Podcast
Questions and Answers
Define organizing as a management function.
Define organizing as a management function.
The process of arranging people and other resources to work together to accomplish a goal.
What is the official state of an organization called?
What is the official state of an organization called?
- Org chart (correct)
- Matrix structure
- Formal structure (correct)
- Hierarchical structure
What is the purpose of an organizational structure?
What is the purpose of an organizational structure?
The system of tasks, workflows, reporting relationships, and communication channels that link together diverse individuals and groups.
What is an organizational chart?
What is an organizational chart?
Two types of structures - formal and informal - know about each.
Formal Structure: The official structure of the organization (shown on an org chart). You can determine the following - division of work, supervisory relationships, _____ and major subunits and levels of management.
Two types of structures - formal and informal - know about each. Formal Structure: The official structure of the organization (shown on an org chart). You can determine the following - division of work, supervisory relationships, _____ and major subunits and levels of management.
What are the advantages of informal structures?
What are the advantages of informal structures?
What 3 structures has departmentalization resulted in? i.e. Functional, Divisional and _____.
What 3 structures has departmentalization resulted in? i.e. Functional, Divisional and _____.
What is Human Resource Management?
What is Human Resource Management?
What are the types of on-the-job training? (job rotation, coaching, mentoring, _____).
What are the types of on-the-job training? (job rotation, coaching, mentoring, _____).
What does selecting (selection) in HR mean?
What does selecting (selection) in HR mean?
What can managers do to make things difficult for unions?
What can managers do to make things difficult for unions?
What can unions do to make things difficult for managers?
What can unions do to make things difficult for managers?
Flashcards
Organizing (management function)
Organizing (management function)
Arranging people and resources to achieve a goal by dividing work and coordinating efforts.
Organizational Chart
Organizational Chart
A diagram showing the formal arrangement of work positions and reporting relationships.
Formal Structure
Formal Structure
The official structure demonstrating division of labor, supervisory relationships, and communication channels.
Informal Structure
Informal Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Matrix Structure
Matrix Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Economies of Scale
Economies of Scale
Signup and view all the flashcards
Functional Chimney Problem
Functional Chimney Problem
Signup and view all the flashcards
Horizontal Structures
Horizontal Structures
Signup and view all the flashcards
Team Structures
Team Structures
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cross-Functional Team
Cross-Functional Team
Signup and view all the flashcards
Human Resources Department
Human Resources Department
Signup and view all the flashcards
Employment Equity
Employment Equity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Human Resource Planning
Human Resource Planning
Signup and view all the flashcards
Recruitment
Recruitment
Signup and view all the flashcards
External Recruitment
External Recruitment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Selecting (in HR)
Selecting (in HR)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Employee Orientation
Employee Orientation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Training
Training
Signup and view all the flashcards
Job Rotation
Job Rotation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Performance Appraisal
Performance Appraisal
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Organizing as a Management Function
- Organizing is the management function of arranging resources and people to work together towards a goal.
- It includes dividing labor and coordinating results for a common purpose.
- Managers must ensure plans are executed effectively after defining the mission, core values, and objectives.
Official Organizational Structure
- The official state of an organization is represented by its formal structure.
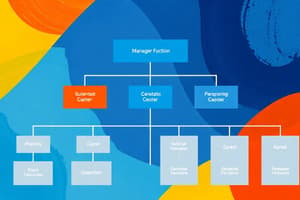
- An org chart identifies job titles, the division of work, communication channels, and lines of authority.
Organizational Structure Purpose
- An organizational structure links individuals and groups through tasks, workflows, reporting relationships, and communication channels.
- It allocates tasks through the division of labor and coordinates performance results.
- A well-designed structure aids in implementing the organization's strategy.
- Organizations modify their structure to improve performance.
- There isn't one best structure suitable for all situations.
- Adaptations to organizational structures should be contingent upon environmental and situational changes.
Organizational Chart
- It is a diagram depicting reporting relationships and the formal arrangement of work positions, along with division of work, job titles, and communication channels.
Formal vs. Informal Structures
- Formal Structure: This is the official structure depicted in the org chart, showing the division of work, supervisory relationships, communication channels, subunits, and management levels.
- Informal Structure: A "shadow" organization comprising unofficial working relationships among members.
- Informal structures involve relationships among organizational members.
Advantages of Informal Structures
- They expedite certain projects and help people accomplish their work.
- Can overcome the limits of the formal structure
- They provide access to interpersonal networks for social interaction.
- Facilitate informal learning and provide support groups.
Disadvantages of Informal Structures
- Activities may work against the organization's best interests.
- Susceptibility to rumors and inaccurate information is more common.
- May breed resistance to change.
- Can cause the diversion of work efforts from important objectives.
- May cause alienation of individuals excluded from informal groupings.
Departmentalization Structures
- Three types of structures resulted from departmentalization: Functional, Divisional, and Matrix Structures
- Knowing about each traditional structure is important
Matrix/Hybrid Structures
- This structure blends the functional and divisional approaches.
- It sets up reporting relationships as a grid instead of a traditional hierarchy.
- Attempts to maximize the advantages and minimize the disadvantages of functional and divisional structures.
- Promotes timely information and expertise sharing via close collaboration of members.
Functional Structure Advantages
- Enables economies of scale with efficient resource utilization which results in cost advantages.
- Allows task assignments consistent with training and employees grouped by skill set which enhances focus.
- Enables high-quality problem solving.
- Provides in-depth training and skill development.
- Offers clear career paths within functions.
Functional Structure Disadvantages
- Makes pinpointing responsibility difficult for outcomes like cost attainment and service quality.
- Suffers from the functional chimney problem (lack of interdepartmental communication and problem solving).
- Weakens the sense of cooperation and purpose across departments.
- Results in employees having a narrow view of performance objectives, focused on individual function responsibilities.
- Leads to slow decision-making due to decisions being referred upwards in the hierarchy.
Divisional Structure Advantages
- Allows more flexibility in response to environmental changes
- Improves coordination across functional departments
- Creates clear responsibility points for delivering products and services
- Positions expertise specific to customers, products, and regions, fostering autonomy within groups.
- Simplifies resizing by adding or removing divisions
Divisional Structure Disadvantages
- It can lead to increased costs due to resource and effort duplication.
- May foster unhealthy competition among divisions.
Matrix/Hybrid Structure Advantages
- Encourages better cooperation across functions and knowledge sharing among employees.
- Improves decision making at the team level.
- Provides increased flexibility in operations to meet changing demands.
- Improves customer service through informed and available program, product, or project managers.
- Enhances performance accountability via program, product, or project managers.
- Improves strategic management by freeing top managers from day to day problem solving.
Matrix/Hybrid Structure Disadvantages
- The two-boss system may lead to power struggles between functional supervisors and team leaders.
- The two-boss system may cause task confusion and conflicting work priorities.
- Team meetings can be time-consuming.
- Adding team leaders increases costs.
Modern Organizational Structures
- Companies are structuring towards more horizontal organizational structures
- Team, Network and Boundaryless structures are key
Team Structures
- Uses temporary and permanent cross-functional teams to improve lateral relations and solve problems.
- Members from various departments collaborate on special projects towards a common goal.
- Team members are creative people with different abilities.
Team Types
- Cross-functional teams: Bring members from different functional departments.
- Project teams: Convened for a specific task and dissolved upon completion.
Network Structures
- A combination of team and network structures, incorporating "temporaries."
- Teams form to address a problem and disband once solved, often online.
- Boundaryless because there are no geographical definitions.
- Breaks down internal boundaries, improving creativity, quality, flexibility, and efficiency through change.
Modern Workplace Organization
- Organized utilizing horizontal structures (flattening).
- Managers seek ways to structure organizations for competitive advantage and better productivity.
- Structures are moving away from the functional, divisional and/or matrix.
- A movement towards horizontal structures decreases hierarchy to increase empowerment of employees.
HR Goal
- Shifting from traditional "employees" with career-long jobs provided by "employers".
- Modern employers seek employees with high performance skills and talents.
Modern HRM Approach
- Attract the right people to the organization, develop effective workers, and maintain a quality workforce.
Human Resource Management
- HR involves major elements like the legal framework, discrimination, qualifications, and employment equity
Legal Framework in Human Resources
- Includes matters like discrimination, bona fide occupational qualifications, and employment equity.
Bona Fide Occupational Qualifications
- Justifiable reasons for not hiring someone based on safety or effectiveness, making it legal.
Employment Equity
- Treating all employees fairly regardless of sex, race, religion, age, national origin, or color.
Canadian Legislation
- The Canadian Human Rights Code prohibits discrimination based on race, colour, and religion.
Human Resource Planning
- Analyzes an organization's human resource needs and determines the best way to fulfill them.
- It includes analyzing jobs, writing job descriptions and specifications, etc.
Attracting the Right People
- An organization must know exactly what it's looking for and have a clear understanding of required talents.
Recruitment
- A set of activities designed to attract a qualified pool of job applicants.
- Recruitment can be external or internal.
External Recruitment
- Job candidates are sought from outside the hiring organization
- Examples: University/college recruiting, websites, employee referrals, employment agencies.
Internal Recruitment
- Internal recruitment seeks applicants from inside the organization.
- It helps in lowering costs, increasing loyalty and accessing access to candidates with established performance records.
Selecting in HR
- Means choosing the best possible person for the job and organization.
Selection Process Includes
- Reviewing applications, conducting interviews, testing, completing reference checks, and making final decisions.
Interview Question Types
- Interview questions include structured, situational, and behavioral questions.
Developing a Quality Workforce
- This involves attracting, selecting, orienting, and training, which takes considerable time and incurs significant costs for any organization.
Employee Orientation
- Designed to familiarize new employees with their jobs, coworkers, values, structure, and aspects of the organization.
- Can be online, in-person sessions, or working with a senior employee.
Employee Training
- A set of activities that provides the opportunity to acquire job related skills.
- The act of training a workforce is an ongoing process
Types of On-the-Job Training
- Job rotation: Working in different jobs to expand skills.
- Coaching: Experienced person provides performance advice.
- Mentoring: Early-career employees assigned to senior mentors.
- Modeling: Learning through observing others' day-to-day behavior.
Performance Appraisal
- It is a regular HR task that monitors and appraises staff member's performance.
- Employee performance appraisals are designed and implemented by the HR department.
Purpose of Performance Appraisal
- Evaluation: Inform employees of their position and how they stack up to objectives and standards.
- Development: Assists in training and continued development.
Career Development
- Career: The sequence of jobs that constitute what a person does for a living.
- Career path: A sequence of jobs held over time during a career.
- Career planning: Matching career goals with opportunities.
- Career plateau: Position unlikely to move to a higher level of responsibility.
Compensation and Benefits
- Organizations can develop and maintain a quality workforce by providing benefits and paying well.
- Employee compensation is how employees are paid for their service and expertise.
Types of Compensation
- Salary: Hourly or annual wage.
- Pay for performance: Based on individual performance and productivity.
- Bonus pay: One-time payments for meeting targets.
- Profit sharing: Distribution of organization profits.
- Stock options: Granting employee shares.
Fringe Benefits
- Additional non-wage or non-salary compensation.
- Examples include health, dental, vision, and life insurance.
Flexible benefits
- Programs where employees choose from a range of options.
Labour-Management Relations
- Many workplaces include the presence of labour unions.
Labour Unions
- A group of employees that organize to improve working conditions.
- Unions deal with employers on workers' behalf.
Labour Contracts
- Specify the rights and obligations of employees and management regarding work rules, seniority, hiring, grievances, and other conditions of employment.
Management's Difficulties for Unions
- Using lockouts, hiring strikebreakers, and seeking injunctions can create difficulties for unions.
Unions' Difficulties for Managers
- Unions can make things difficult for managers by striking, boycotting, and picketing.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.