Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of an organizational structure?
What is the primary function of an organizational structure?
- To increase competition among employees
- To provide training to new hires
- To manage employee salaries and benefits
- To outline how activities are conducted to achieve a mission (correct)
In a functional organizational structure, how are departments arranged?
In a functional organizational structure, how are departments arranged?
- Based on employee personalities
- Based on customer types
- Based on geographical location
- Based on areas of expertise (correct)
Which organizational structure combines functional and divisional aspects?
Which organizational structure combines functional and divisional aspects?
- Hierarchical structure
- Hybrid structure (correct)
- Flat structure
- Matrix structure
What is a key characteristic of a matrix organizational structure?
What is a key characteristic of a matrix organizational structure?
How does the divisional structure differ from the functional structure?
How does the divisional structure differ from the functional structure?
What is the main purpose of job rotation in an organization?
What is the main purpose of job rotation in an organization?
Which of the following best describes job enrichment?
Which of the following best describes job enrichment?
What is the goal of job enlargement?
What is the goal of job enlargement?
What is the primary goal of job simplification?
What is the primary goal of job simplification?
Which of the following is an example of an alternative work schedule?
Which of the following is an example of an alternative work schedule?
Which organizational structure enhances collaboration by bringing together team members from different departments?
Which organizational structure enhances collaboration by bringing together team members from different departments?
What characterizes a decentralized organization?
What characterizes a decentralized organization?
Which type of organizational design is most suitable for a rapidly changing environment?
Which type of organizational design is most suitable for a rapidly changing environment?
What is a key feature of bureaucratic organizational design?
What is a key feature of bureaucratic organizational design?
What defines a boundaryless organization?
What defines a boundaryless organization?
How does flexibility in the workplace benefit employees?
How does flexibility in the workplace benefit employees?
What is an essential aspect of job satisfaction measurement?
What is an essential aspect of job satisfaction measurement?
In an organizational setting, what does the psychological contract refer to?
In an organizational setting, what does the psychological contract refer to?
Which option best describes an organic organizational design?
Which option best describes an organic organizational design?
What does a shorter chain of command typically indicate in an organization?
What does a shorter chain of command typically indicate in an organization?
Flashcards
Organizational Structure
Organizational Structure
A system that determines how tasks are done to achieve a company's goals and shows who reports to whom, communication flow, and decision-making processes.
Functional Structure
Functional Structure
Organizes a company by departments based on expertise (e.g., marketing, sales).
Divisional Structure
Divisional Structure
A company organized by products or markets.
Hybrid Structure
Hybrid Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Matrix Structure
Matrix Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Job Rotation
Job Rotation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Job Enrichment
Job Enrichment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Job Enlargement
Job Enlargement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Job Simplification
Job Simplification
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alternative Work Schedules
Alternative Work Schedules
Signup and view all the flashcards
Network Organizational Structure
Network Organizational Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Boundaryless Organizational Structure
Boundaryless Organizational Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decentralization
Decentralization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mechanistic Organizational Design
Mechanistic Organizational Design
Signup and view all the flashcards
Organic Organizational Design
Organic Organizational Design
Signup and view all the flashcards
Psychological Contract
Psychological Contract
Signup and view all the flashcards
Quality of Work Life
Quality of Work Life
Signup and view all the flashcards
Job Satisfaction
Job Satisfaction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Flexibility in the workplace
Flexibility in the workplace
Signup and view all the flashcards
Job Design
Job Design
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
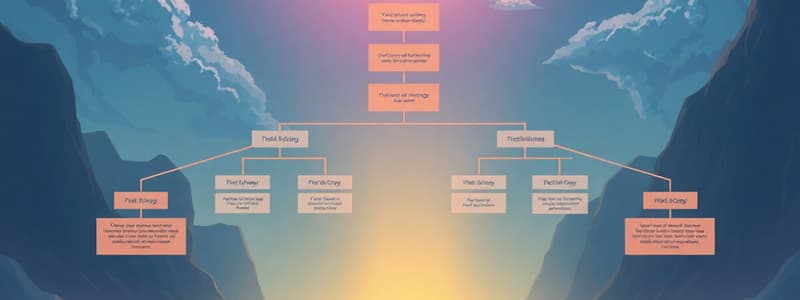
Organizational Structures
- Organizations utilize structures to arrange people and resources for achieving goals.
- Structures outline authority and decision-making processes.
- Official structures are formally documented.
- Structures define employee roles, reporting lines, communication paths, and decision-making processes.
- Charts visualize work arrangements within organizations.
Types of Organizational Structures
Functional Structure
- Groups employees by expertise—departments categorized by specialty.
- Hierarchical, with a president at the top, followed by managers.
Divisional Structure
- Organizes employees based on product or market segments, not job roles.
- Products or regions are prioritized, with a president at the top and multiple product divisions.
Hybrid Structure
- Combines functional and divisional aspects.
- Employees may work on multiple projects and report to multiple managers. Includes several departments—managers, directors and product lines.
Matrix Structure (Horizontal/ Flat)
- Teams report to multiple leaders.
- Fosters communication and innovation.
- Prevents realignment needs with new projects.
- Combines diverse skills and utilizes existing resources.
- President/CEO at the top of the hierarchy.
Team Structure
- Teams work on various tasks while pursuing a shared goal.
- Teams are dynamic in nature, moving around to work on new tasks.
- Fewer levels of hierarchy and more flexibility are emphasized.
- Encourages problem-solving and teamwork.
Network Structure
- Specialized employees in a central organization form partnerships with external specialists for projects.
- Highly flexible, adjusting production and design.
Boundaryless Structure
- Reduced hierarchy and departmental barriers.
- Enhances information flow, innovation, and idea sharing.
Chain of Command
- Instructions are passed through a vertical structure.
- Military and other structured organizations commonly use this style.
- Flatter organizational structures often feature a shorter chain of command.
Decentralization
- Top management delegates daily operations and decision-making authority to middle and lower levels.
- This allows for greater expertise at lower levels, quicker decision-making, and better use of top management time.
- Example of decentralization is a fast food franchise chain; each location is responsible for its own operation.
Move Towards More Organic Structures
- Flexible workplaces with horizontal communication.
- Sharing responsibilities amongst teams across departments.
- Increased empowerment and decision-making autonomy for employees.
- Contributes to a better workplace environment.
Organizational Design
Bureaucracy
- System based on logic, order, and legitimate authority.
- Key features include: clear job division, strict hierarchy, formal rules, merit-based promotion.
- Suitable in stable environments.
Mechanistic Design
- Stable environments, predictable goals.
- Centralized authority, formalized rules and procedures, specialized tasks, and a narrow span of control.
Organic Design
- Adaptable environments, goals.
- Decentralized authority, limited rules, wide spans of control, shared tasks, flexible structures.
Meaning of Work
- Individual values vary, and motivation is driven by factors including money, social pressures, learning, personal goals and socialization.
Psychological Contract
- Employees expect reciprocal benefits from their employers.
Quality of Work Life
- Measured by factors including job satisfaction, general well-being, work-life balance, work stress, and decision-making control concerning the work.
Job Satisfaction
- Measured in terms of cognitive, affective, and behavioral components.
Flexibility
- Employee choice of working times, location, and schedule.
- Improves work-life balance, reduces stress, and increases satisfaction.
Job Design
- Designing tasks and jobs to create better job experiences and improve performance.
- Factors include number and nature of tasks.
Job Rotation
- Moving employees to different departments to gain new experiences.
Job Enrichment
- Expanding a job's dimensions.
- Increase variety, meaning, autonomy, and feedback for greater motivation.
Job Enlargement
- Adding tasks and responsibilities to a job, reducing monotony.
Job Simplification
- Reduces a job's tasks for greater focus.
Alternative Work Schedules
- Flexible hours, compressed work weeks, job-sharing, telecommuting, and part-time work options.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.