Podcast
Questions and Answers
At which type of plate boundary is new crust typically formed?
At which type of plate boundary is new crust typically formed?
- Divergent boundary (correct)
- Transform boundary
- Convergent boundary (oceanic-oceanic)
- Convergent boundary (continental-continental)
The Himalayas are a direct result of which type of plate boundary interaction?
The Himalayas are a direct result of which type of plate boundary interaction?
- Continental-oceanic convergent boundary
- Continental-continental convergent boundary (correct)
- Transform boundary
- Oceanic-oceanic convergent boundary
What geological feature would you most likely observe at a continental-oceanic convergent boundary?
What geological feature would you most likely observe at a continental-oceanic convergent boundary?
- Extensive fault lines
- Mid-ocean ridge
- Rift valley
- Deep ocean trench and volcanoes (correct)
The San Andreas Fault in California is an example of which type of plate boundary?
The San Andreas Fault in California is an example of which type of plate boundary?
At an oceanic-oceanic convergent boundary, what determines which plate will subduct?
At an oceanic-oceanic convergent boundary, what determines which plate will subduct?
Which geological feature is commonly associated with hot spots?
Which geological feature is commonly associated with hot spots?
If a plate map shows the South American Plate and the African Plate moving apart, what geological feature is likely present between them?
If a plate map shows the South American Plate and the African Plate moving apart, what geological feature is likely present between them?
Which of the following processes is most directly associated with the 'destruction' or recycling of crustal material?
Which of the following processes is most directly associated with the 'destruction' or recycling of crustal material?
Compared to oceanic crust, continental crust is generally:
Compared to oceanic crust, continental crust is generally:
Earthquakes are most commonly associated with which type of plate boundary?
Earthquakes are most commonly associated with which type of plate boundary?
Flashcards
Divergent Boundary
Divergent Boundary
Two tectonic plates move apart from each other.
Features at Divergent Boundaries
Features at Divergent Boundaries
Mid-ocean ridges and rift valleys.
Crust at Divergent Boundaries
Crust at Divergent Boundaries
Magma rises, creating new crust.
Continental-Continental Convergent Boundary
Continental-Continental Convergent Boundary
Signup and view all the flashcards
Features at Continental-Continental Convergent Boundaries
Features at Continental-Continental Convergent Boundaries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Crust at Continental-Continental Convergent Boundaries
Crust at Continental-Continental Convergent Boundaries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Continental-Oceanic Convergent Boundary
Continental-Oceanic Convergent Boundary
Signup and view all the flashcards
Features at Continental-Oceanic Convergent Boundaries
Features at Continental-Oceanic Convergent Boundaries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transform Boundary
Transform Boundary
Signup and view all the flashcards
Features at Transform Boundaries
Features at Transform Boundaries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- A plate boundary is the area where two tectonic plates meet.
- The type of plate boundary influences the geological features found there as well as what happens to the crust.
Divergent Boundary
- This is where two tectonic plates move apart.
- Mid-ocean ridges and rift valleys are visible at these boundaries.
- An example is the Mid-Atlantic Ridge.
- Magma rises at divergent boundaries, creating new crust.
Continental-Continental Convergent Boundary
- This occurs when two continental plates collide.
- Big mountains are formed here.
- The Himalayas are an example.
- The land is pushed up into tall mountains.
Continental-Oceanic Convergent Boundary
- This happens when an oceanic plate goes under a continental plate.
- Deep ocean trenches and volcanoes are visible.
- The Andes Mountains are an example.
- The ocean plate sinks and melts, causing volcanic eruptions.
Oceanic-Oceanic Convergent Boundary
- This is where two oceanic plates collide.
- Island arcs and deep trenches are formed.
- The Mariana Islands are an example.
- The older plate sinks, creating volcanoes.
Transform Boundary
- This is where two plates slide past each other.
- Fault lines and earthquakes occur here.
- The San Andreas Fault is an example.
- The crust gets stuck, then slips, causing earthquakes.
Hot Spots
- This is a place in the middle of a tectonic plate where hot lava creates volcanoes.
- The Hawaiian Islands are an example.
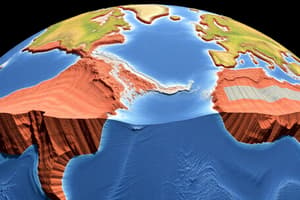
Plate Map Example
- The South American Plate and African Plate move apart at a divergent boundary.
- This forms the Mid-Atlantic Ridge.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.