Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the result of the 1 transformation in the visual system?
What is the result of the 1 transformation in the visual system?
- Electrical signals are transmitted to the brain.
- The image is interpreted as a recognizable object.
- Light is converted into electrical signals. (correct)
- A three-dimensional image is formed on the retina.
Which of these structures is NOT part of the retina?
Which of these structures is NOT part of the retina?
- Lens (correct)
- Fovea
- Rods
- Cones
Which of the following best describes the process of accommodation in the eye?
Which of the following best describes the process of accommodation in the eye?
- The contraction of the iris to regulate the amount of light entering the eye.
- The process of converting light energy into electrical signals.
- The adjustment of the lens's shape to focus on objects at different distances. (correct)
- The transmission of electrical signals from the retina to the brain.
What is the primary difference between rods and cones in the retina?
What is the primary difference between rods and cones in the retina?
Which of the following statements is TRUE about Myopia (nearsightedness)?
Which of the following statements is TRUE about Myopia (nearsightedness)?
What type of ganglion cell is most responsive to low contrast, large, slow-moving objects?
What type of ganglion cell is most responsive to low contrast, large, slow-moving objects?
Which of the following is NOT a landmark of the retino-geniculo-striate pathway?
Which of the following is NOT a landmark of the retino-geniculo-striate pathway?
What does neural convergence mean in terms of receptive fields?
What does neural convergence mean in terms of receptive fields?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the function of the dorsal stream?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the function of the dorsal stream?
A neuron in V1 that is selective for horizontal lines will fire when it receives input from:
A neuron in V1 that is selective for horizontal lines will fire when it receives input from:
Which of the following statements about the fovea is true?
Which of the following statements about the fovea is true?
What is the main function of neural convergence in the visual system?
What is the main function of neural convergence in the visual system?
What happens when a stimulus falls into the inhibitory area of a ganglion cell's receptive field?
What happens when a stimulus falls into the inhibitory area of a ganglion cell's receptive field?
Which type of ganglion cell is specifically sensitive to color?
Which type of ganglion cell is specifically sensitive to color?
What is the main function of the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN)?
What is the main function of the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN)?
Which of the following areas of the visual cortex is responsible for processing object identity?
Which of the following areas of the visual cortex is responsible for processing object identity?
What is the difference between a simple cortical cell and a complex cortical cell in V1?
What is the difference between a simple cortical cell and a complex cortical cell in V1?
How does the visual system contribute to detecting edges of objects?
How does the visual system contribute to detecting edges of objects?
Which of the following is NOT a feature processed by V2 neurons?
Which of the following is NOT a feature processed by V2 neurons?
Which visual pathway is responsible for processing the 'where' information about objects?
Which visual pathway is responsible for processing the 'where' information about objects?
What is the key difference between mesopic and scotopic vision?
What is the key difference between mesopic and scotopic vision?
Which of the following is a feature that V1 neurons are NOT selective for?
Which of the following is a feature that V1 neurons are NOT selective for?
What is the Purkinje shift?
What is the Purkinje shift?
Which of the following statements about M cells is true?
Which of the following statements about M cells is true?
What is the primary function of the visual cortex, particularly V1?
What is the primary function of the visual cortex, particularly V1?
Which of the following statements about the ciliary muscles is TRUE?
Which of the following statements about the ciliary muscles is TRUE?
What is the main difference between photopic and scotopic vision?
What is the main difference between photopic and scotopic vision?
Which of the following scenarios best describes the process of accommodation for a distant object?
Which of the following scenarios best describes the process of accommodation for a distant object?
What is the main reason why a person with myopia (nearsightedness) has difficulty seeing distant objects?
What is the main reason why a person with myopia (nearsightedness) has difficulty seeing distant objects?
What is the primary function of the fovea?
What is the primary function of the fovea?
Which of the following correctly describes how light is transformed during the visual process?
Which of the following correctly describes how light is transformed during the visual process?
What is the primary difference between rods and cones?
What is the primary difference between rods and cones?
What is the "purkinje shift" and what causes it?
What is the "purkinje shift" and what causes it?
What happens to the lens during accommodation for a near object?
What happens to the lens during accommodation for a near object?
Which of the following eye conditions is characterized by the inability to focus on nearby objects?
Which of the following eye conditions is characterized by the inability to focus on nearby objects?
What type of lens is used to correct myopia?
What type of lens is used to correct myopia?
Which of the following statements about the photoreceptors is TRUE?
Which of the following statements about the photoreceptors is TRUE?
Which of the following is NOT a stage in the visual process?
Which of the following is NOT a stage in the visual process?
What is the relationship between neural convergence and visual acuity?
What is the relationship between neural convergence and visual acuity?
Which of the following best describes the role of the lens in the visual process?
Which of the following best describes the role of the lens in the visual process?
Which of the following best describes the process of transduction?
Which of the following best describes the process of transduction?
What is the condition called when the lens of the eye cannot change its shape to focus properly on near and far objects?
What is the condition called when the lens of the eye cannot change its shape to focus properly on near and far objects?
What is the main difference between the ventral and dorsal streams?
What is the main difference between the ventral and dorsal streams?
How does the 'where' stream contribute to object reaching and grasping?
How does the 'where' stream contribute to object reaching and grasping?
Why is the method of limits considered less precise than the method of constant stimuli for measuring the absolute threshold?
Why is the method of limits considered less precise than the method of constant stimuli for measuring the absolute threshold?
Which of the following is NOT a method used to measure the absolute threshold?
Which of the following is NOT a method used to measure the absolute threshold?
What does Weber's Law state about the difference threshold?
What does Weber's Law state about the difference threshold?
What is a psychometric function?
What is a psychometric function?
How does the method of constant stimuli differ from the method of limits in measuring the absolute threshold?
How does the method of constant stimuli differ from the method of limits in measuring the absolute threshold?
Which of the following statements about the method of adjustment is TRUE?
Which of the following statements about the method of adjustment is TRUE?
What does 'response expansion' refer to in relation to Stevens' subjective magnitude estimation?
What does 'response expansion' refer to in relation to Stevens' subjective magnitude estimation?
Which of the following is an advantage of the method of constant stimuli over the method of limits for measuring the absolute threshold?
Which of the following is an advantage of the method of constant stimuli over the method of limits for measuring the absolute threshold?
Stanley Stevens' approach to psychophysics was primarily focused on:
Stanley Stevens' approach to psychophysics was primarily focused on:
Which of the following best describes the main difference between Structuralism and Psychophysics as approaches to studying perception?
Which of the following best describes the main difference between Structuralism and Psychophysics as approaches to studying perception?
What is the primary criticism of Structuralism as a school of thought in psychology?
What is the primary criticism of Structuralism as a school of thought in psychology?
How does Weber's Law differ from Stevens' approach to measuring perception?
How does Weber's Law differ from Stevens' approach to measuring perception?
Which of the following is NOT a valid criticism of Structuralism?
Which of the following is NOT a valid criticism of Structuralism?
What is the main contribution of Psychophysics to the understanding of perception?
What is the main contribution of Psychophysics to the understanding of perception?
Flashcards
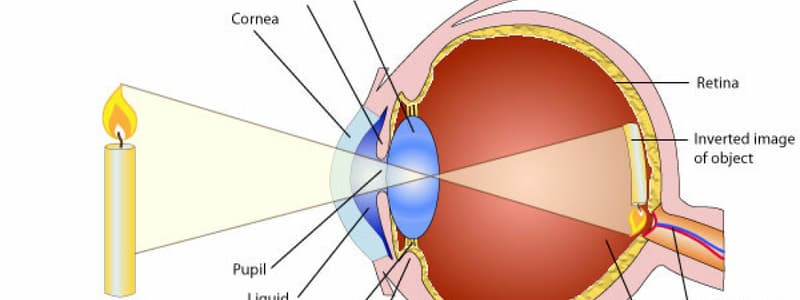
Landmarks on the retina
Landmarks on the retina
The two key landmarks are the fovea and optic disc, critical for vision clarity and blind spot identification.
Accommodation process
Accommodation process
The adjustment of the eye's lens to focus on objects at different distances.
Myopia
Myopia
A vision condition where distant objects appear blurry, caused by an elongated eyeball or strong lens.
Hyperopia
Hyperopia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rods vs. Cones
Rods vs. Cones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Receptive Field
Receptive Field
Signup and view all the flashcards
Types of Ganglion Cells
Types of Ganglion Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Retino-geniculo-striate Pathway
Retino-geniculo-striate Pathway
Signup and view all the flashcards
Orientation Selective Neuron
Orientation Selective Neuron
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cortical Visual Pathways
Cortical Visual Pathways
Signup and view all the flashcards
Macular Degeneration
Macular Degeneration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Accommodation
Accommodation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Far Point
Far Point
Signup and view all the flashcards
Near Point
Near Point
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transduction
Transduction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Photopic Vision
Photopic Vision
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scotopic Vision
Scotopic Vision
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rods and Cones
Rods and Cones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acuity
Acuity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Purkinje Shift
Purkinje Shift
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spectral Sensitivity
Spectral Sensitivity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neural Convergence
Neural Convergence
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mesopic Vision
Mesopic Vision
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dorsal Stream
Dorsal Stream
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ventral Stream
Ventral Stream
Signup and view all the flashcards
Perception
Perception
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sensation
Sensation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Structuralism
Structuralism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Method of Adjustment
Method of Adjustment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Weber's Law
Weber's Law
Signup and view all the flashcards
Difference Threshold
Difference Threshold
Signup and view all the flashcards
Psychophysics
Psychophysics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Response Expansion
Response Expansion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Response Compression
Response Compression
Signup and view all the flashcards
Subjective Magnitude Estimation
Subjective Magnitude Estimation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ciliary Muscles
Ciliary Muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cones
Cones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rods
Rods
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ganglion cells
Ganglion cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fovea
Fovea
Signup and view all the flashcards
Retinal periphery
Retinal periphery
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spectral sensitivity (Rods)
Spectral sensitivity (Rods)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spectral sensitivity (Cones)
Spectral sensitivity (Cones)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ganglion cell types
Ganglion cell types
Signup and view all the flashcards
Orientation selectivity
Orientation selectivity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Structuralism
- Aim: Study the fundamental elements of consciousness.
- Method: Introspection (describing sensory experiences).
- Belief: Perception is a sum of sensory elements.
- Evaluation:
- First school of thought in psychology.
- Low validity and reliability due to subjective observations.
- Not objective or quantifiable.
Psychophysics
- Focus: Measuring the relationship between stimulus intensity and perceived intensity.
- Key figures: Fechner and Weber.
- Absolute threshold: Minimum stimulus intensity needed to perceive a stimulus (measured via various methods: adjustment, limits, constant stimuli).
- Difference threshold (JND): Minimum difference in intensity needed to differentiate two stimuli (Weber's Law).
- Weber's Law: JND is a constant proportion of the original stimulus intensity.
- Subjective magnitude estimation: Stevens' method of measuring the relationship between objective stimulus intensity and subjective perception.
- Response expansion: Perceived stimulus intensity increases faster than the objective stimulus intensity (e.g., electric shock).
- Response compression: Perceived stimulus intensity increases slower than the objective stimulus intensity (e.g., light).
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.