Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which characteristic is more typical of rheumatoid arthritis compared to osteoarthritis?
Which characteristic is more typical of rheumatoid arthritis compared to osteoarthritis?
- Primarily affects weight-bearing joints.
- Involves deterioration of articular cartilage.
- Results from wear and tear on the body.
- Presents with symmetrical joint involvement. (correct)
Osteoarthritis is primarily characterized by inflammation.
Osteoarthritis is primarily characterized by inflammation.
False (B)
What type of cartilage deteriorates in osteoarthritis?
What type of cartilage deteriorates in osteoarthritis?
articular cartilage
In rheumatoid arthritis, the immune system attacks the ______ , leading to inflammation.
In rheumatoid arthritis, the immune system attacks the ______ , leading to inflammation.
Match the following conditions with their typical characteristics:
Match the following conditions with their typical characteristics:
A patient diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis reports a low-grade fever, fatigue, and overall weakness. What systemic effect of RA is most likely the cause of these symptoms?
A patient diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis reports a low-grade fever, fatigue, and overall weakness. What systemic effect of RA is most likely the cause of these symptoms?
Bone consists of mineral deposits only.
Bone consists of mineral deposits only.
Which bone cells are responsible for breaking down bone tissue?
Which bone cells are responsible for breaking down bone tissue?
The process of attaining awareness of the environment by organizing and interpreting sensory information is known as ______.
The process of attaining awareness of the environment by organizing and interpreting sensory information is known as ______.
Match the following bone cells with their functions:
Match the following bone cells with their functions:
A patient exhibiting uncoordinated musculoskeletal function may have an issue with which neurotransmitter?
A patient exhibiting uncoordinated musculoskeletal function may have an issue with which neurotransmitter?
Kyphosis, lordosis, and scoliosis are normal curvatures of the spine.
Kyphosis, lordosis, and scoliosis are normal curvatures of the spine.
What is the term for a spinal curvature described as "sway-back"?
What is the term for a spinal curvature described as "sway-back"?
An increased curvature of the thoracic spine is known as ______.
An increased curvature of the thoracic spine is known as ______.
Match the spinal deformity with its characteristic:
Match the spinal deformity with its characteristic:
Which of the following can lead to a waddled gait?
Which of the following can lead to a waddled gait?
Logrolling prevents the bending of a newly operated spinal site.
Logrolling prevents the bending of a newly operated spinal site.
What post-operative assessment finding could indicate a cerebrospinal fluid leak?
What post-operative assessment finding could indicate a cerebrospinal fluid leak?
The purpose of using orthosis is to prevent deformities from ______ to a point where surgery is necessary.
The purpose of using orthosis is to prevent deformities from ______ to a point where surgery is necessary.
Match the knee condition with its description:
Match the knee condition with its description:
Which of the following is NOT a component that is clustered into the pathophysiology of structural defects involving the knee?
Which of the following is NOT a component that is clustered into the pathophysiology of structural defects involving the knee?
With a patient that has foot drop, the inability to position anatomically would not be a symptom.
With a patient that has foot drop, the inability to position anatomically would not be a symptom.
What type of gait is related to foot drop?
What type of gait is related to foot drop?
In cases of foot drop, the toes are ______ along the ground and knees are bent to lift the foot higher than usual to avoid the dragging motion.
In cases of foot drop, the toes are ______ along the ground and knees are bent to lift the foot higher than usual to avoid the dragging motion.
Match the management with structural defects of the foot:
Match the management with structural defects of the foot:
What term describes the sole of the foot being distinctly hollow when bearing weight?
What term describes the sole of the foot being distinctly hollow when bearing weight?
Corns only appear beneath the skin.
Corns only appear beneath the skin.
What is the primary cause of corns and calluses?
What is the primary cause of corns and calluses?
With corns and calluses, internal pressure results from ______ or acquired abnormality.
With corns and calluses, internal pressure results from ______ or acquired abnormality.
Match the following words with the best desription:
Match the following words with the best desription:
Pain and edema may indicate what condition?
Pain and edema may indicate what condition?
There is no pain when the bone is subject to stress.
There is no pain when the bone is subject to stress.
What is the term for a fracture in which the bone is shattered into many pieces?
What is the term for a fracture in which the bone is shattered into many pieces?
Crepitus, which may involve fractures, are involved with the ______ of bone fragments together.
Crepitus, which may involve fractures, are involved with the ______ of bone fragments together.
Match the fractures with their descriptions below:
Match the fractures with their descriptions below:
What is Pott's disease affecting?
What is Pott's disease affecting?
The bone is specifically your Miliary Tuberculosis.
The bone is specifically your Miliary Tuberculosis.
What is another other name for tubercolosis?
What is another other name for tubercolosis?
These are the risk factors that includes close contact with factors of time proximity and ventilation. That's why you would observe that ______ and its other forms are mostly common in congested areas, where poverty occurs. Dug-ol ang mga balay, so easily it's easy to transmit the condition.
These are the risk factors that includes close contact with factors of time proximity and ventilation. That's why you would observe that ______ and its other forms are mostly common in congested areas, where poverty occurs. Dug-ol ang mga balay, so easily it's easy to transmit the condition.
Match each treatment to its description:
Match each treatment to its description:
What are some side effects of R (Rifampicin)?
What are some side effects of R (Rifampicin)?
There is no pain with rheumatoid arthritis.
There is no pain with rheumatoid arthritis.
Inflammatory condition leading to the loss of articular joints?
Inflammatory condition leading to the loss of articular joints?
Flashcards
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis
Arthritis caused by deterioration of articular cartilage, leading to bone rubbing.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Arthritis due to the immune system attacking the synovium, possibly leading to ankylosis.
Joints affected in Osteoarthritis
Joints affected in Osteoarthritis
Weight-bearing joints, hands, hips, knees, and spine.
Joints affected in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Joints affected in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Symmetry in Osteoarthritis
Symmetry in Osteoarthritis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Symmetry in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Symmetry in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteoblasts
Osteoblasts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteocytes
Osteocytes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteoclasts
Osteoclasts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Perception
Perception
Signup and view all the flashcards
Coordination
Coordination
Signup and view all the flashcards
Congenital Anomalies
Congenital Anomalies
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inadequate sensory-cortical perception
Inadequate sensory-cortical perception
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cerebral Pathology
Cerebral Pathology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Structural Defects
Structural Defects
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spine Anatomy
Spine Anatomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Abnormal Spinal Findings
Abnormal Spinal Findings
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kyphosis
Kyphosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lordosis
Lordosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scoliosis
Scoliosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kyphosis Complications
Kyphosis Complications
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kyphosis treatment
Kyphosis treatment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Genu Valgus
Genu Valgus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Genu Varus
Genu Varus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Genu Recurvatum
Genu Recurvatum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Injured Bone Matrix
Injured Bone Matrix
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nerve motor deficit cause
Nerve motor deficit cause
Signup and view all the flashcards
Knee and walking Deficits
Knee and walking Deficits
Signup and view all the flashcards
Walking issues and support
Walking issues and support
Signup and view all the flashcards
Foot position deficit
Foot position deficit
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gait abnormal compensatory
Gait abnormal compensatory
Signup and view all the flashcards
Claw foot deficit issues
Claw foot deficit issues
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hammer toe issues
Hammer toe issues
Signup and view all the flashcards
Callus irritation and issues
Callus irritation and issues
Signup and view all the flashcards
Strain with injury
Strain with injury
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sprains causes
Sprains causes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Contusion issues with impact
Contusion issues with impact
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fractures causes and forces
Fractures causes and forces
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bone Remodeling for fracture
Bone Remodeling for fracture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Extrea pulmonary tuberculosis
Extrea pulmonary tuberculosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
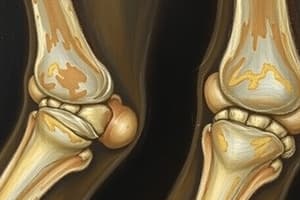
Osteoarthritis vs Rheumatoid Arthritis
- These can be differentiated by cause, affected joints and symmetry
- Both are forms of arthritis affecting the musculoskeletal system
Osteoarthritis (OA)
- Caused by the deterioration of articular (hyaline) cartilage, which leads to rubbing of bones
- Over time, the cartilage wears away, causing pain
- Can cause cartilage to break off and bone to harden abnormally
- Body attempts to compensate with bone spurs, called osteophytes
- Results in stiffness, pain, and limited mobility
- Characterized by no inflammation of tissue in affected areas
- Affects weight-bearing joints like hips, knees, and spine
- Usually affects these weight bearing joints unsymmetrically
- Occurs due to general wear and tear, gradually over time
- Risk factors include repeated injuries, being overweight, genetics, and manual labor
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
- Caused by an autoimmune response attacking the synovium (connective tissue within joints)
- Leads to white blood cells attacking the tissue within the joint, causing inflammation
- Over time, bones can fuse together (ankylosis)
- Marked by inflammation, presents with red, warm, soft/boggy joints
- Affects fingers, wrists, and can extend to neck, shoulders, elbows, feet, and ankles
- Affects these joints very symmetrically
- Accompanied by low-grade fever and anemia
- Exact cause unknown
- Affects women more than men
- May be related to hormonal issues or genetics
- Typically occurs between ages 20-60
Anatomy and Physiology of Bone
- Bones and the musculoskeletal system are essential for perception and coordinated movements
- Bone comprises extracellular matrix, protein matrix, cells, and mineral deposits of calcium and hydroxyapatite
Bone Cells:
- Osteoblasts responsible for forming cells secreting bone matrix
- Osteocytes are mature cells
- Osteoclasts destroy, resorb, and remodel bone. They are in the lacunae
Functions of Bones:
- Provides support
- Protects soft organs
- Enables movement
- Stores minerals
- Facilitates blood cell formation (hematopoiesis)
Perception and Coordination:
- Achieving awareness of the environment by organizing and interpreting sensory information
- Stimuli requiring movement send signals to the CNS for coordination
Coordination:
- Synchronization and integration of activities
Pathology affecting Perception and Coordination:
- Grouped into congenital anomalies, cerebral pathology, and structural defects
Congenital anomalies (birth defects) can affect:
- Perception and coordination
- There is adequate sensory-cortical function, but insufficient musculoskeletal coordination due to in-utero development problems
Cerebral pathology (abnormalities of the brain):
- Usually due to an organic brain problem
- Characterized by inadequate sensory cortex perception and uncoordinated musculoskeletal function
- Most neurotransmitter for movement is acetylcholine
- Problems with acetylcholine production/utilization or neurotransmitter binding receptor cause uncoordinated function
- Examples of Cerebral pathology: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and myasthenia gravis
Structural defects:
- Pathologic, traumatic, acquired, inflammatory, or genetic
- Adequate (though maybe inadequate) Sensory perception that leads to insufficient muscular coordination
- Spinal Assessment
Vertebral Column:
- Vertebrae is irregular bones
- Normal curvature: cervical (concave), thoracic (convex), lumbar (concave), sacral (Convex)
- Assess normal anatomical structures identify problems of the spine. Take note of these anatomical structures for further examination of the spine
- S-shape of the spine: Shock absorber, enhances strength and flexibility, and facilitates balance
Assessment findings
- Gluteal and shoulder-hip folds are symmetric
- Vertebral column is erect and bending forward allows for proper positioning
- Abnormalities suggest kyphosis, lordosis, or scoliosis
Assessment Procedures:
- Expose the back, buttocks, and legs
- Inspect spinal and trunk curves (posterior and lateral)
- Note differences in shoulder/iliac crest height
Kyphosis
- Increased thoracic spine curvature
- Occurs among elderly with osteoporosis/neuromuscular disorders due to bone porosity and ligament deterioration. Spinal ligaments no longer support spinal vertebrae.
Lordosis
- Sway-back posture
- Exaggerated lumbar spine curvature
- Common in pregnancy/abdominal obesity due to weight shifting the center of gravity downward
Scoliosis
- Lateral spine deviation
- Asymmetric waistline/prominent scapula
- Onset often adolescent, degree of activity can increase spinal curvature
Pathophysiology of Structural Spinal defects
- Lordosis: Continuous impact on lumbosacral vertebrae,
- Lumbosacral affectation due to pulling weight from center of gravity in pregnancy or obese clients
- Leads to disc misalignment and exaggerated lumbar concavity
- Ultimately causes a Waddled Gait(duck-like walking) upon ambulation
- Pressure and compression of lumbo-sacral nerve endings
- Nerves impulses are sent like “pain” causing client to experience Acute Pain
- Fluid leaks through vascular congestion
Pregnancy/Edema Consideration
- Some Pregnant women that present Edema in the lower extremity is caused by compression/congestion of the vascular structures within the lower extremities
- The above compression and congestion may also lead to injury to afferent and efferent neuronal pathways which can both lead to bowel and bladder affectation
- Bowel and bladder affectation in clients with Acute onset of pregnancy may cause an additional stress due to potential waistline increase.
Scoliosis specific factors
- Letter "S," spine deviates laterally with prominent scapula
Potential Causes
- Paraspinal injury
- Infectious agents
- Mechanical trauma
- Idiopathic
Kyphosis specific factors
- Kyphosis pathophysiology: excessive osteoclast activity (resorption) and decreased matrix formation
- Reduced structure in the spine, mineral storage in the body
- Osteoporosis is another key symptom. Usually happens in females
- Leads to forward spinal curvature, and therefore shortening
Management Interventions
- Exercise prevent muscle wasting & aid mobility, in either passive or active form
- Weight reduction
- Especially clients with lordosis because they are at risk of increased pressure to their spinal neural endings
- Orthosis prevent deformities from occurring
- Spinal bracing using Boston, Milwaukee, and Charleston braces
Surgical Interventions
- Spinal fusion to correct severe damage
- Insertion of instrumentation/rods to correct alignment
- Bone chips between vertebrae
(Spinal) Preoperative considerations
- Inform patient about potential post-operative numbness/tingling
- Emphasize postoperative importance of wearing prescribed braces
(Spinal) Postoperative considerations:
- Monitor for complications like clear leakage from dressing on affected area
- Cerebrospinal fluid Leakage - causes Spinal Headache
- Fat embolism
- Monitor for chest pain, dyspnea, and anxiety
- Lumbar radiculopathy: spinal nerve root problem, pain that shoots down the arm or leg
- Prevent Infection
- Maintain alignment with logroll maneuvers and prevent bending
- Elevate back to support the alignment
- Assess hypotension, V/S, movement and sensation, ability for patients to void
Knee Structures
- Genu Valgus: Knock-knees, knees angle in and touch
- Straightened legs
- Injury, bone infection, overweight/obesity, and rickets are the main etiologies for Genu Velgus
- Genu Varus: Bowlegs, archer's bow appearance
- Etiologies for Bow-legs are injury, bone infection, overweight/obesity, and rickets
- Genu Recurvatum: hyperextended knees bent backward
Genu Recurvatum Etiology:
- Ligament defect
- Malunion, trauma-related healing of fractured bones
- Gastrocnemius muscle weakness (calf muscle, major connector for both knee and ankle)
- Motor neuron defect
- Ligament defects, connecting to the femur, knees and the tibia and fibula
- Pathophysiology of Structural Knee defects
Three major parts of the knee that cause defects:
- Injury to the bone matrix
- Problems in the skeletal Growth and Development
- Problems with acetylcholine receptors and their function
Injured bone matrix will:
- Cause fracture, infect/ cause inflammation
- Inflammatory mediator migrate from affects site/ causes migration of osteoclasts and macrophages
- Osteoclasts break bone
- Cause the cartilage to be less dense which will cause joint injuries for younger patients of life
- Cause epiphyseal line to close, which leads to improper growth
Problems in Growth :
- Cause vitamin and calcium deficiency
- Demineralization of the epiphyseal cartilage
- Osteoid matrix lead to the different deformaties
Symptoms/Causes of Bone pathology
- Muscle atroghy and failure which causes muscle weakness
- Ach receptor cant reach motor neurons -Complications can cause various of the issues due to knee, Self esteme
Management:
- Physical therapy and brace attachments
- Osteonomy or bone shortening and alter the knees
- Total knee replacements
Structural Foot Defects
- Has 26 bones, has a spring function
- FEET
- Divided into three mainsections
- Flexible structures of bones, joints, muscles, and soft tissues
Main Sections
- Forefoot(5 toes and 5 metatasal)
- Midfoot with the arches _Hind foot (heel and ankle)
Foot drop
- Food is plantar flexed with toe dorsiflexion (ankle bends in direction the sole)
- Characterized in steppage gait
- Toes are dragged along the ground _ the patient will preform high steps or tip toe
Pathopphys:
Ineffective muscle function results the feet
Manifested
- Structural pulls and loss of functions (limited reach and stability )
- Affection from nerves and muscles
Congenital abnormalities
- Structural or motor
Management
- Help client to sit at 90 degrees
- Device installation of foot that supports
- Make frequent skin inspections by position
Nursing Care
- Help client to learn about procedures as well as equipment
Claw foot
-
Disintictiy hollow
-
Pes cavus
-
Etiology Idiapathic or medical condituions
Manifestation
Bone contriction
Nursing Care
- Widen feet wear etc
Club Foot
- Rotate foot and compressed inside to out
- Is adiapathic
- Types of rotation inside / out
etiology
Malunion formation
Nursing Intervention
- Manage and reduce any pressure to site
- Use devices
Management of club foot
- Ponseti method
Hammer Toe:
- Flex
- May need surigcal allieviations
Etioology
- Overload and constricted
Corn and Callues
- Aredss of overgrowth of skin
Etioology or Cause
- Genetics or medical codition
Maintence and Prevautions
- Wear propery attire that will have the joints with space
- Surgery
Common Signs by Defect or disease states
- Pain
- Redness or Swelling
- Heat
- Loss of function
Management
- Maining of joints and muscles through stretching, strength training and more as recommended by physical therapeute.
- Help of balance with the addition of special braces during time of
- Prevent falls
Traumatic events
- Contusion
- Muscle Puling
- Sprain
- Fracture ( bone breaks)
Etiology
- blunt force/ contact that causes
- Puling or over strectging
- Injured by twisting
- Causes swelling, or breaks
Management
- Check area
- RICE- rest ice compres elevation
- Surgaical interveinal
- Heat and therapy for healing
Signs for Trauma (Bone injury)
- Pain swelling , bruising
- Bone or tissue damage that is shown through the bone fractures
Fracture Diagnostic
- Simple fracture
- Compound fracture
- Comminuted fracture(pieces scattered)
- Greenstick fracture (hair line fracture)
Pathophys
- Damaged tissued cause over sensativity that can be both helped and limited function
Key point in Traumatic Event Management
- Proper care following surgerical or non, should allow minimal contact and rest
- Elevation can allow best amount circulation
Key Point in Management and Prevention
- Maintain balance and exercise
- In some cases surgerical procedure
- Maintain hydration to prevent infection or complications.
Bone formation stages
- Damage/ break and hematnma
- Procallus formation
- callus formation
- Remodeled stage
Inflamatory Condition signs:
- Heat
- Redness
- Pain
- Swelling
- Loss function
Pathway of Inflammarory Condition
-
Damage the Injured agents
-
Stimute through immiune to bind and protect damage sites
-
Migrate the cell will bind and make contrictuons to slow the damage
-
With a lot of migration and bonding the vasulatiy is going to cause swelling and irratation in sites
Note of The Signs
- The signs are caused by various reactions to the sites and immune response
Pott Disease
It is Extra pulmarly damage with bacteria
Factor
- Infection or exposure
Pathophys
- Damaging of spine, causes disablility and or muscle function
Management
Testing procedure for for what best helps
Signeand Sypmtoms
Infection and abnormal function
Diagnostic
Test like skin , mTB
Interventions
Medications and or surgery
10F: Care of Clients with Neutral and Autoimmune Disturbances
- Seizure Episode or abnormal motor that the causes
- Nueron A working group of the brain, the causes that stimulate the actual seizures
Causes That
Can affect brian Medications and allergies Tumors
Phases
Phase of seizures and prodromal stage for when symtoms affect
Main Phases
Initial phases Postical - recover Actonic drugs Types of: Genteized
- Onset rapid Focal
- Orgginate on hemisphere
Diagnostic test:
- CT or MRI
Manage
Look for history of events Try precent damage Give care following procedures
Epilepsy
Can by caused by multiple syndromes
Causes of
- Traums
- Medical and health issues
- Tumor or health issue
Nursing
Precauntion for protecttion for the patient during
Headaches
- cephlalgia. Symptoms not disease based. Types and classificarion headache
Headche causes
- Tention
- Strain
How to clasify
- By sypmtoms and location
Diagnostic
- Evalation
Actions
- Dark / comfort
- Medication
Alters ( LOC)
- When orientatation is needed
- How you react
Results
- Brain issue
- Toxic
Diagnostic test
- Use cat to check for bleeding
Manifications
- Alter level changes
Nursing Care
- Check and help client
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.