Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the alveolar process composed of?
What is the alveolar process composed of?
- Lamina dura and spongy trabecular region only
- Alveolar bone proper and other bone types (correct)
- Spongiosa and cortical regions only
- Alveolar bone proper only
What is the radiopaque socket-lining layer in the alveolar process known as?
What is the radiopaque socket-lining layer in the alveolar process known as?
- Alveolar bone proper
- Cortical region
- Lamina dura (correct)
- Spongiosa
What is a common misconception about alveolar bone?
What is a common misconception about alveolar bone?
- It is only found in the mandible
- It is a type of dental tissue
- It is produced by the bone of the jaw (correct)
- It is only found in the maxilla
What is alveolar bone similar to in terms of its origin?
What is alveolar bone similar to in terms of its origin?
What is the term for the spongy trabecular region in the alveolar process?
What is the term for the spongy trabecular region in the alveolar process?
What is the term for the radiopaque outer layer in the alveolar process?
What is the term for the radiopaque outer layer in the alveolar process?
What is the primary function of the alveolar bone?
What is the primary function of the alveolar bone?
What is the term for the tooth socket?
What is the term for the tooth socket?
What is the relationship between the alveolar bone and the tooth during development?
What is the relationship between the alveolar bone and the tooth during development?
What can be seen in radiographs of the alveolar bone?
What can be seen in radiographs of the alveolar bone?
What is the distinction between the terms 'alveolar bone' and 'alveolar process'?
What is the distinction between the terms 'alveolar bone' and 'alveolar process'?
What are the periodontal tissues that support the tooth?
What are the periodontal tissues that support the tooth?
What is the primary texture of the alveolar bone that gets remodeled into a secondary texture?
What is the primary texture of the alveolar bone that gets remodeled into a secondary texture?
What is the result of bone remodeling in the alveolar process?
What is the result of bone remodeling in the alveolar process?
What is the characteristic of the spongiosa in the alveolar process?
What is the characteristic of the spongiosa in the alveolar process?
What is the implication of teeth constantly moving and shifting positions within the jaws?
What is the implication of teeth constantly moving and shifting positions within the jaws?
What is the function of bone marrow in the alveolar process?
What is the function of bone marrow in the alveolar process?
What is the outer layer of bone surrounding the teeth?
What is the outer layer of bone surrounding the teeth?
What is the characteristic of the bundle bone matrix?
What is the characteristic of the bundle bone matrix?
What is the purpose of osteoclasts in bone remodeling?
What is the purpose of osteoclasts in bone remodeling?
What is the result of bone remodeling in the alveolar process?
What is the result of bone remodeling in the alveolar process?
What is the characteristic of the alveolar bone facing the tooth?
What is the characteristic of the alveolar bone facing the tooth?
What is the term for the process of bone turnover?
What is the term for the process of bone turnover?
What is the characteristic of secondary osteons?
What is the characteristic of secondary osteons?
What is the function of osteocytes in the bone tissue?
What is the function of osteocytes in the bone tissue?
What is the purpose of the blood vessels in alveolar bone?
What is the purpose of the blood vessels in alveolar bone?
What is the region of alveolar bone where ligament fiber bundles of the PDL are attached?
What is the region of alveolar bone where ligament fiber bundles of the PDL are attached?
What is the characteristic of the bundle bone layer?
What is the characteristic of the bundle bone layer?
Why is cross-polarized light used to visualize Sharpey's fibers?
Why is cross-polarized light used to visualize Sharpey's fibers?
What characterizes the composition of new layers of alveolar bone?
What characterizes the composition of new layers of alveolar bone?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
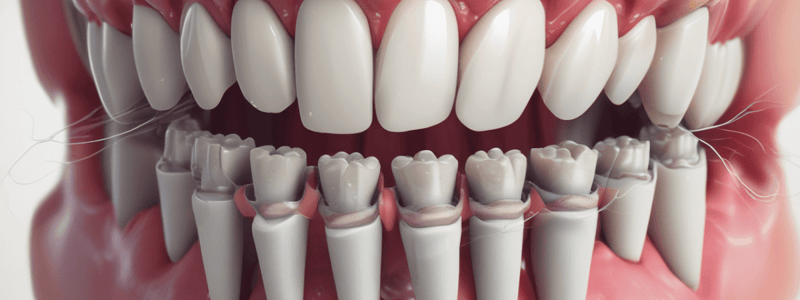
Anatomical Term: Alveolar Process
- Alveolar process is the bone around teeth, made of alveolar bone proper and other bone types.
Alveolar Bone
- Alveolar bone is produced by each tooth, not by the bone of the jaw.
- It is a dental tissue, like cementum and the periodontal ligament (PDL).
Composition of Alveolar Bone
- Bone remodeling in the alveolar process turns woven bone (primary texture) into Haversian bone (secondary, or remodeled texture).
- The spongiosa of the alveolar process is made of trabecular bone, with a strut-like arrangement and bone marrow filling the space.
- The compact bone/compacta, or cortical plates, are the outer walls of bone surrounding the teeth.
- The bundle bone layer is the site of active attachment of PDL fiber bundles to the alveolar bone, and is rapidly changing due to bone remodeling.
- The rest of the bone within the alveolar process has a different texture than the bundle bone facing the tooth, due to bone remodeling.
Alveolar Bone Remodeling
- Bone undergoes a natural turnover process (remodeling), where primary bone matrix is first removed through resorption by osteoclasts, and new bone is laid down around blood vessels in concentric rings (lamellae).
- This produces secondary osteons (blood vessel space surrounded by circumferential lamellae).
Bone Cells
- Osteoblasts deposit bone matrix towards the tooth root, but can become entombed in the matrix, where they differentiate into osteocytes.
- Osteocytes help maintain the mature bone tissue.
Blood Vessels
- Alveolar bone is perforated by many blood vessels, which leave vascular spaces throughout the bone to nourish the osteocytes and mature bone tissue.
Socket-Lining Layer
- The socket-lining layer of alveolar bone is often the region where the ligament fiber bundles of the PDL are attached.
- This layer is called the bundle bone layer, and is less vascularized than the surrounding bone.
- It is seen as the lamina dura in radiographs.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.