Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the speed of electromagnetic radiation?
What is the speed of electromagnetic radiation?
- 2.99792458 x 10^8 m/s (correct)
- 3.5 x 10^8 m/s
- 1.5 x 10^8 m/s
- 4.5 x 10^8 m/s
What is the relationship between wavelength, velocity, and frequency of electromagnetic radiation?
What is the relationship between wavelength, velocity, and frequency of electromagnetic radiation?
- λ=c/F (correct)
- c=F/λ
- λ=F/c
- F=c/λ
Which type of electromagnetic radiation has the most energy?
Which type of electromagnetic radiation has the most energy?
- Microwaves
- Gamma-rays (correct)
- Radio waves
- X-rays
What is the wavelength range of X-rays?
What is the wavelength range of X-rays?
What is the unit of power?
What is the unit of power?
What is the energy gained by an electron accelerated through 1 volt?
What is the energy gained by an electron accelerated through 1 volt?
What is the relationship between joules and electron volts?
What is the relationship between joules and electron volts?
What is the unit of current?
What is the unit of current?
What is the unit of energy?
What is the unit of energy?
What is X-ray used for in medicine?
What is X-ray used for in medicine?
What is the energy level of X-rays used for therapeutic applications?
What is the energy level of X-rays used for therapeutic applications?
What is the outcome of high energetic electrons interacting with matter?
What is the outcome of high energetic electrons interacting with matter?
What are the two types of electron interactions responsible for X-ray production?
What are the two types of electron interactions responsible for X-ray production?
What is the meaning of Bremsstrahlung?
What is the meaning of Bremsstrahlung?
What is the source of acceleration and deceleration in Bremsstrahlung?
What is the source of acceleration and deceleration in Bremsstrahlung?
What is the result of an electron interaction with a nucleus in Bremsstrahlung?
What is the result of an electron interaction with a nucleus in Bremsstrahlung?
What is the characteristic of the incoming electron in Bremsstrahlung?
What is the characteristic of the incoming electron in Bremsstrahlung?
What is the spectrum created from in Bremsstrahlung?
What is the spectrum created from in Bremsstrahlung?
What type of force attracts the electron to the positively charged nucleus in the target?
What type of force attracts the electron to the positively charged nucleus in the target?
What happens to the kinetic energy of the electron when it interacts with the nucleus?
What happens to the kinetic energy of the electron when it interacts with the nucleus?
What is the name of the radiation produced when an electron loses kinetic energy?
What is the name of the radiation produced when an electron loses kinetic energy?
What determines the energy of the X-ray photon produced in Bremsstrahlung radiation?
What determines the energy of the X-ray photon produced in Bremsstrahlung radiation?
What is the result of a direct collision between an electron and the target nucleus?
What is the result of a direct collision between an electron and the target nucleus?
What type of radiation is produced when an electron interacts with other electrons in orbital shells?
What type of radiation is produced when an electron interacts with other electrons in orbital shells?
What is the sequence of events that generates a characteristic X-ray in a target atom?
What is the sequence of events that generates a characteristic X-ray in a target atom?
What is the energy of the characteristic X-ray photon emitted?
What is the energy of the characteristic X-ray photon emitted?
What is the minimum energy required for an incident electron to remove a K-shell electron?
What is the minimum energy required for an incident electron to remove a K-shell electron?
What type of force is responsible for the interaction between the incident electron and the K-shell electron?
What type of force is responsible for the interaction between the incident electron and the K-shell electron?
The kinetic energy of the electron is increased when it interacts with the nucleus.
The kinetic energy of the electron is increased when it interacts with the nucleus.
A characteristic X-ray photon is emitted with an energy equal to the sum of the binding energies of the two shells.
A characteristic X-ray photon is emitted with an energy equal to the sum of the binding energies of the two shells.
Bremsstrahlung radiation is produced when an electron gains kinetic energy.
Bremsstrahlung radiation is produced when an electron gains kinetic energy.
The incident electron interacts with the L-shell electron via a repulsive electrical force.
The incident electron interacts with the L-shell electron via a repulsive electrical force.
The highest X-ray energy is produced when the electron interacts with the target nucleus at a distance.
The highest X-ray energy is produced when the electron interacts with the target nucleus at a distance.
Characteristic radiation is produced when an electron interacts with the nucleus.
Characteristic radiation is produced when an electron interacts with the nucleus.
The X-ray energy depends on the velocity of the electron.
The X-ray energy depends on the velocity of the electron.
The electron is accelerated when it interacts with the nucleus.
The electron is accelerated when it interacts with the nucleus.
The energy of the X-ray photon is always equal to the kinetic energy lost by the electron.
The energy of the X-ray photon is always equal to the kinetic energy lost by the electron.
Bremsstrahlung radiation is a type of characteristic radiation.
Bremsstrahlung radiation is a type of characteristic radiation.
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
X-ray Production and Characteristics
- X-rays are produced when high-energy electrons interact with matter, converting their kinetic energy into electromagnetic energy through atomic interactions.
Bremsstrahlung Mechanism
- Bremsstrahlung is a type of X-ray production that occurs when an electron interacts with the positively charged nucleus of a target atom.
- The electron is decelerated by Columbic forces, resulting in a significant loss of kinetic energy and a change in its trajectory.
- The energy lost by the electron is converted into an X-ray photon with energy equal to the kinetic energy lost (conservation of energy).
- The X-ray energy depends on the interaction distance between the electron and the nucleus.
- A direct collision of an electron with the target nucleus results in the loss of all kinetic energy, producing the highest X-ray energy (although very low probability).
Characteristic Radiation
- Characteristic radiation is another type of X-ray production that occurs when an electron interacts with other electrons occupying orbital shells.
- The incident electron interacts with a K-shell electron via a repulsive electrical force, removing the K-shell electron and creating a vacancy.
- An electron from a higher energy shell (e.g., L-shell) fills the vacancy, emitting a characteristic X-ray photon with energy equal to the difference between the binding energies of the two shells.
Electromagnetic Radiation
- Electromagnetic radiation can be described in terms of a stream of photons, each traveling in a wave-like pattern at the speed of light.
- Each photon contains a certain amount of energy, defining the type of radiation (e.g., radio waves, gamma-rays).
- Electromagnetic radiation can be expressed in terms of energy, wavelength, or frequency.
- It can travel through empty space at the speed of light (approximately 2.99792458 x 10^8 m/s).
X-ray Properties
- X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength range of 0.01-10 nm.
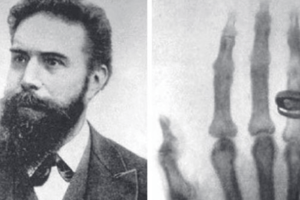
- They have been used as a diagnostic tool in medicine since their discovery by Wilhelm Roentgen in 1895.
- High-energy X-rays (around 10 MeV) are now used for therapeutic applications.
- X-rays can be characterized by their energy, wavelength, or frequency.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.