Podcast
Questions and Answers
What are the top needs in Maslow's hierarchy of needs?
What are the top needs in Maslow's hierarchy of needs?
- Physiological needs
- Belonging and love
- Safety
- Esteem needs and actualization (correct)
What is Pavlov's classical conditioning?
What is Pavlov's classical conditioning?
Connecting two things through unconditioned stimulus and response, leading to a conditioned response.
Who is associated with operant conditioning?
Who is associated with operant conditioning?
Skinner
Positive reinforcement increases positive behaviors.
Positive reinforcement increases positive behaviors.
What happens in negative reinforcement?
What happens in negative reinforcement?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
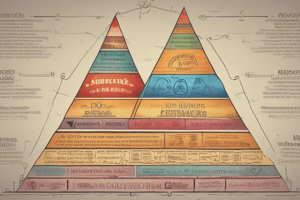
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
- Esteem needs are positioned at the top of Maslow's pyramid, indicating their importance in human motivation.
- Self-actualization is the highest level of the hierarchy, representing personal growth and fulfillment.
- Safety needs include security and protection from physical and emotional harm.
- Love and belonging encompass the need for interpersonal relationships, social connections, and acceptance.
Pavlov and Classical Conditioning
- Classical conditioning involves associating a neutral stimulus with an unconditioned stimulus to elicit a conditioned response.
- Pavlov's experiment demonstrated this with a bell (neutral stimulus) paired with food (unconditioned stimulus) leading to salivation (unconditioned response).
- Over time, the bell became a conditioned stimulus that evoked salivation on its own.
Skinner and Operant Conditioning
- Operant conditioning focuses on voluntary behaviors and their consequences, emphasizing the role of reinforcement.
- B.F. Skinner explored how behaviors could be shaped and maintained through reinforcements.
Positive Reinforcement
- Positive reinforcement involves presenting a rewarding stimulus after a desired behavior, which increases the likelihood of that behavior occurring in the future.
- This technique is commonly utilized in education and behavior modification.
Negative Reinforcement
- Negative reinforcement occurs when the removal of an unpleasant stimulus results in an increase in desired behavior frequency.
- An example includes taking aspirin to alleviate headache pain, leading to an increased likelihood of taking medication when similar discomfort occurs.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.