Podcast
Questions and Answers
What are the three main stages of the process of respiration?
What are the three main stages of the process of respiration?
- Inhalation, transport, exhalation (correct)
- Diffusion, absorption, exhalation
- Inhalation, diffusion, exhalation
- Inhalation, circulation, excretion
Where does oxygen enter the bloodstream during respiration?
Where does oxygen enter the bloodstream during respiration?
- Through the stomach lining
- Through the large intestine
- Through the skin
- Through alveoli in the lungs (correct)
What drives the movement of gases towards the alveoli in the lungs?
What drives the movement of gases towards the alveoli in the lungs?
- High CO2 levels in pulmonary capillaries compared to alveolar air (correct)
- High O2 levels in pulmonary capillaries compared to alveolar air
- Low CO2 levels in pulmonary capillaries compared to alveolar air
- Equal levels of CO2 in pulmonary capillaries and alveolar air
Which type of respiration requires molecular oxygen (O2) for energy transformation?
Which type of respiration requires molecular oxygen (O2) for energy transformation?
During which stage of respiration is carbon dioxide (CO2) expelled from the body?
During which stage of respiration is carbon dioxide (CO2) expelled from the body?
What is the role of anaerobic respiration in the process of respiration?
What is the role of anaerobic respiration in the process of respiration?
What is the first stage of cellular respiration?
What is the first stage of cellular respiration?
Which stage of cellular respiration produces the most ATP from organic nutrients?
Which stage of cellular respiration produces the most ATP from organic nutrients?
Which of the following is a byproduct of anaerobic respiration?
Which of the following is a byproduct of anaerobic respiration?
Which organ is NOT part of the human respiratory system?
Which organ is NOT part of the human respiratory system?
What is the primary function of the human respiratory system?
What is the primary function of the human respiratory system?
Which type of respiration is more efficient in terms of ATP production?
Which type of respiration is more efficient in terms of ATP production?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Respiration
Respiration is a vital biological process essential for life as it provides energy through the breakdown of nutrients. It involves the interplay of several processes, including gas exchange between organisms and their surroundings, transport of gases, cellular respiration, and photosynthesis. In this article, we will explore the mechanism of respiration, its classification into aerobic and anaerobic forms, and its role in the human respiratory system.
Mechanism of Respiration
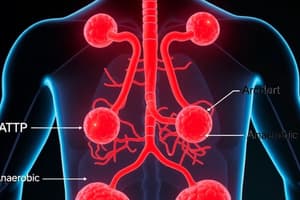
The process of respiration can be divided into three main stages: inhalation, during which air enters the lungs; transport, where oxygen (O2) from the air travels to cells and carbon dioxide (CO2) moves out; and exhalation, when CO2 is expelled from the body. Oxygen enters the bloodstream via alveoli, small sacs in the lungs, while carbon dioxide escapes through the mucosal membranes of the nose and mouth. The exchange of these gases occurs due to pressure differences across the walls of the alveoli: pulmonary capillaries have higher CO2 levels than alveolar air, driving gas movement towards the alveoli.
Types of Respiration
Respiration is classified based on whether oxygen is required for the process. There are two types: aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Aerobic Respiration
Aerobic respiration requires molecular oxygen (O2) for the transformation of potential energy stored in nutrients into the energy currency of a cell, which is adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The process occurs in three stages: glycolysis, which generates ATP; the citric acid cycle, which releases more ATP and generates reducing power; and electron transport chain, which produces most of the ATP from organic nutrients.
Anaerobic Respiration
Anaerobic respiration does not require oxygen and occurs in the absence of oxygen or under conditions in which oxygen is in short supply. It is less efficient than aerobic respiration as it only generates a small amount of ATP and produces byproducts like lactic acid, which can be detrimental to cells.
Human Respiratory System
The human respiratory system is responsible for respiration and includes the following organs: nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, and lungs. Air enters through the nose or mouth, travels down the trachea and into the lungs, where it is exchanged with CO2 and O2, and then is expelled through the nose or mouth.
In conclusion, respiration is a critical biological process that provides energy for cellular activities. It involves the exchange of gases between organisms and their surroundings and the conversion of nutrients into ATP. The human respiratory system enables this process, facilitating the intake of oxygen and the release of carbon dioxide.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.