Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary purpose of gingival flaps in surgical therapy?
What is the primary purpose of gingival flaps in surgical therapy?
- To reduce bleeding during surgery
- To improve access and visibility to the area of concern (correct)
- To remove bacterial plaque
- To promote bone growth
Why should the base of a gingival flap be wider than the top?
Why should the base of a gingival flap be wider than the top?
- To ensure adequate blood supply to the flap (correct)
- To remove more bacterial plaque
- To reduce bleeding during surgery
- To promote bone growth
What can occur if the base of a gingival flap is narrower than the top?
What can occur if the base of a gingival flap is narrower than the top?
- Tissue necrosis (correct)
- Reduced bleeding during surgery
- Increased blood supply to the flap
- Faster bone growth
Where should incisions for gingival flaps be placed?
Where should incisions for gingival flaps be placed?
Why should vertical incisions over bony prominences be avoided?
Why should vertical incisions over bony prominences be avoided?
What is a consequence of placing a vertical incision near a bony defect?
What is a consequence of placing a vertical incision near a bony defect?
What is the relationship between the base and top of a well-designed gingival flap?
What is the relationship between the base and top of a well-designed gingival flap?
What is the goal of local therapy in periodontal disease?
What is the goal of local therapy in periodontal disease?
Where should the flap margin contact the teeth to avoid loss of papilla and formation of black triangles?
Where should the flap margin contact the teeth to avoid loss of papilla and formation of black triangles?
What is the consequence of the edge of the flap coming into contact with the mid facial surface of the teeth?
What is the consequence of the edge of the flap coming into contact with the mid facial surface of the teeth?
What is the importance of postoperative plaque control?
What is the importance of postoperative plaque control?
What is the name of the type of flap that includes the periosteum?
What is the name of the type of flap that includes the periosteum?
What is the purpose of a full thickness flap?
What is the purpose of a full thickness flap?
What happens when alveolar bone is exposed in full thickness flaps?
What happens when alveolar bone is exposed in full thickness flaps?
What is the purpose of a papilla preservation flap?
What is the purpose of a papilla preservation flap?
What is the characteristic of a mucoid periosteal flap?
What is the characteristic of a mucoid periosteal flap?
What is primary closure?
What is primary closure?
Why are vertical releases used in flap design?
Why are vertical releases used in flap design?
What is the primary purpose of the internal or reverse bevel incision in a full thickness flap?
What is the primary purpose of the internal or reverse bevel incision in a full thickness flap?
What is the name of the flap that involves the combination of the internal or reverse bevel incision, circular incision, and interdental incision?
What is the name of the flap that involves the combination of the internal or reverse bevel incision, circular incision, and interdental incision?
What is added to the modified Whitman flap to create an epically repositioned flap?
What is added to the modified Whitman flap to create an epically repositioned flap?
What is the purpose of the periodontal pack after invasive flap surgery?
What is the purpose of the periodontal pack after invasive flap surgery?
What type of surgery only involves the gingiva and soft tissue above the mucogingival junction?
What type of surgery only involves the gingiva and soft tissue above the mucogingival junction?
What is the main ingredient in gutta percha and endodontic sealer?
What is the main ingredient in gutta percha and endodontic sealer?
How long is the periodontal pack typically left in place?
How long is the periodontal pack typically left in place?
What is the purpose of the circular or curricular incision?
What is the purpose of the circular or curricular incision?
What is the goal of the modified Whitman flap?
What is the goal of the modified Whitman flap?
Why is the periodontal pack not used to enhance healing?
Why is the periodontal pack not used to enhance healing?
What is the primary objective of gingival ectomy?
What is the primary objective of gingival ectomy?
What is the difference between gingival ectomy and gingival plasty?
What is the difference between gingival ectomy and gingival plasty?
How does healing occur in gingival surgery?
How does healing occur in gingival surgery?
What type of surgery is used for pocket reduction distal to terminal molars?
What type of surgery is used for pocket reduction distal to terminal molars?
What is the purpose of a free gingival graft?
What is the purpose of a free gingival graft?
What is the most ideal tissue type for gingival grafts?
What is the most ideal tissue type for gingival grafts?
Why is keratinized tissue preferred around natural teeth and implants?
Why is keratinized tissue preferred around natural teeth and implants?
What is the difference between a free gingival graft and a connective tissue graft?
What is the difference between a free gingival graft and a connective tissue graft?
What is the term for the surgical procedure that involves both the gingiva and the mucosa?
What is the term for the surgical procedure that involves both the gingiva and the mucosa?
What is the primary reason for performing a free gingival graft in the given example?
What is the primary reason for performing a free gingival graft in the given example?
What is the main difference between mastectomy and osteotomy in Ostia surgery?
What is the main difference between mastectomy and osteotomy in Ostia surgery?
What is the term for the peaks of bone remaining at the line angles after a step?
What is the term for the peaks of bone remaining at the line angles after a step?
What is the purpose of clinical crown lengthening?
What is the purpose of clinical crown lengthening?
What is the term for the process of healing after surgery, where the architecture and function are completely restored?
What is the term for the process of healing after surgery, where the architecture and function are completely restored?
What is the term for the soft tissue that forms in a previously deep pocket after surgery?
What is the term for the soft tissue that forms in a previously deep pocket after surgery?
What is the purpose of combining osseous resection and cystectomy in clinical crown lengthening?
What is the purpose of combining osseous resection and cystectomy in clinical crown lengthening?
What is the term for the reunion of epithelial and connective tissue with the tooth root surface after incision or injury?
What is the term for the reunion of epithelial and connective tissue with the tooth root surface after incision or injury?
What is the purpose of osseous surgery in dentistry?
What is the purpose of osseous surgery in dentistry?
What is the term for the process of healing after surgery, where the architecture and function are not completely restored?
What is the term for the process of healing after surgery, where the architecture and function are not completely restored?
What is the primary goal of a connective tissue graft?
What is the primary goal of a connective tissue graft?
What is the term for the embedding of fresh new PDL fibers into new cementum that has been previously deprived of its original attachment?
What is the term for the embedding of fresh new PDL fibers into new cementum that has been previously deprived of its original attachment?
What type of graft happens below or apical to the gingival margin?
What type of graft happens below or apical to the gingival margin?
What is the most common donor site for both free gingival grafts and connective tissue grafts?
What is the most common donor site for both free gingival grafts and connective tissue grafts?
What is the purpose of a frenectomy?
What is the purpose of a frenectomy?
What is the difference between a free gingival graft and a connective tissue graft?
What is the difference between a free gingival graft and a connective tissue graft?
What is the term used to describe the visualization of bony architecture?
What is the term used to describe the visualization of bony architecture?
What is an example of a defect that is present in negative architecture?
What is an example of a defect that is present in negative architecture?
What is the primary goal of osseous surgery?
What is the primary goal of osseous surgery?
What is the term used to describe the interproximal bone that is coronal to the radicular bone?
What is the term used to describe the interproximal bone that is coronal to the radicular bone?
What is the purpose of a vestibular plasty?
What is the purpose of a vestibular plasty?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
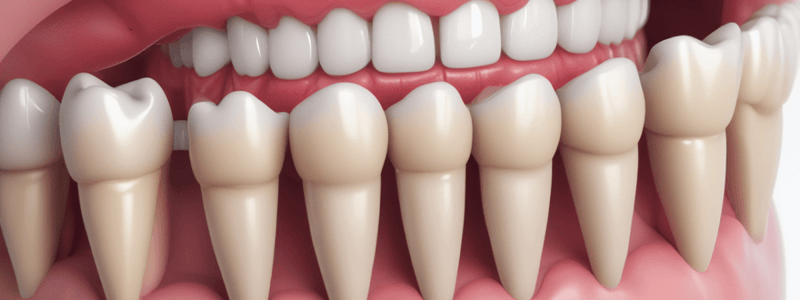
Gingival Flap Design
- The base of a flap should be wider than the top to ensure adequate blood supply and prevent tissue necrosis.
- Incisions should occur over intact bone, avoiding bony defects or eminences.
- Vertical incisions should occur at the line angles of teeth to preserve papilla and prevent black triangles.
- The ideal area for the flap margin to contact teeth is at the line angle.
Types of Flaps
- Partial thickness (mucoperiosteal) flap: includes gingiva, mucosa, submucosa, epithelium, and lamina propria.
- Full thickness (mucoperiosteal) flap: includes periosteum, used for osseous surgery and periodontal regeneration.
Papilla Preservation Flaps
- Designed to preserve papilla and prevent black triangles.
- Margins of the flap contact teeth at the line angles.
Full Thickness Flap Incisions
- Internal or reverse bevel incision: beveled, 1mm from gingival margin, used to remove pocket lining and conserve outer hinged flaps.
- Circular or curvicular incision: right through the base of the pocket to the alveolar crest.
- Interdental or interproximal incision: removes color of tissue around the tooth, used with the first two incisions.
Modified Whitman Flap
- Combination of the three incisions above, provides access to gingival areas for cleaning and calculus removal.
Epically Repositioned Flap
- Requires additional vertical releasing incisions beyond the mucogingival junction.
- Used to attain pocket reduction by physically moving the gingival margin apically.
Periodontal Pack
- A device used after flap surgery to protect the surgical wound, minimize discomfort, and prevent postoperative bleeding.
- Does not enhance healing but provides a soothing quality.
Gingival Surgery
- Involves surgery only on the gingiva, above the mucogingival junction.
- Healing occurs by secondary intention only.
- Types:
- Gingivectomy: excision of gingiva to eliminate pockets or enlargements.
- Gingivoplasty: reshaping and recontouring of gingiva for aesthetics.
Muco-Gingival Surgery
- Involves surgery on both the gingiva and mucosa, above and below the mucogingival junction.
- Types:
- Free Gingival Graft: widens the band of keratinized tissue, uses epithelium layer from the palate.
- Connective Tissue Graft: used for root coverage, takes a layer of connective tissue from the palate.
Osseous Surgery
- Involves surgery on the bone.
- Types:
- Ostectomy: removal of non-supporting bone, away from the tooth.
- Osteotomy: removal of supporting bone, directly contacting the periodontal ligament.
Clinical Crown Lengthening
-
Exposes more tooth structure by lowering the bone, combining osseous resection and cystectomy.
-
Used for various purposes, including gaining more ferrule for crown support.### Wound Healing in Periodontology
-
There are two types of healing: regeneration (complete restoration of architecture and function) and repair (not completely restoring architecture and function, involving healing by a scar or formation of long junctional epithelium)
-
Junctional epithelium has a weak hemi-desmosomal attachment to enamel, indicating healing towards a shallower pocket
-
Long junctional epithelium forms when a deep pocket was present, but the bone and periodontal ligament (PDL) have been irreversibly damaged and destroyed
-
The resulting pocket is physically long, with several millimeters of junctional epithelium attaching to the tooth, representing the best possible natural healing outcome
Definition of Attachment and New Attachment
- Attachment is the reunion of epithelial and connective tissue with the tooth root surface after incision or injury
- New attachment involves embedding fresh new PDL fibers into new cementum that has been previously deprived of its original attachment
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.