Podcast
Questions and Answers
Pulleys are exclusively used to change the direction of force, without altering the magnitude of the applied force.
Pulleys are exclusively used to change the direction of force, without altering the magnitude of the applied force.
False (B)
Sheaves are pulleys without grooved rims and are typically used for high-speed applications.
Sheaves are pulleys without grooved rims and are typically used for high-speed applications.
False (B)
A fixed pulley provides a mechanical advantage by reducing the amount of force needed to lift an object.
A fixed pulley provides a mechanical advantage by reducing the amount of force needed to lift an object.
False (B)
Movable pulleys are characterized by having their axle attached to a stationary object above the load.
Movable pulleys are characterized by having their axle attached to a stationary object above the load.
Compound Pulleys combine both fixed and movable pulleys to change the direction of force and lighten the perceived weight.
Compound Pulleys combine both fixed and movable pulleys to change the direction of force and lighten the perceived weight.
A block and tackle pulley utilizes multiple parallel arrangements of solely movable pulleys to maximize force amplification.
A block and tackle pulley utilizes multiple parallel arrangements of solely movable pulleys to maximize force amplification.
Cone pulleys are named for their distinctive conical configuration formed by a series of pulleys with varying diameters.
Cone pulleys are named for their distinctive conical configuration formed by a series of pulleys with varying diameters.
The axle of a pulley system rotates along with the wheel to minimize friction and maximize efficiency when moving a load
The axle of a pulley system rotates along with the wheel to minimize friction and maximize efficiency when moving a load
The groove found on a pulley's rim is specifically designed to ensure that the belt or rope follows a secure and aligned path.
The groove found on a pulley's rim is specifically designed to ensure that the belt or rope follows a secure and aligned path.
A pulley system decreases the amount of work needed to lift an object by reducing both the force applied and the distance over which it is applied.
A pulley system decreases the amount of work needed to lift an object by reducing both the force applied and the distance over which it is applied.
Flashcards
What is a Pulley?
What is a Pulley?
A simple mechanical device with a flexible rope, cord, chain, or belt on a wheel's rim, used to transmit energy and motion.
Fixed Pulley
Fixed Pulley
Changes the direction of force without changing the amount of force; axle and wheel stay in place.
Movable Pulley
Movable Pulley
Increases the amount of force applied, doesn't change direction; axle is in a movable block.
Compound Pulley
Compound Pulley
Signup and view all the flashcards
Block and Tackle Pulley
Block and Tackle Pulley
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cone Pulley
Cone Pulley
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pulley Groove
Pulley Groove
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pulley Wheel
Pulley Wheel
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pulley Axle
Pulley Axle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pulley Rope
Pulley Rope
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- A pulley is a simple mechanical device.
- Pulleys use a flexible rope, cord, chain, or belt.
- This flexible material is carried on the rim of a wheel.
- Pulleys transmit energy and motion, and those with grooved rims are called sheaves.
Types of Pulleys
- Fixed Pulley
- Movable Pulley
- Compound Pulley
- Block and Tackle Pulley
- Cone Pulley
Fixed Pulley
- A fixed pulley changes the direction of the input force.
- Does not change the amount of force applied.
- Usually attached to a stationary object above the load.
- The axle and wheel stay in one place.
Movable Pulley
- A movable pulley increases the amount of force applied.
- It does not change the direction of the force.
- Attached to the loads as its axle is in a movable block.
Compound Pulley
- Also known as combination pulleys.
- Made up of both fixed and movable pulleys.
- Changes the direction of force and lessens the effort to lift the weight.
- The wheel size and the rope length are designed to lessen the efforts.
Block and Tackle Pulley
- Includes several movable and fixed pulleys arranged in parallel.
- It is a compound pulley where movable pulleys are aligned parallel with movables and fixed pulleys are fixed.
Cone Pulley
- Consists of multiple pulleys.
- They are simple in design.
- They are cost-effective.
- They have larger circumferences.
- Called cone pulleys as multiple pulleys form a cone shape at a point.
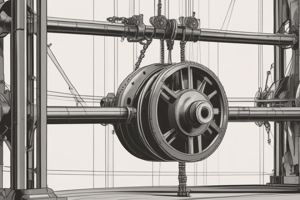
Parts of a Pulley
- Groove
- The area where the rope or belt runs.
- A grooved pulley has a groove to accommodate a belt or cord.
- Provides a secure and aligned path.
- Wheel
- The wheel-shaped part that the rope or belt runs over.
- Has a groove for the rope and rotates on the axle.
- Axle
- The shaft on which the pulley wheel rotates.
- Press-fit, screwed, or riveted into the pulley frame.
- Remains stationary while the wheel rotates around it.
- Rope
- A single continuous rope transmits a tension force around one or more pulleys to lift or move a load.
- Uses rope, cord, chain, or belt being carried on the rim of a wheel.
How Pulleys Work
- A pulley system helps lift heavy objects by changing the direction of the applied force.
- A fixed pulley does not provide mechanical advantage but makes the task easier by changing direction.
- A movable pulley allows for lifting with less effort.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.