins are comparatively smaller.
Important Features
- Rivers develop features like floodplains, oxbow lakes, and deltas (especially during their lower course).
- Erosional activity is more dominant in upper courses, while depositional activity is more pronounced in lower courses.
- There is a wide variety of Lakes in India. Some are natural, like glacial lakes and some are created by human intervention. In addition some are salt lakes.
- The use of rivers for irrigation, navigation, and hydroelectricity is quite prominent in India.
- Rivers are vital for human activities and also crucial for the country's economy.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.