Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the main structural difference between bronchi and bronchioles?
What is the main structural difference between bronchi and bronchioles?
- Bronchi have C-shaped cartilage rings, while bronchioles do not contain cartilage. (correct)
- Bronchi are made of smooth muscle, while bronchioles have C-shaped cartilage rings.
- Bronchi are narrow airways, while bronchioles are wide and contain cartilage.
- Bronchi have elastin, while bronchioles are structured with cartilage rings.
What is the function of cilia and mucus in the airways?
What is the function of cilia and mucus in the airways?
- To absorb oxygen from the air
- To regulate the flow of air in the lungs
- To trap and remove dust and particles from the airways (correct)
- To help expand the bronchioles
Which lung has three lobes?
Which lung has three lobes?
- The left lung
- The right lung (correct)
- Neither lung has three lobes
- Both lungs have three lobes
What occupies the space between the two lungs in the chest cavity?
What occupies the space between the two lungs in the chest cavity?
Which component covers both the surface of the lungs and the inside of the chest?
Which component covers both the surface of the lungs and the inside of the chest?
What allows bronchioles to control the flow of air in the lungs?
What allows bronchioles to control the flow of air in the lungs?
What forms more of the structure in bronchioles compared to bronchi?
What forms more of the structure in bronchioles compared to bronchi?
What is the primary function of the alveoli?
What is the primary function of the alveoli?
Which of the following statements about the structure of the alveoli is correct?
Which of the following statements about the structure of the alveoli is correct?
What is the role of the pleural fluid?
What is the role of the pleural fluid?
Which of the following structures is directly connected to the alveoli?
Which of the following structures is directly connected to the alveoli?
What is the primary purpose of the network of blood capillaries surrounding the alveoli?
What is the primary purpose of the network of blood capillaries surrounding the alveoli?
Which of the following statements about gas exchange in the lungs is correct?
Which of the following statements about gas exchange in the lungs is correct?
What is the significance of the alveoli being the functional units of the lungs?
What is the significance of the alveoli being the functional units of the lungs?
Study Notes
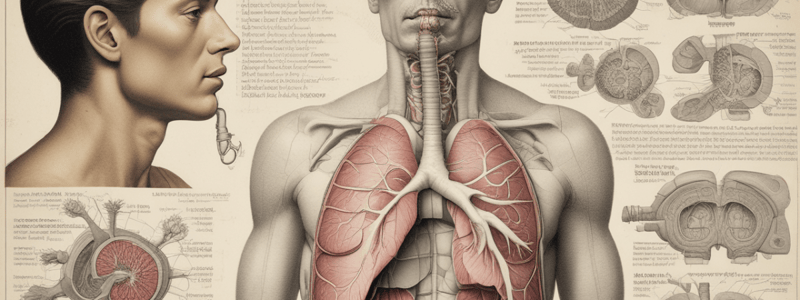
The Respiratory System
- The respiratory system allows for gas exchange between the body and the environment.
Bronchi
- The structure of the bronchi is similar to the trachea, with C-shaped cartilage rings.
- As the bronchi get smaller, the cartilage is more spread out, and smooth muscle and elastin form more of the structure.
- Cilia and mucus work together to trap and remove dust and other particles from the airways.
Bronchioles
- Bronchioles are smaller airways that form when the tertiary bronchi divide.
- They continue to split until they end in millions of terminal bronchioles.
- Unlike bronchi, bronchioles do not contain cartilage; instead, they are made of smooth muscle and elastin.
- This allows the bronchioles to control the flow of air in the lungs, expanding when the body needs more oxygen.
- Cilia and mucus are also present in the bronchioles, protecting the lungs from contaminants.
Lungs
- The two lungs take up the whole of the chest cavity, except for the mediastinum, which is occupied by the heart and blood vessels.
- Each lung is divided into lobes, with the left lung having two lobes and the right lung having three.
- The pleura, a membrane, covers the surface of the lungs (visceral pleura) and also lines the inside of the chest (parietal pleura).
- A thin layer of pleural fluid is between the two layers of membrane, holding the lungs against the inside of the chest wall and allowing them to slide along the wall when breathing.
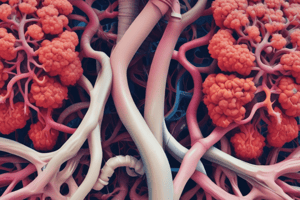
Alveoli
- The smallest bronchioles open into clusters of tiny air sacs called alveoli.
- Each alveolus has a wall that is only one cell thick and is surrounded by a network of blood capillaries.
- This is where gases move between the blood in the capillaries and the air in the alveoli.
- The alveoli are the functional units of the lungs, allowing for gaseous exchange between the airways and the blood.
- Oxygen passes from the airways into the blood, and carbon dioxide passes from the blood into the airways.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Learn about the structure and function of the bronchi and bronchioles in the respiratory system. Understand how the cartilage, smooth muscle, elastin, cilia, and mucus contribute to the process of gas exchange. Explore how tertiary bronchi divide to form bronchioles.