Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of an oscilloscope?
What is the primary function of an oscilloscope?
- To convert analog signals into digital form.
- To analyze data on a digital display.
- To generate different types of waveforms.
- To measure voltage changes over time. (correct)
How is the period of a waveform calculated using an oscilloscope?
How is the period of a waveform calculated using an oscilloscope?
- By adding the vertical and horizontal positions.
- By dividing the total voltage by the time in seconds.
- By multiplying the horizontal scale by the number of divisions. (correct)
- By measuring the peak voltage multiplied by 10.
Which symbol is used to represent the output voltage of a function generator?
Which symbol is used to represent the output voltage of a function generator?
- F
- I
- T
- Vp (correct)
What does the 'Intensity' adjustment control on an oscilloscope do?
What does the 'Intensity' adjustment control on an oscilloscope do?
What is the formula for calculating frequency from the period?
What is the formula for calculating frequency from the period?
What does the Y-axis display on an oscilloscope?
What does the Y-axis display on an oscilloscope?
Which type of waveforms can a function generator produce?
Which type of waveforms can a function generator produce?
In the formula $F(t) = A imes ext{sin}( heta + 2 ext{π}ft)$, what does 'A' represent?
In the formula $F(t) = A imes ext{sin}( heta + 2 ext{π}ft)$, what does 'A' represent?
What is the role of the AC-GND-DC switch on an oscilloscope?
What is the role of the AC-GND-DC switch on an oscilloscope?
What is the primary output control on a function generator?
What is the primary output control on a function generator?
What is the purpose of the delay(100) in the loop function?
What is the purpose of the delay(100) in the loop function?
Which pin is used for reading the button state?
Which pin is used for reading the button state?
How does the first LED's state change over time in the loop function?
How does the first LED's state change over time in the loop function?
What will happen to the second LED when the button is pressed?
What will happen to the second LED when the button is pressed?
What type of control does the first LED utilize for timing?
What type of control does the first LED utilize for timing?
What should be adjusted first when setting up an oscilloscope?
What should be adjusted first when setting up an oscilloscope?
If an oscilloscope is set to a vertical sensitivity of 1 V/div and a signal voltage of 2 V is applied, what will the peak-to-peak measurement on the oscilloscope be?
If an oscilloscope is set to a vertical sensitivity of 1 V/div and a signal voltage of 2 V is applied, what will the peak-to-peak measurement on the oscilloscope be?
What is the cycle duration of a 1 kHz sine wave?
What is the cycle duration of a 1 kHz sine wave?
What is the effect of changing the horizontal sensitivity from 0.2 ms/div to 0.5 ms/div on the waveform display?
What is the effect of changing the horizontal sensitivity from 0.2 ms/div to 0.5 ms/div on the waveform display?
When measuring a 1 kHz sine wave, what is the horizontal scale in divisions if set to 0.5 ms/div?
When measuring a 1 kHz sine wave, what is the horizontal scale in divisions if set to 0.5 ms/div?
What should the vertical sensitivity be adjusted to if the input signal remains the same but you want to use a different sensitivity setting?
What should the vertical sensitivity be adjusted to if the input signal remains the same but you want to use a different sensitivity setting?
What is recorded when using a vertical sensitivity of 2 V/div and measuring a peak-to-peak voltage of 4 V?
What is recorded when using a vertical sensitivity of 2 V/div and measuring a peak-to-peak voltage of 4 V?
During the waveform measurement of a 5 kHz sine wave, what must be done to ensure the wave is clearly displayed?
During the waveform measurement of a 5 kHz sine wave, what must be done to ensure the wave is clearly displayed?
If the horizontal sensitivity is changed to 1 ms/div, how many divisions are needed to display one complete cycle of a 1 kHz signal?
If the horizontal sensitivity is changed to 1 ms/div, how many divisions are needed to display one complete cycle of a 1 kHz signal?
What is the total peak-to-peak voltage recorded when the vertical sensitivity is set to 0.5 V/div and measures 8 divisions?
What is the total peak-to-peak voltage recorded when the vertical sensitivity is set to 0.5 V/div and measures 8 divisions?
What does the effective value of a waveform represent?
What does the effective value of a waveform represent?
Which measurement device is used to assess the effective value of the output from the function generator?
Which measurement device is used to assess the effective value of the output from the function generator?
What is the formula for calculating the percentage error between the calculated and measured values?
What is the formula for calculating the percentage error between the calculated and measured values?
In the context of LED control, which function allows other tasks to be performed while monitoring the elapsed time?
In the context of LED control, which function allows other tasks to be performed while monitoring the elapsed time?
What is a key disadvantage of using the delay function in a microcontroller program?
What is a key disadvantage of using the delay function in a microcontroller program?
When adjusting the output signal of the function generator to 1kHz, 4Vpp, what wave shape is being used?
When adjusting the output signal of the function generator to 1kHz, 4Vpp, what wave shape is being used?
In the sketch for using the delay function, what is the purpose of the line 'LED_state = !LED_state'?
In the sketch for using the delay function, what is the purpose of the line 'LED_state = !LED_state'?
What is required for periodic control of an LED using a variable resistor according to the experiments outlined?
What is required for periodic control of an LED using a variable resistor according to the experiments outlined?
Which pin mode must be set for the LED to output a signal in the Blink sketch?
Which pin mode must be set for the LED to output a signal in the Blink sketch?
In the context of a digital signal, what does the variable 'value' represent when set to HIGH?
In the context of a digital signal, what does the variable 'value' represent when set to HIGH?
What is the primary purpose of the sketch that uses 'analogWrite'?
What is the primary purpose of the sketch that uses 'analogWrite'?
What must be done before calling the 'digitalWrite' function in the LED Blink example?
What must be done before calling the 'digitalWrite' function in the LED Blink example?
During the measurement of the effective value, which of the following results in a lower accuracy?
During the measurement of the effective value, which of the following results in a lower accuracy?
What is indicated by a successfully executed loop in the Blink sketch that tracks the count variable?
What is indicated by a successfully executed loop in the Blink sketch that tracks the count variable?
What is the function of the map() function in the provided code?
What is the function of the map() function in the provided code?
Which pin is used to connect the LED in the code?
Which pin is used to connect the LED in the code?
How is the blinking interval of the LED controlled in the code?
How is the blinking interval of the LED controlled in the code?
What would happen if the variable resistor gave a maximum reading of 1023?
What would happen if the variable resistor gave a maximum reading of 1023?
What is the initial state of the LED as defined in the code?
What is the initial state of the LED as defined in the code?
What does the line time_current = millis(); accomplish in the code?
What does the line time_current = millis(); accomplish in the code?
Which statement correctly describes the loop condition for toggling the LED?
Which statement correctly describes the loop condition for toggling the LED?
What does digitalWrite(pin_LED, LED_state); do in the code?
What does digitalWrite(pin_LED, LED_state); do in the code?
Study Notes
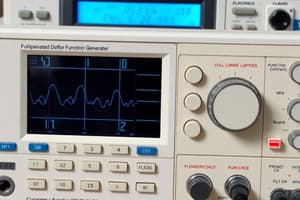
Oscilloscope (OSC)
- A device that displays the change in voltage over a specific time interval
- Displays time-varying signals as a periodic and repetitive voltage pattern
Oscilloscope Functions
- Power switch
- Vertical and horizontal scale controls
- Vertical and horizontal position controls
- Measurement setting switch
- Intensity control
- Measurement switch: selects measurement function (period, RMS, peak to peak)
Oscilloscope Characteristics
- X-axis
- Displays sec/div
- Waveform period = (sec/div) * number of divisions
- Frequency = 1/Period
- Y-axis
-Displays volt/div
- Voltage = (v/div) * number of divisions
- Vp: peak voltage
- Vpp: peak-to-peak voltage
- Waveform display
- F(t) = A * sin(wt + theta) = A * sin(2pi * f * t + theta)
- A: amplitude, f: frequency, theta: phase
- F(t) = A * sin(wt + theta) = A * sin(2pi * f * t + theta)
- Other
- High input impedance, making it more accurate than multimeters
- Requires practice to use effectively
- Basic functions are similar across different models
- RMS value of sinusoidal wave:
- Vrms = 1/T * integral from t0 to t0+T of [V(t)dt] = Vp / sqrt(2)
Function Generator (FG)
- Outputs different kinds of functions as voltage signals
- Can output sine, square, and triangular waves
- Output can be adjusted with an amplitude control
- Switch:
- Power switch
- Frequency control switch
- Waveform control switch
- Amplitude control switch
- Digital input switch
- Output enable switch
Lab.6-1: OSC and FG
- Experiment steps
- Preparation and basic experiment
- Horizontal and vertical sensitivity
- Waveform measurement experiment
- RMS value and error measurement
- Preparation and basic experiment
Lab.6-1
- Basic experiment
- Understand terms related to OSC: Focus, intensity, horizontal and vertical position, AC-GND-DC switch, signal input, mode switch, trigger control
- Preparatory tasks:
- Turn on the oscilloscope and adjust brightness, clarity, and alignment
- Connect the function generator to the oscilloscope's input channel
- Set the function generator output to a 1kHz sine wave
- Set the oscilloscope's vertical sensitivity to 1 V/div and the function generator voltage to 2V to obtain a 4Vpp sine wave
- Horizontal sensitivity:
- Calculate the period of the 1kHz sine wave in ms using T = 1/f
- Set the oscilloscope's horizontal sensitivity to 0.2 ms/div
- Measure the number of horizontal divisions needed to display one cycle of the 1kHz signal
- Repeat steps 5 and 6 for 0.5 ms/div and 1 ms/div sensitivities
- Vertical sensitivity:
- Keep horizontal sensitivity at 0.2 ms/div and change the vertical sensitivity to 2 V/div
- Calculate the number of vertical divisions between peak to peak values
- Multiply by the sensitivity to calculate the peak to peak value
- Repeat step 8 for 0.5 V/div sensitivity
- Waveform measurement
- Adjust the settings to clearly display a 5kHz, 6 Vpp sine wave on the oscilloscope
- Adjust the screen's center to have 0V
- Record the selected sensitivities (ms/div, v/div)
- Draw the waveform on the paper, noting the number of vertical and horizontal divisions
- Repeat step 1 for a 100kHz, 4 Vpp square wave.
- RMS value and error measurement
- Adjust the oscilloscope to display a 1kHz, 4 Vpp sine wave
- Calculate the RMS value of the sine wave
- Disconnect the function generator from the oscilloscope and use a digital multimeter to measure the RMS value of the function generator’s output.
- Calculate the % error using the formula: % error = (VA - VM) / VA * 100%, where VA is the calculated value and VM is the measured value.
Lab.6-2: Periodic Processing
- Experiment steps:
- Connect the button and LED
- Blink using the millis function
- Periodic LED control using the delay function
- Periodic LED control using the millis function
- Variable resistance control of the period
Lab.6-2: delay function vs millis function
- delay function:
- Pauses the microcontroller's operation while it is executing
- millis function:
- Returns the time elapsed since the program started
- Allows other tasks to run while waiting for a specific time interval
Lab.6-2: Periodic LED control using delay function
- In the loop function, the LED state is inverted and a 1-second delay is added
- The button's state is checked, and if pressed, the LED is inverted. (Using delay function for button press event)
Lab.6-2: Periodic LED control using millis Function
- The current time is obtained and the LED state is inverted if one second has elapsed since the initial time
- If the button state is pressed, the LED is inverted. (Using delay function for button event)
Lab.6-2: Variable resistance control of the period
- Read the analog value of the potentiometer
- Map the analog value to an interval range of 500 to 1500 ms
- Use the interval to set the blink frequency
Lab.6-2: map() function
- Remaps a value from one range to another
- Syntax: long map(long value, long fromLow, long fromHigh, long toLow, long toHigh)
- value: the number to map
- fromLow: the lower bound of the value's current range
- fromHigh: the upper bound of the value's current range
- toLow: the lower bound of the value's target range
- toHigh: the upper bound of the value's target range
Lab.6-2: Results
- Show the edited code for Sketch 8-3, 8-5, and 8-6
- Show the execution of Sketch 8-3, 8-5, and 8-6
- Answer the instructor’s questions and enter the grading results in PLMS LAB 6
HW.6
- Create a sketch that performs the following:
- Connect LEDs to digital pins 2 and 3
- Use the potentiometer to adjust the blink speed of the LEDs on pins 2 and 3.
- Submission method:
- Enter the created Sketch code in PLMS HW 6
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
This quiz explores the functions and characteristics of oscilloscopes. Learn about the crucial controls, measurements, and mathematical relationships that define how oscilloscopes display voltage over time. Perfect for electronics students and professionals alike.