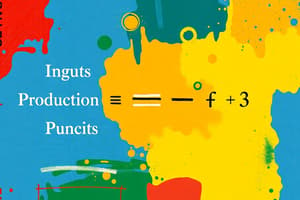Podcast
Questions and Answers
What do inputs consist of in a production function?
What do inputs consist of in a production function?
- Only wages paid to workers
- Only capital factor
- Human effort, raw materials, equipment, land, etc. (correct)
- Only labor factor
Which factor is represented by 'K' in the production function formula Q = f(L, K)?
Which factor is represented by 'K' in the production function formula Q = f(L, K)?
- Wages paid to workers
- Capital factor (correct)
- Physical capital input
- Labor factor
What is the primary role of managers in relation to physical capital input in a production function?
What is the primary role of managers in relation to physical capital input in a production function?
- Set quality standards for final products
- Contribute directly to output
- Adjust physical capital based on demand (correct)
- Determine environmental conditions
What does the 'Q' represent in the production function formula Q = f(L, K)?
What does the 'Q' represent in the production function formula Q = f(L, K)?
Which of the following is NOT considered an input in a production function?
Which of the following is NOT considered an input in a production function?
What do outputs represent in the context of a production function?
What do outputs represent in the context of a production function?
What period in economics is characterized by the inability to quickly change one input, usually labor?
What period in economics is characterized by the inability to quickly change one input, usually labor?
In the short run, what happens to efficiency when firms exceed their current capacity level?
In the short run, what happens to efficiency when firms exceed their current capacity level?
Which phase allows businesses to make decisions regarding both variable and fixed factors of production without time constraints?
Which phase allows businesses to make decisions regarding both variable and fixed factors of production without time constraints?
How do firms attempt to maximize profits in the long run?
How do firms attempt to maximize profits in the long run?
What knowledge is essential for strategic management decision making processes concerning business growth and expansion strategies?
What knowledge is essential for strategic management decision making processes concerning business growth and expansion strategies?
What impact does expanding output beyond current capacity have on costs in the short run?
What impact does expanding output beyond current capacity have on costs in the short run?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
A production function is a mathematical representation of how much output can be produced from different combinations of input factors of production. It's often represented by the formula Q = f(L, K), where Q represents quantity of output, L stands for labor factor, and K denotes capital factor. In this equation, the amount of output increases when more labor and capital resources are used. Here's what you need to know about these key aspects of production functions:
Inputs
Inputs consist of all the resources used in the production process, such as raw materials, equipment, land, human effort, etc. These items are combined with each other according to a specific technology (i.e., the recipe) to produce goods and services which comprise output. Labor input includes wages paid to workers, while physical capital input refers to buildings, machinery, tools, and vehicles. Managers typically adjust their levels of physical capital depending on demand for their products.
Outputs
Outputs represent the end result of the production process—the goods and services produced after combining various inputs using specific technologies. For example, if a factory makes mattresses out of fabric, foam, thread, and plastic zippers, its output would be mattresses. However, the output may vary due to changes in technology, scale of operations, quality standards, and environmental conditions.
Short Run
In economics, the 'short run' refers to a period during which one input, usually labor, cannot change quickly. This means that while managers have control over utilization rates like hours worked per week, they don't have total flexibility in changing labor quantities. As a result, when firms expand output beyond current capacity level under short-run conditions, efficiency decreases because new units of output require additional amounts of labor and capital inputs, leading to higher costs.
Long Run
The opposite of short-run is called the 'long run,' which is characterized by flexible input usage. During this phase, businesses can make decisions regarding both variable and fixed factors of production without constraints related to time horizons. At this stage, firms try to maximize profits by operating at peak efficiency through optimal allocation of resources across multiple industries and countries; investment decisions also become possible within a longer planning horizon.
In summary, understanding production functions helps us assess economic activities better since it provides insights into productive potentiality of enterprises. By examining relationships between inputs and outputs—both in terms of efficiency gains achievable via technological advancements in the short term versus optimum resource deployment strategies applicable over extended periods—we acquire valuable knowledge essential for strategic management decision making processes concerning business growth and expansion strategies.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.