Podcast
Questions and Answers
Match the following components with their functions in the respiratory system:
Match the following components with their functions in the respiratory system:
Match the following components with their locations in the respiratory system:
Match the following components with their locations in the respiratory system:
Match the following processes with their locations in the respiratory system:
Match the following processes with their locations in the respiratory system:
Match the following components with their characteristics in the respiratory system:
Match the following components with their characteristics in the respiratory system:
Match the following components with their roles in the circulatory system:
Match the following components with their roles in the circulatory system:
Match the following components with their roles in the respiratory system:
Match the following components with their roles in the respiratory system:
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
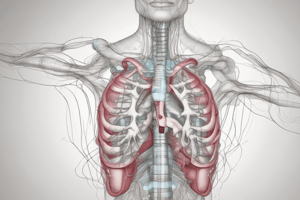
- La fonction principale de l'appareil respiratoire est de fournir du dioxygène à l'organisme et de le débarrasser du dioxyde de carbone.
- L'air entre dans le nez, traverse les voies nasales, le pharynx et le larynx, descend par la trachée et atteint les bronches, puis les bronchioles, aboutissant aux alvéoles.
- Les échanges gazeux entre l'air et le sang se produisent dans les alvéoles, où le dioxygène quitte l'air pour passer dans le sang et le dioxyde de carbone s'échappe du sang pour être rejeté dans l'air.
- Les alvéoles sont au nombre de 600 à 800 millions, ce qui permet une surface de contact totale entre l'air et le sang d'environ 100 mètres carrés, équivalent à la surface d'un terrain de tennis.
- Les échanges se font au niveau des capillaires, vaisseaux sanguins très fin qui tapissent la paroi des alvéoles.
- Le sang qui était pauvre en dioxygène à l'entrée des alvéoles en ressort enrichi, quitte les poumons par la veine pulmonaire pour aller irriguer les différents organes du corps.
- Le coeur agit comme une pompe, propulsant le sang oxygéné à travers le système sanguin pour distribuer le dioxygène à tous les organes et aux cellules.
- Au niveau des cellules des organes, les échanges inverse se produisent, où le dioxygène est consommé par la respiration cellulaire, libérant un déchet, le CO2, qui est récupéré par le sang et reconduit aux alvéoles pulmonaires.
- Le rôle du système respiratoire est donc d'une part de capter le dioxygène de l'atmosphère pour le distribuer dans le sang, et d'autre part d'extraire le CO2 du sang pour l'expulser dans l'atmosphère.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.