Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary role of the diaphragm during normal inhalation?
What is the primary role of the diaphragm during normal inhalation?
- To assist with forced exhalation.
- To compress the thoracic cavity.
- To elevate the ribs and expand the abdomen.
- To increase thoracic cavity volume by moving downward. (correct)
Which muscle directly assists in forced inhalation by elevating the sternum?
Which muscle directly assists in forced inhalation by elevating the sternum?
- Pectoralis Minor
- Serratus Anterior
- Scalene
- Sternocleidomastoid (correct)
Which group of muscles is primarily responsible for compressing the abdominal cavity to aid in forced exhalation?
Which group of muscles is primarily responsible for compressing the abdominal cavity to aid in forced exhalation?
- External Intercostals
- Abdominal Muscles (correct)
- Accessory Respiratory Muscles
- Intercostal Muscles
Which of the following muscles does NOT directly aid in inhalation by elevating the ribs?
Which of the following muscles does NOT directly aid in inhalation by elevating the ribs?
What is the main function of the external intercostal muscles?
What is the main function of the external intercostal muscles?
What is the primary function of the upper respiratory tract structures?
What is the primary function of the upper respiratory tract structures?
Which of the following best describes the role of alveoli in the respiratory system?
Which of the following best describes the role of alveoli in the respiratory system?
Which structure is NOT part of the upper respiratory tract?
Which structure is NOT part of the upper respiratory tract?
What type of epithelium lines the respiratory epithelium?
What type of epithelium lines the respiratory epithelium?
What is one of the key functions of cilia in the respiratory system?
What is one of the key functions of cilia in the respiratory system?
Which structure acts as the passageway for air to enter the lower respiratory tract?
Which structure acts as the passageway for air to enter the lower respiratory tract?
What role does the respiratory system play in regulating body fluid pH?
What role does the respiratory system play in regulating body fluid pH?
What is the primary function of the conducting division in the respiratory system?
What is the primary function of the conducting division in the respiratory system?
Which of the following structures is NOT part of the conducting division?
Which of the following structures is NOT part of the conducting division?
What type of epithelial tissue lines the trachea?
What type of epithelial tissue lines the trachea?
In which part of the respiratory system does gas exchange predominantly occur?
In which part of the respiratory system does gas exchange predominantly occur?
What is the function of the nasal cavity in the respiratory system?
What is the function of the nasal cavity in the respiratory system?
Which of the following structures has stratified squamous epithelium due to increased abrasion?
Which of the following structures has stratified squamous epithelium due to increased abrasion?
Which structure connects the pharynx to the trachea?
Which structure connects the pharynx to the trachea?
Which epithelial tissue type is found in the nasopharynx?
Which epithelial tissue type is found in the nasopharynx?
What role do the respiratory bronchioles play in the respiratory system?
What role do the respiratory bronchioles play in the respiratory system?
What role does surfactant play in the alveoli?
What role does surfactant play in the alveoli?
How do fenestrations in endothelial cells contribute to gas exchange?
How do fenestrations in endothelial cells contribute to gas exchange?
What is the significance of the fused basement membranes in the respiratory system?
What is the significance of the fused basement membranes in the respiratory system?
What is the primary function of the parietal pleura?
What is the primary function of the parietal pleura?
What is the role of the pleural cavity during breathing?
What is the role of the pleural cavity during breathing?
Which feature allows gases to diffuse quickly in the alveoli?
Which feature allows gases to diffuse quickly in the alveoli?
What characteristic of alveoli primarily contributes to a large area for gas exchange?
What characteristic of alveoli primarily contributes to a large area for gas exchange?
How does smooth muscle in the nasal cavity assist in respiration?
How does smooth muscle in the nasal cavity assist in respiration?
What effect does a concentration gradient have on gas exchange in the alveoli?
What effect does a concentration gradient have on gas exchange in the alveoli?
What role does smooth muscle play in the bronchi?
What role does smooth muscle play in the bronchi?
Which respiratory structure contains more smooth muscle relative to cartilage?
Which respiratory structure contains more smooth muscle relative to cartilage?
Where are peripheral chemoreceptors located and what do they primarily monitor?
Where are peripheral chemoreceptors located and what do they primarily monitor?
What is the primary function of the Ventral Respiratory Group (VRG) located in the medulla oblongata?
What is the primary function of the Ventral Respiratory Group (VRG) located in the medulla oblongata?
Which of the following describes the role of the hypothalamus in respiratory regulation?
Which of the following describes the role of the hypothalamus in respiratory regulation?
What is the composition of the interalveolar septum in the alveoli?
What is the composition of the interalveolar septum in the alveoli?
Which component is NOT part of the primary respiratory muscle system?
Which component is NOT part of the primary respiratory muscle system?
What happens when CO2 levels in the cerebrospinal fluid increase?
What happens when CO2 levels in the cerebrospinal fluid increase?
Which respiratory center is responsible for modifying and fine-tuning the breathing rhythm?
Which respiratory center is responsible for modifying and fine-tuning the breathing rhythm?
In what way does the temperature regulation function of the hypothalamus influence respiration?
In what way does the temperature regulation function of the hypothalamus influence respiration?
Flashcards
Pulmonary Ventilation
Pulmonary Ventilation
The process of moving air into and out of the lungs.
Gas Exchange
Gas Exchange
The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the alveoli and the blood.
Gas Transport
Gas Transport
The movement of oxygen from the lungs to the body cells and carbon dioxide from the cells to the lungs.
Cellular Respiration
Cellular Respiration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Upper Respiratory Tract
Upper Respiratory Tract
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lower Respiratory Tract
Lower Respiratory Tract
Signup and view all the flashcards
Respiratory Epithelium
Respiratory Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Conducting Division
Conducting Division
Signup and view all the flashcards
Respiratory Division
Respiratory Division
Signup and view all the flashcards
Respiratory Bronchioles
Respiratory Bronchioles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveoli
Alveoli
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nostrils (External Nares)
Nostrils (External Nares)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nasal Cavity
Nasal Cavity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pharynx
Pharynx
Signup and view all the flashcards
Larynx
Larynx
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trachea
Trachea
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diaphragm
Diaphragm
Signup and view all the flashcards
External Intercostal Muscles
External Intercostal Muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scalene Muscles
Scalene Muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Abdominal Muscles
Abdominal Muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Internal Intercostal Muscles
Internal Intercostal Muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is connective tissue's role in the nose?
What is connective tissue's role in the nose?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the trachealis muscle do?
What does the trachealis muscle do?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do bronchi control airflow?
How do bronchi control airflow?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What enables alveoli to expand and contract?
What enables alveoli to expand and contract?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where is the respiratory rhythm controlled?
Where is the respiratory rhythm controlled?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What do peripheral chemoreceptors detect?
What do peripheral chemoreceptors detect?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does the hypothalamus influence breathing?
How does the hypothalamus influence breathing?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Explain the action of the diaphragm.
Explain the action of the diaphragm.
Signup and view all the flashcards
What do central chemoreceptors detect?
What do central chemoreceptors detect?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are accessory respiratory muscles?
What are accessory respiratory muscles?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Type II Alveolar Cells
Type II Alveolar Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endothelial Cells
Endothelial Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fenestrations
Fenestrations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fused Basement Membranes
Fused Basement Membranes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thin Membrane
Thin Membrane
Signup and view all the flashcards
Large Surface Area
Large Surface Area
Signup and view all the flashcards
Concentration Gradient
Concentration Gradient
Signup and view all the flashcards
Surfactant
Surfactant
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pleura
Pleura
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parietal Pleura
Parietal Pleura
Signup and view all the flashcards
Visceral Pleura
Visceral Pleura
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pleural Cavity
Pleural Cavity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Learning Outcomes
- Compare and contrast the structure and function of respiratory epithelium in the respiratory tract, considering specialized cells and epithelial types.
- Describe respiratory defense mechanisms and how anatomical features support them.
- Identify structures in the respiratory tract composed of smooth muscle or connective tissue.
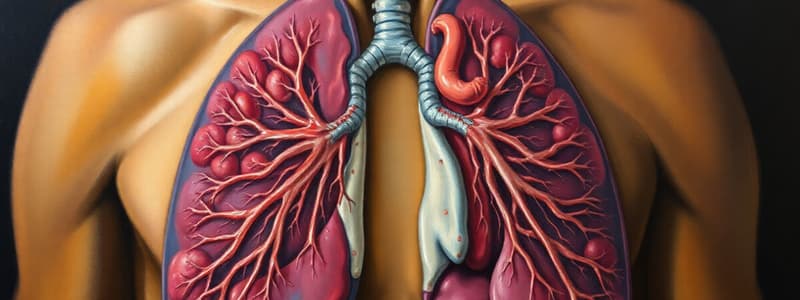
- Detail the functions and key features of the nose, mouth, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree (including alveoli).
- Distinguish between upper and lower respiratory structures, and the conducting and respiratory divisions; list respiratory structures in order from mouth/nose to alveoli.
- Explain the primary functions of the respiratory system.
- Identify and describe the two types of alveolar cells and their purposes.
- List receptors involved in regulating respiration.
- List primary and accessory respiratory muscles and their actions.
- State the structures of the respiratory membrane and factors facilitating gas exchange.
- Describe pleural cavities and membranes.
- Define pulmonary ventilation, eupnea, and hyperpnea.
- Explain the function of the vagus and phrenic nerves related to the respiratory system.
- Recall the location of respiratory centers.
- Describe the effects of sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation on bronchial tree and lungs.
Functions of the Respiratory System
- Moves air to and from lung exchange surfaces.
- Warms, filters, and humidifies inhaled air.
- Produces sound for verbal communication.
- Enables sense of smell (olfaction).
- Protects respiratory surfaces from irritants (dust, viruses, bacteria).
- Regulates blood volume, blood pressure, and body fluid pH.
Structures in the Upper vs. Lower Respiratory Tract
Upper Respiratory Tract
- Nose/Nasal Cavity: Passage for air, filtering, warming, and humidifying.
- Pharynx (Throat): Nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx
- Larynx (Voice Box): Houses vocal cords, produces sound.
- Cartilage: Thyroid, cricoid, epiglottis (unpaired); arytenoid, corniculate, cuneiform (paired).
- Function: Air intake, filtration, warming, sound production.
Lower Respiratory Tract
- Trachea: Cartilaginous tube conducting air from larynx to bronchi.
Distinction Between Conducting and Respiratory Divisions
Conducting Division
- Structures: Nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles (before respiratory bronchioles)
- Function: Warming, filtering, and humidifying air; no gas exchange.
Respiratory Division
- Structures: Respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveoli
- Function: Gas exchange (oxygen uptake, carbon dioxide release).
Respiratory Structures (Nostrils to Pulmonary Capillaries)
- Nostrils (External Nares): Air entry point.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.