Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of alveoli in the respiratory system?
What is the primary function of alveoli in the respiratory system?
- To transport oxygen to the heart
- To filter blood in the lungs
- To connect the trachea to the bronchi
- To facilitate gas exchange (correct)
Which component of the respiratory system is primarily responsible for regulating air pressure during breathing?
Which component of the respiratory system is primarily responsible for regulating air pressure during breathing?
- Diaphragm (correct)
- Ribs
- Heart
- Trachea
What process allows for the movement of gases between the alveoli and blood capillaries?
What process allows for the movement of gases between the alveoli and blood capillaries?
- Filtration
- Diffusion (correct)
- Convection
- Osmosis
How do red blood cells assist in the respiratory process?
How do red blood cells assist in the respiratory process?
Which type of white blood cell is primarily involved in responding to inflammation?
Which type of white blood cell is primarily involved in responding to inflammation?
What is the role of the heart in the respiratory system?
What is the role of the heart in the respiratory system?
What is the characteristic of a solute in a solution?
What is the characteristic of a solute in a solution?
Which muscle groups aid in the movement of the chest during respiratory actions?
Which muscle groups aid in the movement of the chest during respiratory actions?
What defines a solution in the context of mixing substances?
What defines a solution in the context of mixing substances?
Which of the following statements about the respiratory system is false?
Which of the following statements about the respiratory system is false?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Respiration
- Respiration is a series of chemical reactions that break down glucose to release energy.
- Aerobic respiration requires oxygen and is essential for generating substantial energy in cells.
The Human Respiratory System
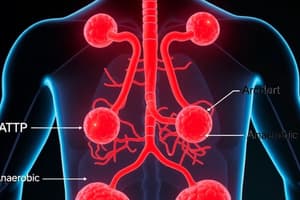
- Alveoli are small air sacs in the lungs responsible for gas exchange, providing a large surface area.
- The trachea, or windpipe, serves as a primary airway in the respiratory system.
- Bronchioles are small branching tubes within the lungs contributing to airflow distribution.
- Ribs and intercostal muscles facilitate the expansion and contraction of the thoracic cavity during breathing.
- The diaphragm is a major muscle that separates the lungs from the abdominal cavity, playing a crucial role in inhalation and exhalation.
- The heart functions as a pump, circulating blood throughout the body via arteries and veins.
Gas Exchange
- Gas exchange refers to the transfer of oxygen from the lungs to the bloodstream and the removal of carbon dioxide from the blood to the lungs.
- This process occurs in the alveoli, characterized by thin walls and a network of blood capillaries that enhance the efficiency of gas exchange.
Diffusion
- Diffusion is the natural movement of gases between the alveoli and capillaries in the lungs, occurring without physical effort from the body.
Blood Components
- Red blood cells transport oxygen throughout the body and are involved in carbon dioxide removal.
- White blood cells are diverse in types, each with specific roles in the immune response.
Function of White Blood Cells
- Monocytes respond to inflammation and assist in immune function.
- Neutrophils play a role in recruiting other immune cells to sites of infection.
- Lymphocytes are vital for the adaptive immune system, including T-cells and B-cells.
- Eosinophils help recruit immune cells to inflammatory sites, particularly in allergic responses.
- Basophils release histamines, contributing to inflammation during allergic reactions.
Mixing and Solutions
- Mixing example: Ground coffee (solute) combined with milk (solvent) creates a solution, hot chocolate.
- Definitions:
- Solution: A homogeneous mixture of solute and solvent.
- Solute: The substance that is dissolved.
- Solvent: The liquid in which the solute is dissolved.
- Dissolve: The process of a substance integrating into a liquid.
- Soluble: Describes a substance capable of dissolving in a solvent.
- Insoluble: Describes a substance that cannot dissolve in a solvent.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.