Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which function of the respiratory system involves the elimination of carbon dioxide from the body?
Which function of the respiratory system involves the elimination of carbon dioxide from the body?
- Gas exchange
- Regulation of pH
- Removal of waste products (correct)
- Filtration and humidification
What is the role of the vocal cords in the respiratory system?
What is the role of the vocal cords in the respiratory system?
- Sense of smell
- Gas exchange
- Immune defense
- Voice production (correct)
Which function of the respiratory system involves the filtration of airborne particles and the addition of moisture to inhaled air?
Which function of the respiratory system involves the filtration of airborne particles and the addition of moisture to inhaled air?
- Breathing
- Filtration and humidification (correct)
- Gas exchange
- Regulation of pH
What is the role of the olfactory receptors in the respiratory system?
What is the role of the olfactory receptors in the respiratory system?
Which of the following is NOT part of the structural organization of the respiratory system?
Which of the following is NOT part of the structural organization of the respiratory system?
Which of the following is a function of the respiratory system?
Which of the following is a function of the respiratory system?
What is the function of mucus produced by the mucosa?
What is the function of mucus produced by the mucosa?
Which of the following is a structure found in the nasal cavity?
Which of the following is a structure found in the nasal cavity?
Which type of epithelium lines the inner lining of the trachea?
Which type of epithelium lines the inner lining of the trachea?
How many tracheal cartilages are there in total?
How many tracheal cartilages are there in total?
What is the function of the tracheal cartilages?
What is the function of the tracheal cartilages?
What is the smallest subdivision of the bronchial tree?
What is the smallest subdivision of the bronchial tree?
Which nerve provides extensive innervation to the lungs?
Which nerve provides extensive innervation to the lungs?
What is the function of serous fluid in the pleural cavity?
What is the function of serous fluid in the pleural cavity?
What is the role of surfactant in the lungs?
What is the role of surfactant in the lungs?
What creates a negative pressure between the lung surface and the chest wall?
What creates a negative pressure between the lung surface and the chest wall?
Which of the following sinuses is located deep within the skull, behind the eyes?
Which of the following sinuses is located deep within the skull, behind the eyes?
Which of the following structures is responsible for preventing food and liquids from entering the trachea during swallowing?
Which of the following structures is responsible for preventing food and liquids from entering the trachea during swallowing?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the larynx?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the larynx?
What is the structure of the trachea composed of?
What is the structure of the trachea composed of?
Which type of cells in the alveoli produce surfactant, a substance that reduces surface tension in the alveoli?
Which type of cells in the alveoli produce surfactant, a substance that reduces surface tension in the alveoli?
What is the function of alveolar macrophages?
What is the function of alveolar macrophages?
What is the structure of the respiratory membrane?
What is the structure of the respiratory membrane?
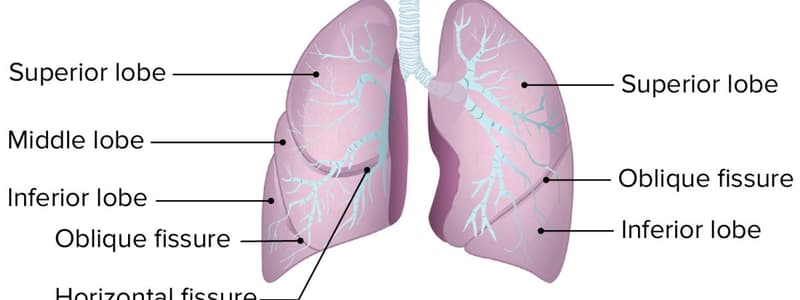
Which lung is larger and heavier?
Which lung is larger and heavier?
During inspiration, the diaphragm contracts and flattens, while the intercostal muscles between the ribs contract, expanding the chest cavity vertically and laterally. This creates a negative pressure within the thoracic cavity, causing air to
During inspiration, the diaphragm contracts and flattens, while the intercostal muscles between the ribs contract, expanding the chest cavity vertically and laterally. This creates a negative pressure within the thoracic cavity, causing air to
Which muscles play a crucial role in maintaining lung inflation?
Which muscles play a crucial role in maintaining lung inflation?
What is the process of moving air in and out of the lungs called?
What is the process of moving air in and out of the lungs called?
What prevents individual alveoli from collapsing during exhalation?
What prevents individual alveoli from collapsing during exhalation?
What happens to the chest cavity during inspiration?
What happens to the chest cavity during inspiration?
What are the two main phases of pulmonary ventilation?
What are the two main phases of pulmonary ventilation?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Functions of the Respiratory System
- Elimination of carbon dioxide occurs through gas exchange in the alveoli, a critical function to maintain acid-base balance in the body.
- The filtration of airborne particles and addition of moisture to inhaled air are facilitated by mucous membranes lining the respiratory tract, ensuring air quality before reaching the lungs.
- The vocal cords in the larynx vibrate to produce sound, playing a key role in speech production.
Structures and Organization
- Larynx is responsible for preventing food and liquids from entering the trachea during swallowing due to its epiglottic function.
- The trachea is lined with ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium, important for trapping and moving particles out of the airways.
- Tracheal cartilages, numbering 16 to 20, provide structural support to maintain an open airway.
- The nasal cavity contains structures like the turbinates, which enhance air filtration and humidification.
Components of the Respiratory System
- Alveolar type II cells are responsible for surfactant production, which decreases surface tension and prevents alveolar collapse.
- Alveolar macrophages serve as immune cells that engulf debris and pathogens within the alveoli.
- The respiratory membrane is composed of the alveolar epithelium, capillary endothelium, and their fused basement membranes, facilitating efficient gas exchange.
Lung Mechanics
- The diaphragm and intercostal muscles are crucial for lung inflation, with the diaphragm contracting to increase thoracic cavity volume during inspiration.
- Serous fluid in the pleural cavity lubricates lung movement and maintains surface tension, facilitating breathing.
- Negative pressure between the lung surface and chest wall is created by the pleural cavity, essential for keeping lungs expanded.
Additional Facts
- The larger and heavier lung is typically the right lung, which has three lobes compared to the left lung's two lobes.
- Pulmonary ventilation involves the process of moving air in (inspiration) and out (expiration) of the lungs, with two main phases: inhalation and exhalation.
- The sinuses, including the sphenoid sinus located behind the eyes, play a role in air warming and lightening the skull, but are not involved in primary respiratory functions.
- Maintaining alveolar expansion during exhalation is achieved by surfactant action, which prevents collapse under surface tension stresses.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.