Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the correct order of the components that make up the periodontium, starting from the outermost layer?
What is the correct order of the components that make up the periodontium, starting from the outermost layer?
- Alveolar bone, periodontal ligament, cementum, gingiva
- Gingiva, periodontal ligament, cementum, alveolar bone (correct)
- Gingiva, alveolar bone, periodontal ligament, cementum
- Cementum, periodontal ligament, alveolar bone, gingiva
What is the function of the alveolar bone?
What is the function of the alveolar bone?
- To provide a pathway for blood vessels and nerves to reach the tooth
- To provide a solid base for the teeth and support chewing forces (correct)
- To produce enamel and dentin
- To protect the tooth from decay and injury
What is the specific function of the periodontal ligament?
What is the specific function of the periodontal ligament?
- To attach the tooth to the alveolar bone (correct)
- To provide a barrier against bacteria and infection
- To produce new tooth enamel
- To provide sensory input for the tooth
Which radiographic assessment is considered relevant in diagnosing periodontal disease?
Which radiographic assessment is considered relevant in diagnosing periodontal disease?
What are the two key GDC Learning Outcomes referenced in the content?
What are the two key GDC Learning Outcomes referenced in the content?
Which of the following is NOT a radiographic feature of the alveolar bone?
Which of the following is NOT a radiographic feature of the alveolar bone?
What is a key characteristic of the spongy bone in aging individuals?
What is a key characteristic of the spongy bone in aging individuals?
What does the term 'lamina dura' refer to in the context of the alveolar bone?
What does the term 'lamina dura' refer to in the context of the alveolar bone?
Which of the following describes a radiographic characteristic of the periodontal ligament space?
Which of the following describes a radiographic characteristic of the periodontal ligament space?
What is the primary effect of osteoporosis on the alveolar bone?
What is the primary effect of osteoporosis on the alveolar bone?
Based on the images provided, which of the following radiographic techniques is most likely used to assess alveolar bone crest height?
Based on the images provided, which of the following radiographic techniques is most likely used to assess alveolar bone crest height?
What is the significance of the cemento-enamel junction (CEJ) in the radiographic evaluation of alveolar bone height?
What is the significance of the cemento-enamel junction (CEJ) in the radiographic evaluation of alveolar bone height?
Which radiographic characteristic is indicative of a healthy periodontal ligament space?
Which radiographic characteristic is indicative of a healthy periodontal ligament space?
What radiographic feature is specifically associated with bone loss in the furcation region of a multi-rooted tooth?
What radiographic feature is specifically associated with bone loss in the furcation region of a multi-rooted tooth?
Based on the provided information, what is the primary relevance of alveolar bone crest height in the assessment of periodontitis?
Based on the provided information, what is the primary relevance of alveolar bone crest height in the assessment of periodontitis?
Which of the following is NOT a radiographic feature indicating periodontal disease?
Which of the following is NOT a radiographic feature indicating periodontal disease?
Which of the following radiographic techniques is MOST effective for visualizing the entire alveolar bone crest, including its height and shape?
Which of the following radiographic techniques is MOST effective for visualizing the entire alveolar bone crest, including its height and shape?
Based on the provided content, how does radiographic assessment of alveolar bone contribute to the foundation of dental health?
Based on the provided content, how does radiographic assessment of alveolar bone contribute to the foundation of dental health?
According to the diagram, what is the relationship between alveolar bone and basal bone?
According to the diagram, what is the relationship between alveolar bone and basal bone?
What is the primary function of the alveolar bone as indicated by the text?
What is the primary function of the alveolar bone as indicated by the text?
Based on the diagram, what can you infer about the distribution of alveolar bone?
Based on the diagram, what can you infer about the distribution of alveolar bone?
From the content, what does the term 'basal bone' refer to in this context?
From the content, what does the term 'basal bone' refer to in this context?
The text mentions that the 'Longitudinal cross-section of Maxillary canine in alveolar bone' is from Berkovitz et al. What does this suggest?
The text mentions that the 'Longitudinal cross-section of Maxillary canine in alveolar bone' is from Berkovitz et al. What does this suggest?
What is the typical range for the height of the Cemento-Enamel Junction (CEJ) to alveolar bone crest in healthy individuals?
What is the typical range for the height of the Cemento-Enamel Junction (CEJ) to alveolar bone crest in healthy individuals?
What type of bone is the alveolar bone predominantly composed of?
What type of bone is the alveolar bone predominantly composed of?
What is the main function of Sharpey's fibers in the periodontal ligament?
What is the main function of Sharpey's fibers in the periodontal ligament?
Which of the following factors contribute to the continuous remodeling of alveolar bone?
Which of the following factors contribute to the continuous remodeling of alveolar bone?
What is the difference between a dehiscence and a fenestration in the context of alveolar bone?
What is the difference between a dehiscence and a fenestration in the context of alveolar bone?
Which of the following statements about the function of the alveolar bone is NOT true?
Which of the following statements about the function of the alveolar bone is NOT true?
How does periodontal disease affect the alveolar bone?
How does periodontal disease affect the alveolar bone?
What is the role of the periodontal ligament in the health and function of the alveolar bone?
What is the role of the periodontal ligament in the health and function of the alveolar bone?
Flashcards
Alveolar Bone
Alveolar Bone
The bone that surrounds and supports the roots of teeth.
Structure and Function of Alveolar Bone
Structure and Function of Alveolar Bone
Alveolar bone supports teeth and provides attachment for periodontal ligaments.
Healthy vs. Diseased Alveolar Bone
Healthy vs. Diseased Alveolar Bone
Healthy alveolar bone is dense and supports teeth; diseased bone shows loss and changes in structure.
Radiographic Assessment in Periodontal Disease
Radiographic Assessment in Periodontal Disease
Signup and view all the flashcards
Components of the Periodontium
Components of the Periodontium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Basal Bone
Basal Bone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Relationship of Alveolar & Basal Bone
Relationship of Alveolar & Basal Bone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Structure of Alveolar Bone
Structure of Alveolar Bone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Maxillary Canine
Maxillary Canine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteoporosis in Alveolar Bone
Osteoporosis in Alveolar Bone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brittleness of Alveolar Bone
Brittleness of Alveolar Bone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thin Trabecular Bone
Thin Trabecular Bone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Radiographic Features of Alveolar Bone
Radiographic Features of Alveolar Bone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cancellous Bone
Cancellous Bone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveolar Crest
Alveolar Crest
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cemento-Enamel Junction (CEJ)
Cemento-Enamel Junction (CEJ)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Radiographic Features of Healthy Bone
Radiographic Features of Healthy Bone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Disease State of Alveolar Bone
Disease State of Alveolar Bone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bitewing Radiograph
Bitewing Radiograph
Signup and view all the flashcards
Periapical Radiograph
Periapical Radiograph
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dental Panoramic Tomography (DPT)
Dental Panoramic Tomography (DPT)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Periodontitis Severity Classification
Periodontitis Severity Classification
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sharpey's Fibres
Sharpey's Fibres
Signup and view all the flashcards
Periodontitis
Periodontitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dehiscence
Dehiscence
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fenestration
Fenestration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Healthy Alveolar Bone
Healthy Alveolar Bone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Shock Absorber
Shock Absorber
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Alveolar Bone Overview
- Alveolar bone is a specialized bone type found only where teeth are present.
- It forms in relation to the teeth.
Aim of Presentation
- To outline the clinical and radiographic anatomy of alveolar bone.
Learning Outcomes
- Students will be able to identify the structure and function of alveolar bone.
- They will be able to identify features of alveolar bone ranging from healthy to diseased states.
- They will understand the relevance of radiographic assessment in periodontal diseases.
Alveolar Bone: Structure and Function
- Images of a Maori whale bone carving.
Periodontium
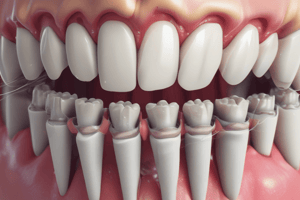
- The periodontium consists of: gingiva, periodontal ligament, cementum, and alveolar bone.
- Displayed is a demineralised section of a tooth.
Development of Alveolar Bone
- Diagrams show the different stages of tooth development, including initiation, bud, cap, bell, and secretory stages.
- Key players in the development are ameloblasts, alveolar bone, dentin, dental pulp, dental follicle, embryonic day, enamel, and odontoblasts.
Structure of Alveolar Bone
- Alveolar bone is continuous with the basal bone.
- Displayed are diagrams showing compact and spongy bone structures.
- Images show buccolingual sections through the maxilla and mandible, illustrating the distribution of alveolar bone in relation to the tooth roots.
Function of Alveolar Bone
- Supports the teeth.
- Protects the tooth.
- Provides attachment for teeth.
- Acts as a shock absorber.
- Histology slide depicting Sharpey's fibers.
Alveolar Bone, Health to Disease
- Displayed is an Inuit snow goggle.
Healthy Alveolar Bone
- The cemento-enamel junction (CEJ) to alveolar bone crest is typically between 1 and 2 mm.
- Image of healthy teeth and gums.
Disease: Periodontitis
- Characterized by inflammatory infiltrate, biofilm, periodontal pocket, and bone resorption.
- Image of a patient's mouth with signs of periodontal disease.
Defects: Dehiscence and Fenestration
- Dehiscence and fenetration are clinical defects.
- Visual representations of these defects are provided.
Age Changes to Alveolar Bone
- Age-related changes.
- Osteoporosis: bone loss.
- Brittleness: decreased water content.
- Sponge bone: becomes thin and trabecular with wide marrow spaces.
Radiographic Appearance: Alveolar Bone
- X-rays of the head and neck in relation to alveolar bone.
- Radiographic features include the alveolar bone crest, lamina dura, periodontal ligament space, and cancellous/spongy bone.
- Images of healthy and diseased states.
Radiographic features of alveolar bone in healthy state
- Radiographic images of bite-wing and periapical radiographs.
- Displays include the alveolar crest, cemento-enamel junction (CEJ).
Radiographic features of alveolar bone in disease state
- Radiographic images showing alveolar bone in disease state (e.g., calculus spur, widening of periodontal ligament space, loss of bone in the furcation region) and examples of the inflammatory process.
Radiographic relevance of alveolar bone crest height in severity of periodontitis classification
- Display is an image depicting staging and grading of periodontitis.
- Displays radiographic assessment methods (e.g., panoramic x-rays, bitewings).
- Shows various stages of the disease, such as early/mild, moderate, severe, and very severe.
- Provides grades for progression.
Bibliography
- A list of sources, including books and websites. These sources may contain more detailed information on the specific topics.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.