Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the conducting zone?
What is the primary function of the conducting zone?
- To produce sound for vocal resonance
- To filter out particles from inspired air
- To transport gas in and out of the lungs (correct)
- To facilitate gas exchange
What is the name of the structure that contains the vocal cords?
What is the name of the structure that contains the vocal cords?
- Trachea
- Pharynx
- Larynx (correct)
- Bronchi
Why do physiotherapists encourage clients to breathe through their nose?
Why do physiotherapists encourage clients to breathe through their nose?
- Because of its functions of filtering, warming, and humidifying the air (correct)
- To reduce breathlessness
- To improve vocal resonance
- To facilitate gas exchange
What is the main purpose of the respiratory zone?
What is the main purpose of the respiratory zone?
What is the name of the tube-like structure that connects the larynx to the bronchi?
What is the name of the tube-like structure that connects the larynx to the bronchi?
What is the common passageway for both food and air?
What is the common passageway for both food and air?
What is the angle of branching of the right main bronchus?
What is the angle of branching of the right main bronchus?
What type of muscle is present in the bronchioles?
What type of muscle is present in the bronchioles?
What is the purpose of the cartilaginous rings in the trachea?
What is the purpose of the cartilaginous rings in the trachea?
What are the tiny sacs responsible for gas exchange between the lungs and the bloodstream?
What are the tiny sacs responsible for gas exchange between the lungs and the bloodstream?
How many functional zones does the respiratory system have?
How many functional zones does the respiratory system have?
What is the name of the upper part of the respiratory system?
What is the name of the upper part of the respiratory system?
What is the name of the process by which air enters the alveoli through pathways that bypass the normal airways?
What is the name of the process by which air enters the alveoli through pathways that bypass the normal airways?
What is the average number of pores of Kohn present in each adult alveolus?
What is the average number of pores of Kohn present in each adult alveolus?
What is the primary function of the alveolar ducts?
What is the primary function of the alveolar ducts?
What is the name of the membrane where perfusion occurs?
What is the name of the membrane where perfusion occurs?
What is the branching pattern of a person's airway called?
What is the branching pattern of a person's airway called?
What is the purpose of collateral ventilation?
What is the purpose of collateral ventilation?
At what age do Pores of Kohn typically develop?
At what age do Pores of Kohn typically develop?
What is the effect of age on the number of collateral channels in humans?
What is the effect of age on the number of collateral channels in humans?
What is the approximate diameter of an alveolar sac?
What is the approximate diameter of an alveolar sac?
What is the cross-sectional area of the lungs?
What is the cross-sectional area of the lungs?
How many generations of airways are typically cleared when coughing?
How many generations of airways are typically cleared when coughing?
What is the shape of the lungs?
What is the shape of the lungs?
What holds the lungs in position?
What holds the lungs in position?
How many lobes does the right lung have?
How many lobes does the right lung have?
What is the purpose of the pleural cavity?
What is the purpose of the pleural cavity?
Why is it important to understand the anatomy of the lungs?
Why is it important to understand the anatomy of the lungs?
Which muscles are recruited to assist with inspiration during increased work of breathing?
Which muscles are recruited to assist with inspiration during increased work of breathing?
What is the result of quiet breathing during expiration?
What is the result of quiet breathing during expiration?
Which nerve innervates the diaphragm?
Which nerve innervates the diaphragm?
What is the spinal level that innervates the diaphragm?
What is the spinal level that innervates the diaphragm?
Which muscles contribute to expiration?
Which muscles contribute to expiration?
What is the purpose of the handy mnemonic 'C3, 4, 5, keeps the diaphragm alive'?
What is the purpose of the handy mnemonic 'C3, 4, 5, keeps the diaphragm alive'?
What is the result of a spinal cord injury at the level of C5?
What is the result of a spinal cord injury at the level of C5?
What is true about inspiration?
What is true about inspiration?
Which intercostal muscles contribute to inspiration?
Which intercostal muscles contribute to inspiration?
What is the main muscle of respiration?
What is the main muscle of respiration?
What is the role of the internal intercostal muscle during increased work of breathing?
What is the role of the internal intercostal muscle during increased work of breathing?
What is the purpose of the pleural fluid in the pleural cavity?
What is the purpose of the pleural fluid in the pleural cavity?
What is the pressure in the pleural cavity during normal breathing?
What is the pressure in the pleural cavity during normal breathing?
What is the role of the respiratory muscles in inspiration and expiration?
What is the role of the respiratory muscles in inspiration and expiration?
What is the result of a weak respiratory muscle?
What is the result of a weak respiratory muscle?
What is the purpose of inspiratory muscle training?
What is the purpose of inspiratory muscle training?
What is the unit of respiration being referred to throughout this section?
What is the unit of respiration being referred to throughout this section?
What is the lining of the rib cage?
What is the lining of the rib cage?
What is the direction of air movement during respiration?
What is the direction of air movement during respiration?
What is the natural tendency of the chest wall and lungs?
What is the natural tendency of the chest wall and lungs?
What is the primary function of the costovertebral and costotransverse joints?
What is the primary function of the costovertebral and costotransverse joints?
What is the term used to describe the movement of the ribs during inspiration?
What is the term used to describe the movement of the ribs during inspiration?
Which of the following is NOT a condition that can impact involuntary breathing?
Which of the following is NOT a condition that can impact involuntary breathing?
What is the principal muscle of inspiration?
What is the principal muscle of inspiration?
What is the stimulus for breathing in involuntary breathing?
What is the stimulus for breathing in involuntary breathing?
Which of the following is a type of voluntary breathing control?
Which of the following is a type of voluntary breathing control?
What is the purpose of the respiratory control centers in the brain?
What is the purpose of the respiratory control centers in the brain?
Which of the following muscles is responsible forexpiration?
Which of the following muscles is responsible forexpiration?
What is the term used to describe the movement of the sternum during inspiration?
What is the term used to describe the movement of the sternum during inspiration?
What is the primary function of the diaphragm?
What is the primary function of the diaphragm?
What is the main difference between lung volumes and lung capacities?
What is the main difference between lung volumes and lung capacities?
What is functional residual capacity (FRC) of the lungs?
What is functional residual capacity (FRC) of the lungs?
Which of the following factors affects lung volumes?
Which of the following factors affects lung volumes?
What is the purpose of understanding lung volumes and lung capacities in physiotherapy?
What is the purpose of understanding lung volumes and lung capacities in physiotherapy?
What is the outward spring of the rib cage responsible for?
What is the outward spring of the rib cage responsible for?
What is the name of the graph that demonstrates different variables related to inspiration and expiration?
What is the name of the graph that demonstrates different variables related to inspiration and expiration?
Why do people living at altitude have larger lung volumes?
Why do people living at altitude have larger lung volumes?
What is the effect of aging on lung volumes?
What is the effect of aging on lung volumes?
What is the difference between tidal volume and inspiratory reserve volume?
What is the difference between tidal volume and inspiratory reserve volume?
What is the relationship between lung volumes and surfactant?
What is the relationship between lung volumes and surfactant?
What is the result of the diaphragm contracting during inspiration?
What is the result of the diaphragm contracting during inspiration?
What is the purpose of accessory muscles in pulmonary ventilation?
What is the purpose of accessory muscles in pulmonary ventilation?
What is airway compliance?
What is airway compliance?
What contributes to the elastic recoil of the lungs?
What contributes to the elastic recoil of the lungs?
What is the effect of surfactant on pulmonary compliance?
What is the effect of surfactant on pulmonary compliance?
What is hysteresis?
What is hysteresis?
What is the purpose of the chest wall in pulmonary ventilation?
What is the purpose of the chest wall in pulmonary ventilation?
What happens to the intrapulmonary pressure at the end of inspiration?
What happens to the intrapulmonary pressure at the end of inspiration?
What is the result of the recoil of the lungs and chest wall at the end of inspiration?
What is the result of the recoil of the lungs and chest wall at the end of inspiration?
Why is pulmonary surfactant essential for efficient gas exchange in the lungs?
Why is pulmonary surfactant essential for efficient gas exchange in the lungs?
Study Notes
The Respiratory System: Anatomy and Physiology
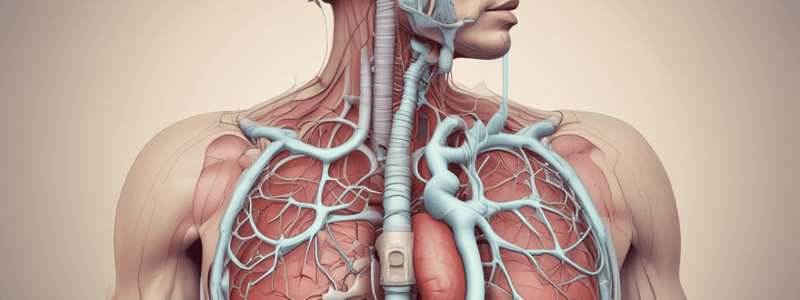
- The respiratory system is divided into two functional zones: the conducting zone and the respiratory zone.
Conducting Zone
- The conducting zone transports gas in and out of the lungs.
- It consists of the nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles.
- The nose:
- Filters, warms, and humidifies the air during inspiration.
- Has multiple functions, including olfaction and vocal resonance.
- The pharynx:
- Is the common passageway for food and air.
- Connects the nasal cavity and mouth to the larynx.
- The larynx:
- Contains the vocal cords.
- Is located between the pharynx and trachea.
- The trachea:
- Is a tube-like structure that connects the larynx to the bronchi.
- Composed of cartilaginous rings that provide structural support.
- The bronchial tree:
- Is the branching pattern of the airway.
- Has approximately 23 generations of branching.
- Features of note:
- The right main bronchus is more vertical than the left.
- Bronchioles lack cartilage but have smooth muscles.
Respiratory Zone
- The respiratory zone is responsible for gas exchange.
- It includes the respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, and alveoli.
- Alveoli:
- Are tiny sacs responsible for gas exchange between the lungs and bloodstream.
- Have a liquid membrane where perfusion occurs.
- Are bunched together, forming a "grape-like" structure.
Collateral Ventilation
- Is the ventilation of alveolar structures via pathways that bypass the normal airways in the lungs.
- Occurs when the airways are restricted or obstructed.
- Enables the preservation of ventilation and gas exchange in distal parts of the lung.
The Lungs
- Are cone-shaped and positioned vertically in the chest cage, around the heart.
- Are held in position by negative pressure between the pleural spaces.
- Have a membrane called the visceral pleura, which covers the surface of the lungs.
Clinical Note
- Understanding the anatomy of the lungs is crucial for clinical reasoning and auscultation (listening to lung sounds with a stethoscope).
Respiratory Mechanics
- The biomechanics of the respiratory system is essential for understanding respiration.
- The morphology of the joints in the rib cage, the origin and insertions of muscles, and their planes of action contribute to understanding normal function.
- The movement of the rib cage:
- Moves like a bucket handle during inspiration.
- Moves like a pump handle during inspiration.
Muscles of Respiration
- The principal muscles of inspiration are the external intercostals, the interchondral part of the internal intercostals, and the diaphragm.
- Accessory muscles that contribute to inspiration include the sternocleidomastoid and scalenes.
- Muscles of expiration:
- Quiet breathing is a passive process, resulting from the recoil of the lungs.
- Active expiration occurs through the recruitment of internal intercostal muscles and abdominal muscles.
Innervation of the Diaphragm
- The phrenic nerve innervates the diaphragm.
- The phrenic nerve originates from the anterior rami of the C3-C5 roots.
Respiratory Pathways
- The neural pathways to the respiratory muscles operate similarly to all other neural pathways.
- Conditions that impact the neural pathways to respiratory muscle include:
- Guillain-Barré syndrome
- Spinal cord injury
- Poliomyelitis
Clinical Note
-
As a physiotherapist, consider the muscles of respiration as trainable muscles that can be strengthened.
-
Inspiratory muscle training can be used to improve respiratory function.### Pulmonary Ventilation
-
Three air pressures are involved in pulmonary ventilation: intrapulmonary pressure (within the lungs), intrapleural pressure (in the pleural cavity), and atmospheric pressure (surrounding air).
-
Air moves from high pressure to low pressure, and this pressure gradient drives air in and out of the lungs.
-
The chest wall and lungs have natural tendencies: the chest wall pulls outwards, and the lungs tend to pull inwards and collapse, resulting in a slightly negative pressure (-4cm of water) in the intra-pleural space.
-
At the beginning of inspiration, the intrapulmonary pressure is equal to atmospheric pressure (0).
-
When the diaphragm contracts, it creates a negative intrapulmonary pressure, allowing air to enter the lungs.
-
During inspiration, the intra-pleural pressure becomes more negative (-7), and the chest wall expands.
-
At the end of inspiration, the intrapulmonary pressure is higher than atmospheric pressure, and air moves out of the lungs.
Muscle Movement and Rib Expansion
- Muscle movement and rib expansion change the pressures in the lungs during breathing.
- Accessory muscles are used to increase thoracic volume.
Airway Compliance
- Compliance refers to how easily air can move in and out of the lungs.
- It is calculated as the change in volume over the change in pressure.
- High compliance means a large change in volume for a small change in pressure; low compliance means a small change in volume for a large change in pressure.
- Factors contributing to compliance include:
- Elastic recoil of the lungs (due to elastin fibers and surface tension)
- Recoil of the chest wall (pulling outwards)
- A compliant lung is like inflating a thin balloon, whereas a poorly compliant lung is like inflating a thick balloon.
Surfactant
- Surfactant is a surface-active lipoprotein complex that reduces the surface tension of alveoli.
- It decreases elasticity and increases pulmonary compliance.
- Surfactant is essential for efficient gas exchange in the lungs and is important for understanding lung function and respiratory diseases.
Hysteresis
- Hysteresis is the energy applied to the lung during inspiration that is not recovered in expiration.
- It is a phenomenon that occurs due to the surface tension that needs to be overcome during inspiration.
- Hysteresis is calculated by plotting change in volume over change in pressure.
Lung Volumes and Capacities
- Lung volumes refer to the amount of air contained within specific parts of the respiratory system.
- Lung capacities refer to the sum of two or more lung volumes.
- Important lung volumes and capacities include:
- Tidal volume (TV)
- Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
- Expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
- Residual volume (RV)
- Functional residual capacity (FRC)
- Vital capacity (VC)
- Total lung capacity (TLC)
Factors Affecting Lung Volumes
- Body size: taller people tend to have larger lung volumes, while obese people have smaller lung volumes.
- Age: lung tissue loses elasticity with age, leading to a reduction in lung volume.
- Gender: men tend to have larger lung volumes due to their physical size.
- Muscle training: inspiratory muscle training increases lung volumes.
- Respiratory disease: may lead to an increase or decrease in lung volumes.
- Altitude: people living at high altitude have larger lung volumes to increase gas exchange.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Revise the anatomy and physiology of the respiratory system from a physiotherapy perspective. This quiz covers the upper respiratory tract, including the sinuses, nasal cavity, pharynx, and glottis.