Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary purpose of introducing OSPF areas in OSPF design?
What is the primary purpose of introducing OSPF areas in OSPF design?
- To limit Link State Advertisement propagation to specific areas (correct)
- To increase the complexity of the network
- To reduce the number of routers in a network
- To eliminate the need for backbone routers
What type of router has at least one interface in Area 0?
What type of router has at least one interface in Area 0?
- Area Border Router
- Backbone Router (correct)
- Internal Router
- Autonomous System Border Router
Which type of router maintains separate link state databases for each area?
Which type of router maintains separate link state databases for each area?
- Area Border Router (correct)
- Autonomous System Border Router
- Backbone Router
- Internal Router
What is the maximum number of areas that can exist in OSPF?
What is the maximum number of areas that can exist in OSPF?
What is the term for the OSPF area hierarchy?
What is the term for the OSPF area hierarchy?
What is the role of a router that performs redistribution from a foreign routing protocol into OSPF?
What is the role of a router that performs redistribution from a foreign routing protocol into OSPF?
What is the benefit of using OSPF areas?
What is the benefit of using OSPF areas?
What is the term for a router that has all interfaces in a single area?
What is the term for a router that has all interfaces in a single area?
Which type of router has one or more interfaces in Area 0 and one or more interfaces in another area?
Which type of router has one or more interfaces in Area 0 and one or more interfaces in another area?
What is the purpose of the backbone area in OSPF?
What is the purpose of the backbone area in OSPF?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
OSPF Design - Understanding OSPF Areas
- OSPF areas are crucial to understanding OSPF design, and OSPF areas are divided into two types: Area 0 (backbone) and other areas (1-4.2 billion).
- OSPF areas are introduced to limit LSA (Link State Advertisement) propagation to specific areas, reducing the need for every router to update its network map.
Benefits of OSPF Areas
- OSPF areas allow routers to maintain a separate link state database for each area, reducing unnecessary updates.
- Areas prevent routers from having to recalculate their network maps every time a change occurs in the network.
OSPF Area Hierarchy
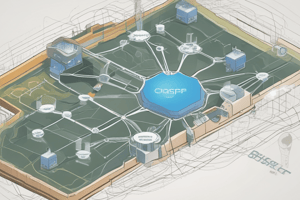
- OSPF areas create a two-tier hierarchy, with Area 0 (backbone) at the top and other areas (1-4.2 billion) below.
- Communication between areas must traverse through Area 0, ensuring a loop-free area topology.
- This design creates a hub-and-spoke topology, with Area 0 as the hub and each area as a spoke.
Types of OSPF Routers
- Internal Routers: Routers with all interfaces in a single area.
- Backbone Routers: Routers with at least one interface in Area 0.
- Area Border Routers (ABRs): Routers with one or more interfaces in Area 0 and one or more interfaces in another area.
- Autonomous System Border Routers (ASBRs): Routers that perform redistribution from a foreign routing protocol into OSPF.
OSPF Router Roles
- Internal Routers: Routers 1, 2, 5, 6, and 7 are internal routers in this topology.
- Backbone Routers: Routers 1, 2, 3, and 4 are backbone routers.
- Area Border Routers: Routers 3 and 4 are ABRs, maintaining separate link state databases for each area.
- Autonomous System Border Routers: Router 7 becomes an ASBR when redistributing routes from a foreign routing protocol into OSPF.
OSPF Areas
- OSPF areas are divided into two types: Area 0 (backbone) and other areas (1-4.2 billion).
- OSPF areas limit LSA (Link State Advertisement) propagation to specific areas, reducing the need for every router to update its network map.
Benefits of OSPF Areas
- OSPF areas allow routers to maintain a separate link state database for each area, reducing unnecessary updates.
- Areas prevent routers from having to recalculate their network maps every time a change occurs in the network.
OSPF Area Hierarchy
- OSPF areas create a two-tier hierarchy, with Area 0 (backbone) at the top and other areas below.
- Communication between areas must traverse through Area 0, ensuring a loop-free area topology.
- This design creates a hub-and-spoke topology, with Area 0 as the hub and each area as a spoke.
Types of OSPF Routers
- Internal Routers: have all interfaces in a single area.
- Backbone Routers: have at least one interface in Area 0.
- Area Border Routers (ABRs): have one or more interfaces in Area 0 and one or more interfaces in another area.
- Autonomous System Border Routers (ASBRs): perform redistribution from a foreign routing protocol into OSPF.
OSPF Router Roles
- Internal Routers: have all interfaces in a single area and do not connect to other areas.
- Backbone Routers: connect to Area 0 and enable communication between areas.
- Area Border Routers: maintain separate link state databases for each area and connect multiple areas.
- Autonomous System Border Routers: connect OSPF to other routing protocols and enable route redistribution.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.