Podcast
Questions and Answers
What type of collagen is primarily found in hyaline cartilage?
What type of collagen is primarily found in hyaline cartilage?
- Type IV collagen
- Type III collagen
- Type II collagen (correct)
- Type I collagen
Where is hyaline cartilage NOT typically found?
Where is hyaline cartilage NOT typically found?
- External ear (correct)
- Articular surfaces of joints
- Trachea
- Nose
What is the primary method of growth for hyaline cartilage?
What is the primary method of growth for hyaline cartilage?
- Appositional growth
- Perichondrial growth
- Interstitial growth (correct)
- Mature growth
Which characteristic is NOT associated with hyaline cartilage?
Which characteristic is NOT associated with hyaline cartilage?
What type of cartilage is found in structures requiring more elasticity, such as the external ear?
What type of cartilage is found in structures requiring more elasticity, such as the external ear?
What type of fibers are predominantly found in mature cartilage?
What type of fibers are predominantly found in mature cartilage?
What type of growth is characterized by the addition of new cells and matrix from the perichondrium?
What type of growth is characterized by the addition of new cells and matrix from the perichondrium?
Which characteristic best describes chondrocytes in mature cartilage?
Which characteristic best describes chondrocytes in mature cartilage?
Which component is primarily responsible for providing elasticity to the cartilage matrix?
Which component is primarily responsible for providing elasticity to the cartilage matrix?
What do axial isogenic groups in cartilage reflect?
What do axial isogenic groups in cartilage reflect?
What type of strength is associated with cartilage?
What type of strength is associated with cartilage?
Which component contributes to the overall consistency of the cartilage matrix?
Which component contributes to the overall consistency of the cartilage matrix?
Which attribute does not apply to mature cartilage?
Which attribute does not apply to mature cartilage?
What primary function does fibrous cartilage serve in the body?
What primary function does fibrous cartilage serve in the body?
Which component is NOT found in the structure of fibrous cartilage?
Which component is NOT found in the structure of fibrous cartilage?
In which anatomical locations is fibrous cartilage primarily found?
In which anatomical locations is fibrous cartilage primarily found?
Which type of collagen is predominantly present in fibrous cartilage?
Which type of collagen is predominantly present in fibrous cartilage?
What is the characteristic staining property of the matrix in fibrous cartilage?
What is the characteristic staining property of the matrix in fibrous cartilage?
Which of the following cells are immature cartilage cells that produce the extracellular matrix?
Which of the following cells are immature cartilage cells that produce the extracellular matrix?
What mechanical advantage does articular cartilage provide?
What mechanical advantage does articular cartilage provide?
What is the main role of elastic fibers in cartilage tissue?
What is the main role of elastic fibers in cartilage tissue?
Which best describes the overall function of fibrous cartilage?
Which best describes the overall function of fibrous cartilage?
What differentiates chondrogenic cells from mature cartilage cells?
What differentiates chondrogenic cells from mature cartilage cells?
What is the role of glycoproteins like chondronectin in cartilage?
What is the role of glycoproteins like chondronectin in cartilage?
What best describes the growth pattern of cartilage referred to as interstitial growth?
What best describes the growth pattern of cartilage referred to as interstitial growth?
Which statement is true regarding the perichondrium?
Which statement is true regarding the perichondrium?
Why is cartilage considered avascular?
Why is cartilage considered avascular?
Which type of tissue surrounds most forms of cartilage?
Which type of tissue surrounds most forms of cartilage?
What function do chondroblasts serve in cartilage?
What function do chondroblasts serve in cartilage?
What characteristic is true of isogenic groups in cartilage?
What characteristic is true of isogenic groups in cartilage?
What is the primary role of chondrogenic cells in the perichondrium?
What is the primary role of chondrogenic cells in the perichondrium?
Which statement accurately describes cartilage composition?
Which statement accurately describes cartilage composition?
What unique feature differentiates fibrous cartilage from other types of cartilage?
What unique feature differentiates fibrous cartilage from other types of cartilage?
Flashcards
What is Hyaline cartilage?
What is Hyaline cartilage?
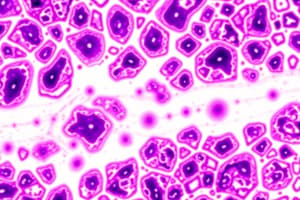
Hyaline cartilage is the most common type of cartilage, found in areas like the nose, larynx, trachea, joint surfaces, and growing bone ends.
What is the main protein in Hyaline cartilage?
What is the main protein in Hyaline cartilage?
Type II collagen is a major structural component of hyaline cartilage, making up roughly 40% of its weight.
How does Hyaline cartilage stain?
How does Hyaline cartilage stain?
The matrix of hyaline cartilage is basophilic, meaning it stains blue with basic dyes due to the presence of proteoglycans.
How does Hyaline cartilage grow?
How does Hyaline cartilage grow?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What makes Elastic cartilage different?
What makes Elastic cartilage different?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyaline cartilage
Hyaline cartilage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Type II collagen
Type II collagen
Signup and view all the flashcards
Basophilic staining
Basophilic staining
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interstitial growth
Interstitial growth
Signup and view all the flashcards
Elastic cartilage
Elastic cartilage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibrocartilage
Fibrocartilage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Elasticity and resilience
Elasticity and resilience
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chondroblasts
Chondroblasts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chondrocytes
Chondrocytes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Perichondrium
Perichondrium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Appositional growth
Appositional growth
Signup and view all the flashcards
Isogenic group
Isogenic group
Signup and view all the flashcards
Extracellular matrix
Extracellular matrix
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proteoglycans
Proteoglycans
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chondrogenic Cells
Chondrogenic Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chondronectin
Chondronectin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cartilage Avascularity
Cartilage Avascularity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Coronal Arrangement
Coronal Arrangement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Axial Arrangement
Axial Arrangement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chondrogenic Layer
Chondrogenic Layer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Cartilage Tissue Overview
- Specialized connective tissue with a firm matrix
- Resists mechanical stress
- Supports body parts
- Cushions and absorbs forces in joints
- Reduces friction in joints
Components of Cartilage
-
Cells:
- Chondrogenic cells: Precursor cells that differentiate into chondroblasts
- Chondroblasts: Immature cartilage cells that produce the extracellular matrix. They eventually mature into chondrocytes.
- Chondrocytes: Mature cartilage cells, housed in lacunae (small spaces), which maintain the matrix.
-
Extracellular Matrix:
- Primarily composed of collagen fibers (mostly Type II)
- Contains proteoglycans (like aggrecan) for matrix consistency
- Includes glycoproteins (like chondronectin) for cell-matrix adhesion
-
Avascular: Relies on diffusion for nutrients (no blood vessels).
Cartilage Growth
- Appositional Growth: New cartilage matrix is added from the perichondrium (dense irregular tissue surrounding cartilage)
- Chondroblasts in the perichondrium divide and secrete matrix, leading to outward growth. Chondrocytes divide, forming isogenic groups arranged coronally or axially.
- Interstitial Growth: Growth occurs within the cartilage. Chondrocytes divide and secrete new matrix, expanding the cartilage from within. The cells form isogenic groups that reflect the direction of stress
Types of Cartilage
- Hyaline Cartilage: Most common type, found in areas like nose, larynx, trachea, articular surfaces of joints, and growing bones.
- Primarily Type II collagen, basophilic (metachromatic) matrix.
- Elastic Cartilage: Found in structures needing flexibility, like external ear (pinna).
- Abundant elastic fibers for resilience and flexibility. Contains Type II collagen.
- Fibrocartilage: Found in areas with high stress, like intervertebral discs, menisci, and Achilles tendon.
- Primarily Type I and Type II collagen, eosinophilic matrix (stains pink)
- No perichondrium
- High tensile strength and resistance to compressive forces. Cells form linear groups reflecting stress direction.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.