Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which anatomical area of the gingiva is the shallow linear groove that separates the free gingiva from the attached gingiva?
Which anatomical area of the gingiva is the shallow linear groove that separates the free gingiva from the attached gingiva?
- Interdental gingiva
- Gingival sulcus
- Attached gingiva
- Free gingival groove (correct)
Which of the following best describes the location of the attached gingiva?
Which of the following best describes the location of the attached gingiva?
- Tightly connected to the cementum on the cervical third of the root and alveolar bone. (correct)
- Unattached portion of the gingiva surrounding the tooth crown.
- Fills the interdental embrasure between two adjacent teeth
- Portion of the gingiva that forms the base of the gingival sulcus.
What is the primary component of the base of a gingival sulcus?
What is the primary component of the base of a gingival sulcus?
- Collagen fibers
- Junctional epithelium (correct)
- Fibroblasts
- Gingival crevicular fluid
What is the normal depth of a healthy gingival sulcus, measured from the gingival margin to the base of the sulcus?
What is the normal depth of a healthy gingival sulcus, measured from the gingival margin to the base of the sulcus?
Healthy gingival tissue is characterized by several clinical signs. Which of the following is an attribute of healthy gingiva?
Healthy gingival tissue is characterized by several clinical signs. Which of the following is an attribute of healthy gingiva?
The contour of healthy gingival tissue is described as:
The contour of healthy gingival tissue is described as:
What does the consistency of healthy attached gingiva feel like when gently palpated?
What does the consistency of healthy attached gingiva feel like when gently palpated?
What is the clinical term for the dimpled appearance sometimes seen on the surface of healthy attached gingiva?
What is the clinical term for the dimpled appearance sometimes seen on the surface of healthy attached gingiva?
In healthy gingival tissue, where is the gingival margin typically located in relation to the cementoenamel junction (CEJ)?
In healthy gingival tissue, where is the gingival margin typically located in relation to the cementoenamel junction (CEJ)?
During gingival inflammation, a subtle color change from light pink to darker pink or red is described as:
During gingival inflammation, a subtle color change from light pink to darker pink or red is described as:
In the context of gingival inflammation, what is the clinical term for tissues that appear bluish-red or purplish-red?
In the context of gingival inflammation, what is the clinical term for tissues that appear bluish-red or purplish-red?
Increased tissue fluid can lead to changes in the size of the gingival tissue. What is the term used to describe papillae that are enlarged and swollen?
Increased tissue fluid can lead to changes in the size of the gingival tissue. What is the term used to describe papillae that are enlarged and swollen?
When gingival tissue becomes soft, spongy, and nonelastic due to inflammation, how is its consistency best described?
When gingival tissue becomes soft, spongy, and nonelastic due to inflammation, how is its consistency best described?
In the context of gingival inflammation, which term describes tissue that deflects easily when air is gently blown into the sulcus?
In the context of gingival inflammation, which term describes tissue that deflects easily when air is gently blown into the sulcus?
What is the term for inflammation that is confined to the gingival papilla?
What is the term for inflammation that is confined to the gingival papilla?
Which distribution of inflammation involves the gingival margin, papilla, and extends to the attached gingiva and mucogingival junction?
Which distribution of inflammation involves the gingival margin, papilla, and extends to the attached gingiva and mucogingival junction?
Which of the following best describes localized inflammation?
Which of the following best describes localized inflammation?
Which of the following is a characteristic of gingival crevicular fluid (GCF)?
Which of the following is a characteristic of gingival crevicular fluid (GCF)?
Which of the following characteristics is typically associated with healthy interdental papillae?
Which of the following characteristics is typically associated with healthy interdental papillae?
Which of the following represents the most accurate description of the mucogingival junction?
Which of the following represents the most accurate description of the mucogingival junction?
A patient presents with gingiva that exhibits a smooth, shiny surface with loss of stippling. Which change in tissue texture is most likely?
A patient presents with gingiva that exhibits a smooth, shiny surface with loss of stippling. Which change in tissue texture is most likely?
A 74-year-old male patient is observed to have gingival recession and wedge-shaped defects on several teeth. The patient reports using a horizontal scrubbing technique when brushing. Which factor is most likely contributing to this patient's condition?
A 74-year-old male patient is observed to have gingival recession and wedge-shaped defects on several teeth. The patient reports using a horizontal scrubbing technique when brushing. Which factor is most likely contributing to this patient's condition?
A patient's gingival margin has moved coronally, further above the cementoenamel junction (CEJ). What is the MOST likely cause?
A patient's gingival margin has moved coronally, further above the cementoenamel junction (CEJ). What is the MOST likely cause?
Which of the following best describes the interdental gingiva?
Which of the following best describes the interdental gingiva?
What is the composition of the interdental papillae?
What is the composition of the interdental papillae?
Which of the following statements best describes healthy gingival tissues?
Which of the following statements best describes healthy gingival tissues?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic that we use to describe gingiva?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic that we use to describe gingiva?
When describing the color of healthy tissue, what is correct?
When describing the color of healthy tissue, what is correct?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of healthy tissue contour (size and shape)?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of healthy tissue contour (size and shape)?
Which of the following is true about healthy tissue consistency?
Which of the following is true about healthy tissue consistency?
A patient's tissue is rolled and has a cratered interdental papilla. When referring to consistency, how should you describe this?
A patient's tissue is rolled and has a cratered interdental papilla. When referring to consistency, how should you describe this?
Select the option that is NOT an indicator of gingival inflammation.
Select the option that is NOT an indicator of gingival inflammation.
Which of the following tissue size changes indicates the healthiest tissue?
Which of the following tissue size changes indicates the healthiest tissue?
Tissue that is compressed and leaves an indentation denotes which tissue's consistency?
Tissue that is compressed and leaves an indentation denotes which tissue's consistency?
If a patient has a disease that is described as 'Diffuse', what does this mean?
If a patient has a disease that is described as 'Diffuse', what does this mean?
What is 'localized' inflammation?
What is 'localized' inflammation?
All adults are susceptible to severe periodontal disease.
All adults are susceptible to severe periodontal disease.
Which of the following is true about salivary flow?
Which of the following is true about salivary flow?
Tooth loss is an inevitable part of the normal aging process.
Tooth loss is an inevitable part of the normal aging process.
Dental caries is a common oral disease in older patients.
Dental caries is a common oral disease in older patients.
Flashcards
Interdental gingiva
Interdental gingiva
The portion of the gingiva that fills the interdental space between two adjacent teeth, located apical to the contact area.
Gingival sulcus
Gingival sulcus
The space between the free gingiva and the tooth surface; depth is normally 1-3mm.
Healthy periodontal tissue
Healthy periodontal tissue
Healthy tissue is free of inflammation and has not been altered by disease or trauma.
Healthy gingiva
Healthy gingiva
Signup and view all the flashcards
Healthy tissue color
Healthy tissue color
Signup and view all the flashcards
Healthy tissue contour
Healthy tissue contour
Signup and view all the flashcards
Healthy consistency
Healthy consistency
Signup and view all the flashcards
Color changes with inflammation
Color changes with inflammation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Changes in papillae
Changes in papillae
Signup and view all the flashcards
Changes in consistency
Changes in consistency
Signup and view all the flashcards
Changes in texture
Changes in texture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Localized inflammation
Localized inflammation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Generalized inflammation
Generalized inflammation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Papillary inflammation
Papillary inflammation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Marginal inflammation
Marginal inflammation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diffuse inflammation
Diffuse inflammation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Common misconceptions of aging
Common misconceptions of aging
Signup and view all the flashcards
Free gingiva
Free gingiva
Signup and view all the flashcards
Attached gingiva
Attached gingiva
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- The University of Sydney acknowledges the tradition of custodianship and law of the Country on which its campuses stand
Mid Semester Quiz Information
- It is an online quiz.
- The quiz contains 15 questions.
- The questions cover the topics of periodontics and cariology.
- The questions are multiple-choice style (labeling diagrams, multiple choice, multiple answer, matching, true/false).
- Some questions are worth more than one mark.
- The exam time is 15 minutes, with a reading time of 5 minutes.
- There is only one attempt to complete the quiz.
- The quiz opens on Wed 2nd April at 5pm and closes on Thurs 3rd April 2025 at 23.59pm.
Learning Outcomes
- Identify and describe the four anatomical areas of the gingiva.
- Identify and describe the clinical characteristics of healthy gingiva.
- Identify and describe the clinical characteristics of gingival inflammation.
- Identify and describe the extent and distribution of gingival inflammation.
- Identify some common misconceptions about aging and oral health.
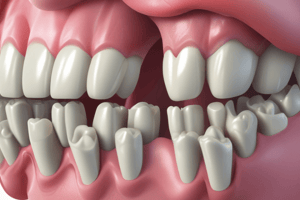
Gingival Anatomy
- There are four anatomical areas: free gingiva, attached gingiva, interdental gingiva, and gingival sulcus.
Boundaries of Gingiva
- The coronal boundary is the gingival margin.
- The apical boundary is the alveolar mucosa.
Demarcations of Gingiva
- The free gingival groove is a shallow linear depression separating free from attached gingiva.
- The mucogingival junction is a clinically visible boundary where attached gingiva meets alveolar mucosa.
Free Gingiva
- The unattached portion of the gingiva surrounds the tooth near the CEJ.
Attached Gingiva
- The part of the gingiva connected tightly to the cementum cervical third of the root or the periosteum of the alveolar bone.
Interdental Gingiva
- Interdental gingiva is the portion of gingiva that fills the interdental embrasure between two adjacent teeth apical to the contact area.
- It consists of two interdental papillae, one on the facial aspect and one on the lingual or palatal.
Gingival Sulcus
- The gingival sulcus is the space between the free gingiva and tooth surface.
- The depth of a normal gingival sulcus ranges from 1 to 3mm.
- The junctional epithelium forms the sulcus base.
- Gingival crevicular fluid (GCF), or gingival sulcular fluid, seeps into the sulcular space from underlying connective tissue.
Periodontium in Health
- Healthy tissue is free of inflammation and has not been altered by disease or trauma.
- Healthy tissue does not bleed when stimulated by clinical procedures such as gentle probing.
- Healthy gingiva exhibits a uniform pink or pigmented colour, tapered margins, pointed papilla, and firm consistency.
- Gingiva is easily distinguished from darker alveolar mucosa.
- Gingiva is described using the "three C's": colour, contour, and consistency.
Healthy Tissue Colour
- Healthy tissue colour shows a uniform pink.
- Blondes with a light complexion have a lighter shade of pink, while brunettes with darker complexions have a darker shade of pink.
- Pink gingiva is easily distinguished from darker alveolar mucosa.
- Tissue may also be pigmented.
Healthy Tissue Contour (Size and Shape)
- Healthy tissue contour lies snugly around the tooth, firmly against the alveolar bone.
- The gingival margin appears smooth and evenly scalloped.
- The free gingival margin meets the tooth in a knife-like edge that is either flat or slightly rounded.
- Papillae come to a point and fill the interdental space; in large spaces between teeth, papillae will be flat.
Healthy Tissue Consistency
- Healthy tissue consistency sees attached gingiva firmly bound to the underlying cementum and bone.
- Healthy tissue is resilient and springs back quickly when pressed gently with the side of a probe.
- It does not pull away from the tooth when air is blown into the sulcus.
Healthy Tissue Texture
- Healthy tissue texture is firm and may appear dimpled (stippling).
- Stippling is detected by drying the tissue gently with an air syringe.
- Texture varies greatly from one individual to the next.
Healthy Tissue Margin
- A healthy tissue margin is at or slightly coronal to the CEJ.
Tissue Colour Change in Gingival Inflammation
- Subtle colour changes from light pink to darker pink or red (erythematous) begin to appear.
- Chronic inflammation can cause tissues to appear bluish-red to purplish-red (cyanotic).
Tissue Size Changes
- Increased tissue fluid enlarges the marginal and interproximal gingival tissue.
- Enlargement may be localised to a few areas, or it may involve the whole mouth.
- Changes in papillae - bulbous, blunted or cratered.
Change in Tissue Consistency
- Inflammation increases the fluid in the area.
- Tissue becomes soft, spongy, and non-elastic.
- Compression of tissue with the side of a probe leaves an indentation.
- Tissue deflects when air is gently blown into the sulcus (flaccid).
Change in Tissue Texture
- Increased fluid in the area of inflammation gives the tissue a smooth, shiny appearance.
- Texture appears like stretched plastic wrap.
Change in Marginal Position
- The margin may move coronally further above the CEJ due to swelling and enlargement.
- Bleeding may occur upon gentle probing.
- Sulcus lining becomes ulcerated, and blood vessels engorge, resulting in a direct relation between the degree of inflammation and amount of blood.
Extent of Inflammation
- Localized inflammation is confined to the tissue of a single tooth or group of teeth.
- Generalized inflammation occurs in all or most of the mouth.
Distribution of Inflammation
- Papillary inflammation is confined to the papilla.
- Marginal inflammation is confined to the gingival margin and papilla.
- Diffuse inflammation is throughout the gingival margin, papilla, and attached gingiva, extending to the mucogingival junction.
Case Study
- A 74-year-old male with a horizontal scrubbing technique.
- Gingival recession, retraction, and wedge-shaped defects were observed.
- No significant pocketing or signs of inflammation were present.
Common Misconceptions of Aging
- Tooth loss is an inevitable part of the normal aging process.
- Most teeth are lost as people become long in the tooth because of advancing periodontal disease.
- All adults are susceptible to severe periodontal disease.
- Dental caries is not a common oral disease in older patients and occurs mainly in the young.
- Salivary flow is decreased in all older adults.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.