Podcast
Questions and Answers
What adaptation must a baby make at the level of the lungs for gas exchange after birth?
What adaptation must a baby make at the level of the lungs for gas exchange after birth?
- Reliance on placental oxygen delivery
- Increased fetal lung fluid retention
- Breathing through adaptation (correct)
- Decreased surfactant production
What is the direct result of the first breaths of life with regard to the heart?
What is the direct result of the first breaths of life with regard to the heart?
- Opening of the foramen ovale
- Increased pressure in the left atrium (correct)
- Increased pressure in the right atrium
- Closure of the ductus venosus before other shunts
What stimulates the respiratory center after birth?
What stimulates the respiratory center after birth?
- Chemical, thermal, and mechanical changes (correct)
- Increased maternal antibody transfer
- Decreased air flow
- Retention of fetal lung fluid
Which statement is correct regarding breast milk production and ejection?
Which statement is correct regarding breast milk production and ejection?
What is the primary role of colostrum in newborn nutrition?
What is the primary role of colostrum in newborn nutrition?
Which reflex prevents choking from solids in newborns?
Which reflex prevents choking from solids in newborns?
When does the rooting reflex occur?
When does the rooting reflex occur?
What anatomical feature aids neonatal nasal breathing?
What anatomical feature aids neonatal nasal breathing?
Which statement is true regarding "tongue thrust habit"?
Which statement is true regarding "tongue thrust habit"?
At what time does the swallowing reflex occur during feeding?
At what time does the swallowing reflex occur during feeding?
What is the origin of Epstein pearls?
What is the origin of Epstein pearls?
What is the typical management for Bohn's nodules in newborns?
What is the typical management for Bohn's nodules in newborns?
What characterizes natal teeth?
What characterizes natal teeth?
What oral anomaly is caused by a shortened, thickened, or wrongly placed frenulum?
What oral anomaly is caused by a shortened, thickened, or wrongly placed frenulum?
What is a possible intervention for severe cases of tongue-tie?
What is a possible intervention for severe cases of tongue-tie?
What is the primary source of initial oral microbiota for a newborn?
What is the primary source of initial oral microbiota for a newborn?
Which bacterial species is among the first to colonize the oral cavity?
Which bacterial species is among the first to colonize the oral cavity?
When do infants develop an acute sense of taste?
When do infants develop an acute sense of taste?
What is the typical age range when saliva glands function increases (before teething)?
What is the typical age range when saliva glands function increases (before teething)?
When does lip closure typically develop, leading to mature muscular reflexes that reduce drooling?
When does lip closure typically develop, leading to mature muscular reflexes that reduce drooling?
At what time does the formation of the mandible begin in utero?
At what time does the formation of the mandible begin in utero?
At what time during postnatal life does the mandible grow most, especially in the vertical dimension?
At what time during postnatal life does the mandible grow most, especially in the vertical dimension?
What characterizes the oral cavity of an infant?
What characterizes the oral cavity of an infant?
When does the back of the tongue raise to burst air at the back of the mouth during speech?
When does the back of the tongue raise to burst air at the back of the mouth during speech?
Until about what age does the speech requires no teeth?
Until about what age does the speech requires no teeth?
What molecule needs to function for a tooth eruption?
What molecule needs to function for a tooth eruption?
What is secreted by osteoblasts that is needed for a tooth eruption?
What is secreted by osteoblasts that is needed for a tooth eruption?
For what duration of age is the tooth eruption of incisors expected to appear?
For what duration of age is the tooth eruption of incisors expected to appear?
At what time does the tooth eruption for first molars happen?
At what time does the tooth eruption for first molars happen?
At what time does the biting force increases due to tooth eruption?
At what time does the biting force increases due to tooth eruption?
What can cause dental anomalies?
What can cause dental anomalies?
What is a possible result of severe dental anomalies with misalignments or malocclusion?
What is a possible result of severe dental anomalies with misalignments or malocclusion?
Which genetic disorder can lead to speech disorder due to small jaws and periodontal diseases?
Which genetic disorder can lead to speech disorder due to small jaws and periodontal diseases?
The tongue moves toward the lips leading to malocclusion known as:
The tongue moves toward the lips leading to malocclusion known as:
What is one of the neurological causes for malocclusion?
What is one of the neurological causes for malocclusion?
What problems does a thumb-sucking habit after three years cause for the patient?
What problems does a thumb-sucking habit after three years cause for the patient?
What is a effect does tongue thrust have?
What is a effect does tongue thrust have?
What is one of the main causes by Malnutrition?
What is one of the main causes by Malnutrition?
Besides digit sucking or tongue tie, what is another cause that that Malocclusions?
Besides digit sucking or tongue tie, what is another cause that that Malocclusions?
If a speech difficulty presents as a Lisp, caused by dental or skeletal malformation, what sound would be affected?
If a speech difficulty presents as a Lisp, caused by dental or skeletal malformation, what sound would be affected?
What sounds have difficulties because of Irregular incisors, especially lingual position of maxillary incisors?
What sounds have difficulties because of Irregular incisors, especially lingual position of maxillary incisors?
Flashcards
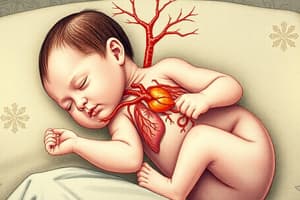
Neonatal Adaptation: Gas Exchange
Neonatal Adaptation: Gas Exchange
In newborns, the lungs adapt for gas exchange by breathing, which involves clearance of fetal lung fluid, surfactant secretion and pulmonary vasodilation.
Fetal Circulatory Shunts
Fetal Circulatory Shunts
At birth, these close due to increased oxygen and pressure changes, redirecting blood flow, for example, the ductus arteriosus becomes the ligamentum arteriosum.
Colostrum Importance
Colostrum Importance
It is rich provides essential nutrients, antibodies, and immune factors, supporting the newborn's immune system and gut health.
Benefits of Breastfeeding for Oral Health
Benefits of Breastfeeding for Oral Health
Signup and view all the flashcards
Newborn Persistent Reflexes
Newborn Persistent Reflexes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Infant Airways
Infant Airways
Signup and view all the flashcards
Swallowing Reflex
Swallowing Reflex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neonatal/Primitive Reflexes
Neonatal/Primitive Reflexes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Extrusion Reflex
Extrusion Reflex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rooting, Suckling, Swallowing Reflexes
Rooting, Suckling, Swallowing Reflexes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Infantile Swallowing and Breathing
Infantile Swallowing and Breathing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oral Cysts in Neonates
Oral Cysts in Neonates
Signup and view all the flashcards
Natal Teeth
Natal Teeth
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tongue-Tie (Ankyloglossia)
Tongue-Tie (Ankyloglossia)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oral Microbiota
Oral Microbiota
Signup and view all the flashcards
Development of Taste
Development of Taste
Signup and view all the flashcards
Salivary Function
Salivary Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mandibular Growth
Mandibular Growth
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pediatric Maturation of Swallowing-Breathing
Pediatric Maturation of Swallowing-Breathing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acquisition of Speech
Acquisition of Speech
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tooth Eruption
Tooth Eruption
Signup and view all the flashcards
Deciduous Teeth
Deciduous Teeth
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dental Anomalies (Abnormal Dentition)
Dental Anomalies (Abnormal Dentition)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- RD-5 is about dentition and neonatal/childhood oral function development.
- The study aims to cover neonatal adaptations, reflexes, oral microbiota acquisition, oral anomalies, oral function maturation, malocclusion, and speech acquisition timelines.
Neonatal Adaptations for Survival
- Neonates need to adapt to breathing for gas exchange outside the womb.
- First breath depends on internal chemical changes and external sensory stimuli.
- Internal stimuli include decreased oxygen, increased carbon dioxide, and decreased pH, which send messages to the respiratory center in the medulla..
- External stimuli include sensory, thermal, and mechanical changes triggering the respiratory center.
- Fetal lung fluid is cleared via surfactant secretion and pulmonary vasodilation for efficient gas exchange.
- The fetus has to rely on oxygen from lungs for gas exchange because it loses oxygen supply from the placenta.
Circulatory Transition at Birth
- The pressure is raised in the left atrium of the heart and lowers the pressure in the right atrium, the foramen ovale close.
- Changes occur at the heart-lung interface.
- Initial breaths expand the lungs, clearing fluid from the alveoli, and the ductus arteriosus closes.
- Ductus arteriosus connects the pulmonary artery to the aortic arch, diverting deoxygenated blood away from the lungs and becomes the ligamentum arteriosum.
- Oxygenated blood entering the right atrium is diverted into the left atrium and delivers oxygenated blood throughout the body via the fossa ovalis.
- Oxygenated blood returning from the placenta is shunted from the liver to the inferior vena cava becoming the ligamentum venosum.
Metabolic Adaptation
- Neonates needs nutrients from breast milk when the umbilical cord is clamped.
- Milk production depends on prolactin and milk ejection relies on oxytocin.
- The newborn depends on colostrum (initial milk) rich in proteins, vitamin A, and salts, along with carbohydrates, lipids, and antibodies.
- Full breastfeeding length is positively correlated with oral health.
Newborn Reflexes - Persistent Reflexes
- Newborn reflexes are autonomic involuntary motor/muscle responses controlled by the brain stem.
- Persistent reflexes include breathing, blinking, pupillary, sneeze, cough, gag, and swallowing reflexes.
- Infant’s anatomy differs in size, composition, position, and shape.
- Breathing reflex is essential; neonates are obligate nose breathers.
- Neonates have nasal breathing aided by short larynx that moves forward towards the epiglottis.
Swallowing reflex
- Tongue and pharyngeal muscles push bolus to back of mouth.
- Three phases: oral, pharyngeal, and esophageal.
- There’s a voluntary oral phase and involuntary pharyngeal/esophageal phases.
Newborn Reflexes- Primitive Reflexes
- Primitive reflexes are present at birth and disappear by 4-6 months.
- Brain maturation initiates voluntary motor activities; reflexes may persist in neurological diseases.
- Moro (startle) reflex occur during first 2 months.
- Tonic neck reflex (fencing position) lasts until 5-7 months.
- Grasp reflex (hand grasping) occurs for 6 months.
- Babinski reflex (toes crunching).
- Step reflex (walking/dancing reflex).
- Swim reflex lasts until 6 months.
- Crawl reflex.
Oro-Pharyngeal Reflexes
- Extrusion reflex prevents choking when solids are introduced.
- The tongue extends, and lips close so solid foods should not be introduced until the reflex has disappeared.
- The Newborn muscles are not developed to swallow anything other than liquids.
- Normally disappears by 4 months.
- Persistence beyond 4 months leads to tongue thrust habit, causing speech/dental issues.
Feeding Reflexes
- Rooting, suckling, and swallowing reflexes crucial for feeding.
- The first change in the oral area occurs at 60 days in utero development.
- Suckling develops at the 10th week and swallowing at the 12th week.
- Neonates are born with feeding reflexes requiring coordinated suck-swallow breath cycle.
- Rooting prompts the baby to turn towards touch around corner of mouth.
- Sucking occurs when something touches the palate.
- Swallowing occurs when mouth fills with milk/liquid.
- Mature swallowing reflex persists while infantile swallowing reflex disappears.
Sucking and Feeding Behavior
- The sucking system may not be functionally ready for preterm infants.
- Neonatal swallowing and breathing reflexes are coordinated.
- Infants breathe through the nose with a relaxed soft palate.
- During swallowing, that soft palate lifts and stretches to close off the nose.
Neonatal Oral Anomalies
- Oral cysts occur in newborns.
- Oral cysts are found in 65-85% of newborns; no intervention is necessary.
- Epstein pearls are benign whitish-yellow cysts on the roof of the mouth from epithelium entrapment; disappear within weeks.
- Bohn's nodules are keratin-filled cysts in the gingival region (buccal or lingual surface), or the hard palate away from the midline derived from minor salivary glands.
- Dental lamina cysts are benign oral mucosal lesions of transient nature of the dental lamina; on the gums and disappear in weeks or months.
Natal Teeth
- Natal teeth are uncommon but present at birth.
- Intervention is necessary: natal teeth need to be removed shortly after birth.
- Natal teeth often develop on the lower gum.
- Natal teeth that attached to the end of the gum by soft tissue are may cause a risk of “breathing in” the tooth.
- Natal causes irritation or injury to the tongue of the infant.
- Causes of natal teeth include Ellis van Creveld syndrome, Hallermann-Streiff syndrome, cleft palate, Pierre-Robin syndrome/sequence, Sotos syndrome.
Tongue-Tie (Ankyloglossia)
- A shortened, thickened, or wrongly placed frenulum (lingual frenulum) may restrict the tongue's movement.
- Tongue-tie could cause problems with breastfeeding and speech later in life.
- Intervention advised for with sterile scissors or laser.
Oral Microbiota
- Newborn's mouth is inhabited by microbes from mother's mucous membranes/urogenital system during childbirth.
- Early colonizers include streptococcus, staphylococcus, fusobacterium, veillonella, lactobacillus, and candidia.
- Adult/Primary Dentition consists of development of a specific set of microorganisms.
- Second colonizers appear around 3-6 months including gemella, granulicatella, haemophilus, and rothia.
Development of Taste
- Taste buds are present at birth and newborns can discriminate tastes.
- Neural connections to the brain are immature thus taste perception is not fully developed.
- Infants have acute sense of taste by 3 months.
- Taste buds are activated during the 30th week of gestation;
- Amnionic fluid influenced by the maternal diet stimulates fetal taste receptors.
Development of Salivary Function
- Salivary glands develop from ectodermal proliferations.
- Small amounts are produced by the newborn, increase at 3 months (before teething).
- Salivary glands at birth produces small amounts of saliva
- Lip closure matures which reduces drooling at about 2 years old
- Drooling is seen until the muscular reflexes mature and irritation can stimulate drooling
Growth of Mandible
- Mdndibular bone is formed by intramembranous ossification off the first pharyngeal arch at 6 weeks in utero.
- Growth is mediated by endochondral ossification of the condylar cartilage.
- Small mandible with short ramus.
- The mandibular fossa is flat and there is a low mandibular canal
- Growth is the most vertically in its first year.
- Growth continues during primary teeth appearance and replacement.
Maturation of Oral Functions -Swallowing-Breathing
- Size and shape of oral and pharyngeal structures change.
- Infant: Tongue filling oral cavity, high hyoid bone/larynx location decreases elevation during pharyngeal phase.
- Toddler: Adult-like phases with less larynx elevation and discrete swallow.
- Older Child: Mandible grows down/forward as intraoral space increases, and the tongue/palate space increases.
- The larynx and hyoid bone lower as that pharynx elongates/enlarges.
Acquisition of Speech:
- Sound is created by the vibration of the vocal cords.
- During speech, the soft palate lifts off from the mouth.
- Air passes through the voice box and lungs up through the windpipe .
- Speech acquisition is shaped into words by muscles controlling the soft palate, tongue, and lips.
- Bilabial (p, b, m, w) are formed by closure/near closure of lips at 2-3 years.
- Labial velar sound (q, we) via moving lips & air from back of mouth at 2-4 years.
- Velar sounds (k, g) - raising the back of the tongue and create quick air burst at the back of the mouth at 2.5-4 years.
- There is no teeth involved
Maturation of Oral Functions - Dentition & Mastication
- Masticatory force increases with the second primary molar eruption.
- Biting force is further increased when the first permanent molars are occluded at 6 years.
Speech Acquisition
- Alveolar sounds (†)- tongue tapping inside of top teeth at 2.5-4
- Top teeth are being added now
Deciduous Teeth
- There’ll be a slight change from now
Speech Acquisition w/ teeth present:
- Speech occurs through the help of the teeth
- labial-dental sound (f) - formed via top teeth on top of the bottom lip at 3-4 years.
- Alveolar sounds- formed with tongue touching behind the top teeth : developed often at age of 3. 5-5 years.
- Alveolar sound (sh) emerge (spider, snake, slide, skip, swim and stop etc) at 4-6 years.
- Affricate sounds (ch and J) at 4.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.