Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the respiratory system?
What is the primary function of the respiratory system?
- To facilitate digestion
- To regulate body temperature
- To generate energy for the body
- To bring oxygen into the body and remove carbon dioxide (correct)
Which of the following is a characteristic of anaerobic respiration?
Which of the following is a characteristic of anaerobic respiration?
- It produces a large amount of ATP
- It requires oxygen to generate energy
- It occurs in the presence of oxygen
- It produces lactic acid, which can lead to muscle fatigue (correct)
During anaerobic respiration, what is the end product of glucose breakdown?
During anaerobic respiration, what is the end product of glucose breakdown?
- Carbon dioxide
- Pyruvate
- Lactic acid (correct)
- Oxygen
What is the name of the muscle that separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity and helps expand the lungs?
What is the name of the muscle that separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity and helps expand the lungs?
In which of the following situations is anaerobic respiration essential?
In which of the following situations is anaerobic respiration essential?
How many ATP molecules are generated during anaerobic respiration?
How many ATP molecules are generated during anaerobic respiration?
What is the primary location where glycolysis takes place?
What is the primary location where glycolysis takes place?
What is the byproduct of the electron transport chain in cellular respiration?
What is the byproduct of the electron transport chain in cellular respiration?
What is the purpose of the Krebs cycle in cellular respiration?
What is the purpose of the Krebs cycle in cellular respiration?
Why is cellular respiration important in plants?
Why is cellular respiration important in plants?
What is unique about the electron transport chain in plants compared to animals?
What is unique about the electron transport chain in plants compared to animals?
How many ATP molecules are generated during oxidative phosphorylation?
How many ATP molecules are generated during oxidative phosphorylation?
Study Notes
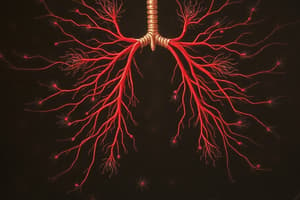
Respiratory System
- The respiratory system is a biological system that brings oxygen into the body and removes carbon dioxide
- Consists of:
- Nose or mouth: air enters the body
- Trachea (windpipe): air passes through
- Bronchi: air tubes that branch off into smaller tubes
- Bronchioles: smaller air tubes that lead to alveoli
- Alveoli: tiny air sacs where gas exchange occurs
- Diaphragm: muscle that separates chest cavity from abdominal cavity and helps expand lungs
- Lungs: organs where gas exchange occurs
Anaerobic Respiration
Definition
- Anaerobic respiration: a metabolic process that generates energy without using oxygen
- Occurs in the absence of oxygen or when oxygen is scarce
Importance
- Essential for muscles during high-intensity, short-duration activities (e.g., sprinting)
- Helps muscles recover from intense activity
- Allows some organisms to survive in low-oxygen environments
Process
- Glucose (C6H12O6) broken down into lactic acid (C3H6O3)
- Glycolysis: glucose converted into pyruvate (C3H4O3)
- Fermentation: pyruvate converted into lactic acid
- Energy generated: 2 ATP (net gain)
Characteristics
- Less efficient than aerobic respiration (2 ATP vs. 36-38 ATP)
- Produces lactic acid, which can lead to muscle fatigue and soreness
- Does not require oxygen, but still releases energy
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Learn about the human respiratory system, including its components and functions. Also, understand anaerobic respiration, a metabolic process that generates energy without oxygen, its importance, process, and characteristics.