Podcast
Questions and Answers
Where does external respiration occur?
Where does external respiration occur?
- Lungs (correct)
- Liver
- Brain
- Kidneys
What is transported into an animal's lungs during external respiration?
What is transported into an animal's lungs during external respiration?
- Carbon Dioxide
- Hydrogen
- Oxygen (correct)
- Nitrogen
What process happens all over the body?
What process happens all over the body?
- Internal respiration (correct)
- External respiration
- Digestion
- Filtration
Which of the following is part of the respiratory system?
Which of the following is part of the respiratory system?
Which part of the respiratory system connects the nasal cavity to the larynx?
Which part of the respiratory system connects the nasal cavity to the larynx?
What is the function of the trachea?
What is the function of the trachea?
What are the tiny air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange occurs called?
What are the tiny air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange occurs called?
What is the name of the structure that connects the terminal bronchiole to the alveolus?
What is the name of the structure that connects the terminal bronchiole to the alveolus?
What is the primary function of the alveoli?
What is the primary function of the alveoli?
Which part of the respiratory system is referred to as the upper respiratory tract?
Which part of the respiratory system is referred to as the upper respiratory tract?
Which structure does the trachea connect to in the lower respiratory tract?
Which structure does the trachea connect to in the lower respiratory tract?
What happens to cartilage as the bronchi divide into smaller bronchioles?
What happens to cartilage as the bronchi divide into smaller bronchioles?
What is the collective term for the branching of the bronchi within the lungs?
What is the collective term for the branching of the bronchi within the lungs?
Which of the following is part of the upper respiratory tract?
Which of the following is part of the upper respiratory tract?
The lower respiratory tract extends from the trachea to which structures?
The lower respiratory tract extends from the trachea to which structures?
What creates a vacuum-like effect in the thorax?
What creates a vacuum-like effect in the thorax?
Which muscle flattens to increase space in the thoracic cavity during inhalation?
Which muscle flattens to increase space in the thoracic cavity during inhalation?
What signals when the lungs are full, preventing over-inflation?
What signals when the lungs are full, preventing over-inflation?
Which blood vessels contain chemical receptors that monitor pH, oxygen, and carbon dioxide levels?
Which blood vessels contain chemical receptors that monitor pH, oxygen, and carbon dioxide levels?
Which part of the brain alters the respiratory rate based on chemical receptor signals?
Which part of the brain alters the respiratory rate based on chemical receptor signals?
What substance is produced as a byproduct when an animal cannot obtain oxygen effectively?
What substance is produced as a byproduct when an animal cannot obtain oxygen effectively?
What condition is the body trying to correct when it increases the respiratory rate to expel carbon dioxide?
What condition is the body trying to correct when it increases the respiratory rate to expel carbon dioxide?
If an animal is unable to obtain oxygen effectively, what happens to the ADP?
If an animal is unable to obtain oxygen effectively, what happens to the ADP?
What is the role of mitochondria in cellular respiration?
What is the role of mitochondria in cellular respiration?
Which molecule is used as a fuel by mitochondria during cellular respiration?
Which molecule is used as a fuel by mitochondria during cellular respiration?
Why is oxygen essential for aerobic organisms?
Why is oxygen essential for aerobic organisms?
What happens to cells when they don't have oxygen?
What happens to cells when they don't have oxygen?
What does the respiratory center do if oxygen levels drop in the body?
What does the respiratory center do if oxygen levels drop in the body?
What happens if a patient's oxygen levels remain critically low?
What happens if a patient's oxygen levels remain critically low?
What triggers a reduction in the respiratory rate?
What triggers a reduction in the respiratory rate?
What is the typical respiratory rate for a dog?
What is the typical respiratory rate for a dog?
What is a potential unwanted side effect of an animal breathing 100% oxygen?
What is a potential unwanted side effect of an animal breathing 100% oxygen?
Which has a greater impact on an animal's respiratory drive?
Which has a greater impact on an animal's respiratory drive?
What is a potential effect of oxygen on the respiratory tract?
What is a potential effect of oxygen on the respiratory tract?
What should be used to humidify long-term oxygen supplementation?
What should be used to humidify long-term oxygen supplementation?
What is an important consideration when using oxygen tents or kennels?
What is an important consideration when using oxygen tents or kennels?
When is the preferable time to assess respiration in veterinary patients?
When is the preferable time to assess respiration in veterinary patients?
Which method of oxygen delivery is generally preferred?
Which method of oxygen delivery is generally preferred?
What is a crucial consideration when handling patients with respiratory compromise?
What is a crucial consideration when handling patients with respiratory compromise?
What should be done to a circle circuit before delivering oxygen?
What should be done to a circle circuit before delivering oxygen?
What is the purpose of the APL valve?
What is the purpose of the APL valve?
What is the recommended approach when handling a patient with respiratory issues?
What is the recommended approach when handling a patient with respiratory issues?
What might a patient in respiratory distress NOT do normally?
What might a patient in respiratory distress NOT do normally?
What physical sign might indicate respiratory distress in a patient?
What physical sign might indicate respiratory distress in a patient?
What is the purpose of using a well-fitting mask for oxygen delivery?
What is the purpose of using a well-fitting mask for oxygen delivery?
If a mask causes excessive stress, what is a better alternative for providing oxygen?
If a mask causes excessive stress, what is a better alternative for providing oxygen?
Which of the following is NOT a reliable indicator of true respiratory rate?
Which of the following is NOT a reliable indicator of true respiratory rate?
Flashcards
Upper Respiratory Tract
Upper Respiratory Tract
The part of the respiratory system from the nose to the larynx.
Lower Respiratory Tract
Lower Respiratory Tract
The part of the respiratory system from the trachea to the alveoli.
Larynx
Larynx
The organ connecting the upper and lower respiratory tracts.
Trachea
Trachea
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bronchi
Bronchi
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bronchioles
Bronchioles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bronchial Tree
Bronchial Tree
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveoli
Alveoli
Signup and view all the flashcards
External Respiration
External Respiration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Internal Respiration
Internal Respiration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Veterinary Respiration
Veterinary Respiration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Respiratory System Components
Respiratory System Components
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nasopharynx
Nasopharynx
Signup and view all the flashcards
Frontal Sinus
Frontal Sinus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nasal Cavity
Nasal Cavity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Negative Thoracic Pressure
Negative Thoracic Pressure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diaphragm's Role in Breathing
Diaphragm's Role in Breathing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intercostal Muscles Function
Intercostal Muscles Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Herring-Breuer Reflex
Herring-Breuer Reflex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chemical Receptors in Respiration
Chemical Receptors in Respiration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Medulla's Role in Breathing
Medulla's Role in Breathing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lactate and Poor Perfusion
Lactate and Poor Perfusion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Respiratory Compensation for Metabolic Acidosis
Respiratory Compensation for Metabolic Acidosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cellular Respiration
Cellular Respiration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Medulla's Role in Respiration
Medulla's Role in Respiration
Signup and view all the flashcards
ETCO2 During Weaning
ETCO2 During Weaning
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ventilator takeover
Ventilator takeover
Signup and view all the flashcards
Body's Response to Low Oxygen
Body's Response to Low Oxygen
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypoxia's Effect on Respiratory Center
Hypoxia's Effect on Respiratory Center
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chemoreceptor Function
Chemoreceptor Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Handling Respiratory Patients
Handling Respiratory Patients
Signup and view all the flashcards
Flushing Circle Circuits
Flushing Circle Circuits
Signup and view all the flashcards
APL Valve Function
APL Valve Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
APL Valve During Ventilation
APL Valve During Ventilation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Signs of Respiratory Distress
Signs of Respiratory Distress
Signup and view all the flashcards
Eating/Drinking and Respiratory Distress
Eating/Drinking and Respiratory Distress
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxygen Mask Fit
Oxygen Mask Fit
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alternative to Mask Oxygen
Alternative to Mask Oxygen
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxygen's effect on respiration
Oxygen's effect on respiration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Respiratory drive factors
Respiratory drive factors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxygen delivery methods
Oxygen delivery methods
Signup and view all the flashcards
Humidifying oxygen
Humidifying oxygen
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxygen Tents/Kennels
Oxygen Tents/Kennels
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxygen tent/kennel considerations
Oxygen tent/kennel considerations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Temperature control in O2 tents
Temperature control in O2 tents
Signup and view all the flashcards
Respiratory assessment
Respiratory assessment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Respiration involves both external and internal processes
- External respiration involves gas exchange between air and blood in the lungs
- Internal respiration involves gas exchange between blood and tissues throughout the body
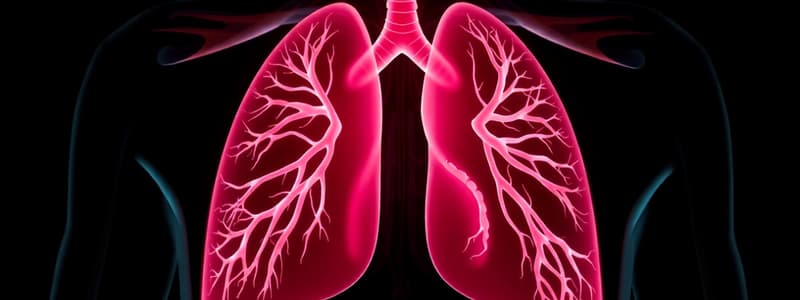
Anatomy of the Respiratory System
- The respiratory system is composed of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli
- The upper respiratory tract spans from the nose to the larynx
- The lower respiratory tract spans from the trachea to the alveoli
- The nose is divided into chambers with nasal turbinates lined with a ciliated mucous membrane, which warms, moistens, and filters incoming air
- The pharynx, or throat, connects the nose, mouth, eustachian tubes, esophagus, and larynx.
- Caudally, the pharynx divides into the esophagus and the larynx ventrally
- The larynx is a rigid structure of cartilage that forms the entrance to the lower respiratory tract
- The opening to the larynx is the epiglottis, which is depressed during intubation
- The larynx also functions as the voice box
- The trachea is made of incomplete C-shaped cartilage rings connected by fibrous tissue and smooth muscle and is lined with ciliated epithelium
- The trachea enters the thorax and divides into the left and right bronchi
Bronchial Tree
- The bronchi divide into bronchioles, ultimately reaching the terminal bronchiole and forming the bronchial tree
- As the bronchi divide, cartilage decreases and eventually disappears
Alveoli
- Alveolar ducts are located at the end of each terminal bronchiole
- Alveoli are vascularized air sacs where gas exchange occurs through diffusion
- Oxygen moves from the alveoli into the blood, while carbon dioxide moves from the blood into the alveoli for exhalation
Lungs
- The lungs are spongy organs in the thorax on either side of the mediastinum and connect to the trachea via the bronchi
- The right lung has four lobes: cranial, middle, accessory, and caudal
- The left lung has three lobes: cranial, middle, and caudal
- Fissures divide the lobes to increase surface area, maximize gas exchange, and isolate problem areas if necessary
- Each lobe has its own arterial and venous supply
- Pulmonary arteries branch into capillaries near the alveoli
- Oxygenated blood returns to the heart via capillaries to the pulmonary veins
Pleural Lining and Alveolar Surfactant
- The lungs are covered by the pleural lining to reduce friction
- Each alveolus is lined with a surfactant to prevent collapse during air movement
Breathing Mechanics
- Pressure in the thorax is negative compared to atmospheric pressure
- Inhalation is achieved by the movement of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, which expands the thoracic cavity and draws air into the lungs
- Exhalation occurs when the diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax, compressing the lungs and pushing air out
- The Herring-Breuer reflex signals when the lungs are full to prevent over-inflation
Cellular Respiration
- Mitochondria use glucose and oxygen to produce ATP, carbon dioxide, and water
- ATP is required for essential cellular processes
- The body maintains a narrow range for carbon dioxide levels (pH 7.4)
- Monitoring end-tidal carbon dioxide (ETCO₂) helps maintain correct body pH during anaesthesia and assessment of blood gasses
Control of Respiration
- Respiratory centres in the medulla oblongata control automatic and conscious respiration
- Mechanical stretch receptors set the volume of inflation and deflation in the lungs
- Chemical receptors in the carotid arteries and aorta monitor pH and the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide to adjust respiratory rate and depth
- If animals cannot obtain oxygen, ADP converts to ATP and lactic acid is produced as a by-product
- The medulla oblongata speeds up the repiratory rate to expel carbon dioxide during metabolic acidosis
- ETCO₂ levels are adjusted during ventilation weaning and initiation
Respiratory distress
- The body increases respiratory rate and depth should oxygen levels drop
- An increase in resiratory rate will trigger a reduction in respiratory rate by chemorecepters
- Carbon dioxide and hydrogen ion (H+) concentrations impact respiratory drive more than oxygen requirements
Nursing Considerations
- Respiratory rate, depth, and effort require assessment and observation
- Monitor respiration before attempting any nursing care
- Minimize stress when handling compromised patients to prevent potentially fatal decompensation
Respiratory Rates
- Dog: 10-30 breaths per minute (higher in small dogs)
- Cat: 20-30 breaths per minute
- Rabbit: 30-60 breaths per minute
Supplemental considerations
- Methods to deliver oxygen include: flow-by oxygen, cannulas, face masks, collars, tents/kennels and intubation; adopt the least stressful method
- Drying effects on respiratory tract can results in respiratory infections
- Use oxygen tents/kennels to reduce stress of patients, but monitor temperatures inside
- Flush circle circuits to ensure to residual agent is not present or volatile
- During the use of masks and circuits, APL valves must be managed correctly
- Steady-flow-by oxygen is better for patientes that masks causes stress
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.