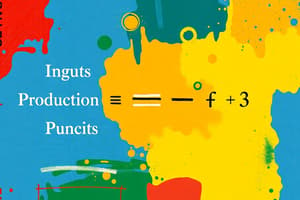Podcast
Questions and Answers
What does a production function primarily illustrate?
What does a production function primarily illustrate?
- The marketing strategies for selling goods.
- The relationship between the quantity of inputs used and the quantity of output produced. (correct)
- The financial capital required for production.
- The organizational structure of a firm.
How does technological advancement typically affect a firm's production function?
How does technological advancement typically affect a firm's production function?
- It leads to a new production function, potentially increasing output with the same inputs. (correct)
- It only affects the firm's marketing strategies.
- It has no impact on the production function.
- It decreases the firm's output capacity.
In the production function $Q = f(Ld, L, C, O)$, what does 'C' represent?
In the production function $Q = f(Ld, L, C, O)$, what does 'C' represent?
- Contracts
- Cost
- Capital (correct)
- Consumption
What additional factors are emphasized by modern managerial economists in the production function?
What additional factors are emphasized by modern managerial economists in the production function?
In the Cobb-Douglas production function, what does the function primarily apply to?
In the Cobb-Douglas production function, what does the function primarily apply to?
What is a key characteristic of the short run in the context of production?
What is a key characteristic of the short run in the context of production?
Which of the following statements best describes the long run in production?
Which of the following statements best describes the long run in production?
What does the 'law of variable proportions' primarily address?
What does the 'law of variable proportions' primarily address?
What is a key assumption underlying the law of variable proportions?
What is a key assumption underlying the law of variable proportions?
During the first stage of the law of variable proportions, what typically happens to the marginal product?
During the first stage of the law of variable proportions, what typically happens to the marginal product?
At which point does the first stage of the law of variable proportions typically end?
At which point does the first stage of the law of variable proportions typically end?
What is a characteristic of the second stage of the law of variable proportions?
What is a characteristic of the second stage of the law of variable proportions?
In the third stage of the law of variable proportions, what happens to the marginal product?
In the third stage of the law of variable proportions, what happens to the marginal product?
What does the 'law of returns to scale' describe?
What does the 'law of returns to scale' describe?
Which assumption is NOT part of the law of returns to scale?
Which assumption is NOT part of the law of returns to scale?
What characterizes 'increasing returns to scale'?
What characterizes 'increasing returns to scale'?
Which of the following is a cause of increasing returns to scale?
Which of the following is a cause of increasing returns to scale?
What defines 'constant returns to scale'?
What defines 'constant returns to scale'?
Which of the following can cause constant returns to scale?
Which of the following can cause constant returns to scale?
What is a characteristic of 'diminishing returns to scale'?
What is a characteristic of 'diminishing returns to scale'?
Which of the following can lead to diminishing returns to scale?
Which of the following can lead to diminishing returns to scale?
What does 'Cost' refer to in economics?
What does 'Cost' refer to in economics?
Which of the following is an example of 'Opportunity cost'?
Which of the following is an example of 'Opportunity cost'?
What is the primary difference between accounting costs and economic costs?
What is the primary difference between accounting costs and economic costs?
How are 'explicit costs' best described?
How are 'explicit costs' best described?
What is an example of an 'Implicit cost'?
What is an example of an 'Implicit cost'?
What is the definition of 'Fixed costs'?
What is the definition of 'Fixed costs'?
How are 'Variable costs' best described?
How are 'Variable costs' best described?
What is 'Marginal cost'?
What is 'Marginal cost'?
How is 'Total cost' calculated?
How is 'Total cost' calculated?
What does 'Total revenue' represent?
What does 'Total revenue' represent?
What is 'Profit'?
What is 'Profit'?
What characterizes the 'Break-even Point'?
What characterizes the 'Break-even Point'?
In break-even analysis, how is the break-even point typically represented on a chart?
In break-even analysis, how is the break-even point typically represented on a chart?
Flashcards
Production Function
Production Function
The relationship between the quantity of inputs used and the quantity of output produced.
Short Run
Short Run
A period where at least one input amount is fixed.
Long Run
Long Run
A period sufficient for all inputs to be variable.
Production function formula
Production function formula
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cobb-Douglas function
Cobb-Douglas function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Marginal Product
Marginal Product
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diminishing marginal product
Diminishing marginal product
Signup and view all the flashcards
Law of Variable Proportions
Law of Variable Proportions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Variable Proportions Assumptions
Variable Proportions Assumptions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Marginal Product Increasing
Marginal Product Increasing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Marginal Zero, Total Max
Marginal Zero, Total Max
Signup and view all the flashcards
Negative Marginal Product
Negative Marginal Product
Signup and view all the flashcards
Marginal Below Average
Marginal Below Average
Signup and view all the flashcards
First Stage of Production
First Stage of Production
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cause of stage one increasing returns?
Cause of stage one increasing returns?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Second Stage of Production
Second Stage of Production
Signup and view all the flashcards
Third Stage of Production
Third Stage of Production
Signup and view all the flashcards
Law of Returns to Scale
Law of Returns to Scale
Signup and view all the flashcards
Increasing Returns to Scale
Increasing Returns to Scale
Signup and view all the flashcards
What causes increasing returns?
What causes increasing returns?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What causes constant returns to scale?
What causes constant returns to scale?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Constant Returns to Scale
Constant Returns to Scale
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diminishing Returns to Scale
Diminishing Returns to Scale
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reason of diminishing returns.
Reason of diminishing returns.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cost Definition
Cost Definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Opportunity costs
Opportunity costs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Explicit costs
Explicit costs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Implicit costs
Implicit costs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fixed costs
Fixed costs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Variable costs
Variable costs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Marginal cost
Marginal cost
Signup and view all the flashcards
Total Cost
Total Cost
Signup and view all the flashcards
Total revenue
Total revenue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Profit Definition
Profit Definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Break-even Point
Break-even Point
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Production Function
- Relationship between quantity of input and quantity of output.
- Functional relationship exists between physical inputs and physical output of a firm.
- Production Function includes minimum quantity of steel, color, labor, machine-time, and electricity needed to makes 50 steel chairs
- Production function consists of the maximum number of chairs that can be produced with given quantities of inputs
Technology and the Production Function
- Largely determined by technology.
- Production function changes with technology improvements which creates a new production function.
Mathematical Expression
- Q = f (Ld, L, C, O)
- Q represents output.
- Ld represents Land.
- L represents Labour.
- C represents Capital.
- O represents Organisation.
Modern Managerial Factors
- Managerial economists emphasize quality of technology and quality of management as additional factors.
- Q = f (Ld, L, C, M, T)
- M represents Management.
- T represents Technology.
Linear Homogeneous Function
- Also known as the Cobb-Douglas Function.
- Profounded by Paul H. Douglas and C.W. Cobb.
- Applies to manufacturing in the country and not to individual firms.
- Output is manufacturing production, with labor and capital being the inputs.
- Cobb-Douglas function is Q = k* La * C(1-a)
- Q is quantity produced
- L is Labour
- C is Capital
- k and a are positive constants
- The production function works out for the American economy is Q = 1.01* L75 * C25
Short Run vs. Long Run
- Short run is a brief time where at least one input is fixed, featuring both fixed and variable factors.
- Long run is is a period that is sufficient for all inputs to be variable for an individual firm.
Marginal Product
- Increase in quantity of output from one additional unit of input.
- The marginal product declines because the number of workers increases.
- This property is called diminishing marginal product
Law of Variable Proportions
- A short run function that is also called the law of non-proportional output.
- If quantity of one variable is varied and the quantities of other variable factors are kept constant, then the output would not respond in a proportionate manner.
- Production increases at an increasing rate initially, then at a diminishing rate.
- Relationship between input and output is not constant during production.
Assumptions for the Law of Variable Proportions
- Only one factor is variable while others are held constant.
- Units of the variable factor are homogeneous.
- There is no change in technology.
- Possible to vary the proportions in which different inputs are combined.
- Assumes a short-run situation since factors are variable in the long-run.
- Product is measured in physical units i.e in quintals, tonnes, etc.
Marginal, Average, and Total Product Relationships
- When marginal product increases, total product increases at an increasing rate.
- When marginal product is zero, total product is at its maximum.
- When marginal product becomes negative, total product starts falling.
- Average product rises as long as the marginal product is above it.
- Average product starts falling when marginal product is below it.
- The marginal product curve cuts the average product curve at its maximum.
Stages of Production
First Stage
- Marginal and average products are increasing.
- Stage ends when marginal product cuts average product at its maximum.
- The first stage indicates increasing returns.
- The cause of increasing returns is the indivisibility of factors of production
- Indivisibility of factors of production as factors of production are not subject to division.
- Capacity can be under-utilized
Second Stage
- Marginal product diminishes until zero.
- Happens due to diseconomies.
- Diseconomies means Under-utilization initially transitions to optimum point and output increases but at a diminishing rate.
- Example: Fishing in the sea
Third Stage
- Additional variable factors lead to a fall in total production.
- Marginal product tends to be negative.
- Excessive variable factors hurt the efficiency of a fixed factor.
- This stage is theoretical, and no producer would want to be in it.
Law of Returns to Scale
- The relationship as outputs and scale of inputs in the long-run when all the inputs are increased in the same proportion
- Returns to scale is the relationship between changes in output and proportionate changes in all factors of production
- A firm increases its scale of production (long-run change in demand) by using more space, machines, and labor.
- Assumes all inputs are variable but enterprise is fixed.
- This law assumes that a worker works with given tools and implements
- Technological changes are absent.
- There is perfect competition.
- Product is measured in quantities.
Increasing Returns to Scale
- Increase in total output > proportional increase in all inputs.
- Causes
- Indivisibility of Factors
- Specialization and Division of Labour
- Internal Economies.
- External Economies
Constant Returns to Scale
- Increase in total output = increase in inputs.
- Causes
- Internal Economies and Diseconomies
- External Economies and Diseconomies
- Divisible Factors
Diminishing Returns to Scale
- Increase in output < increase in inputs
- Causes
- Indivisible factors become inefficient. - Business becomes unwieldy.
- Supervision/coordination problems.
- Higher factor prices.
Concept of Cost
- Total money expenditure to pay all the factors of production for their participation.
- Production requires different factors to be hired, involving production costs.
- Cost is in terms of money for understanding and comparison.
- Interpretations of cost can be opportunity cost, real cost and money cost of production
Types of Costs
Accounting Costs
- Costs associated with producing.
Economic Costs
- The costs of producing a good along with opportunity costs.
Opportunity Costs
- Sacrifices made to obtain an item.
- If a firm is producing Computers then the Accounting costs are the costs incurred for producing the computers. Economic costs include the cost of producing the computers as well as opportunity cost. If this firm could lease its office and the plant for say Rs. 100,000 then that is the opportunity cost
Explicit costs
- Input costs requiring money outlay by firm.
- Includes all money expenditure incurred by a firm in the process of production
- Money spent on fuels, raw materials, power, advertising and transportation
Implicit costs
- Input costs not requiring money outlay by firm.
- Costs not included by accounting authority.
- e.g., opportunity cost of entrepreneur's services and/or cost of land belonging to him
Fixed costs
- Doesn't vary with output quantity.
- Incurred even if the firm produces nothing.
Variable costs
- Changes as firm alters output quantity.
Marginal cost
- Increase in total cost from extra unit of production.
Total cost
- Sum of fixed and variable costs.
Total revenue
- Amount a firm receives from selling its output.
Profit
- Total revenue - total cost.
Break-Even Point
- No-profit, no-loss point where total costs equal total revenues.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.